Abnormal anatomy of inferior orbital fissure and herniation of buccal
... the superficial facial muscles, and allows the masticatory and mimetic muscles to glide. It can be divided into a body and 4 processes, and is fixed by 6 ligaments to the maxilla, posterior zygoma, temporalis tendon, and the inner and outer aspects of the inferior orbital fissure. The inferior orbit ...
... the superficial facial muscles, and allows the masticatory and mimetic muscles to glide. It can be divided into a body and 4 processes, and is fixed by 6 ligaments to the maxilla, posterior zygoma, temporalis tendon, and the inner and outer aspects of the inferior orbital fissure. The inferior orbit ...
Amphibians and Reptiles - Vernon Hills High School
... They can be divided into identical halves across exactly one plane Cephalized Concentration of brain cells near the anterior end of the amphibian ...
... They can be divided into identical halves across exactly one plane Cephalized Concentration of brain cells near the anterior end of the amphibian ...
Lecture 06, Annelida 1 - Cal State LA
... - segmented bodies divided into repeating blocks (metamerism) - formed by teloblastic growth in larvae - blocks of segments are specialized for different functions - complete digestive system; excretory system w/ metanephridia - closed circulatory system; well-developed nervous system - chetae: spin ...
... - segmented bodies divided into repeating blocks (metamerism) - formed by teloblastic growth in larvae - blocks of segments are specialized for different functions - complete digestive system; excretory system w/ metanephridia - closed circulatory system; well-developed nervous system - chetae: spin ...
Neuroanatomy: Blood Supply
... (ipsilateral corticospmal and cerebellar- like dysfunction due to supratentorial and brainstem lesions) ...
... (ipsilateral corticospmal and cerebellar- like dysfunction due to supratentorial and brainstem lesions) ...
Organ Systems in Animals and Plants
... (Figure 2.27). The shoot system is everything that is above ground: the stem, leaves, buds, flowers, and fruits. The root system is everything underground, as well as aerial roots even though they are above ground. To understand the interdependence between the shoot and root system, consider how wat ...
... (Figure 2.27). The shoot system is everything that is above ground: the stem, leaves, buds, flowers, and fruits. The root system is everything underground, as well as aerial roots even though they are above ground. To understand the interdependence between the shoot and root system, consider how wat ...
Femur Tibia Fibula Patella Lateral Meniscus
... Within the knee, the surfaces of the bones are covered with a layer of articular cartilage. This tough, smooth tissue protects the bones. It allows them to glide smoothly as the knee flexes and extends. Menisci Between the tibia and femur are two thick pads called "menisci." Each one individually is ...
... Within the knee, the surfaces of the bones are covered with a layer of articular cartilage. This tough, smooth tissue protects the bones. It allows them to glide smoothly as the knee flexes and extends. Menisci Between the tibia and femur are two thick pads called "menisci." Each one individually is ...
BACK OF THE LEG
... Thrombosis of the veins of the soleus muscle gives rise to mild pain or tightness in the calf and calf muscle tenderness. ...
... Thrombosis of the veins of the soleus muscle gives rise to mild pain or tightness in the calf and calf muscle tenderness. ...
Past Exam 1 for University of Minnesota students
... administer an epidural block to one of the patients. After a few minutes of composed panic, the student remembers the opening for administering an epidural. 11. This opening would be the… A. ventral sacral foramina - exits for ventral rami of sacral spinal cord located on ventral surface of sacrum B ...
... administer an epidural block to one of the patients. After a few minutes of composed panic, the student remembers the opening for administering an epidural. 11. This opening would be the… A. ventral sacral foramina - exits for ventral rami of sacral spinal cord located on ventral surface of sacrum B ...
Human Body Systems DR. I MCSNEER
... hard and dense, but not solid. Small canals run through the compact bone, carrying blood vessels and nerves from the bone’s surface to the living cells within the bone. Just inside the compact bone is a layer of spongy bone, which has many small spaces within it. ...
... hard and dense, but not solid. Small canals run through the compact bone, carrying blood vessels and nerves from the bone’s surface to the living cells within the bone. Just inside the compact bone is a layer of spongy bone, which has many small spaces within it. ...
Human Body Systems DR. I MCSNEER
... hard and dense, but not solid. Small canals run through the compact bone, carrying blood vessels and nerves from the bone’s surface to the living cells within the bone. Just inside the compact bone is a layer of spongy bone, which has many small spaces within it. ...
... hard and dense, but not solid. Small canals run through the compact bone, carrying blood vessels and nerves from the bone’s surface to the living cells within the bone. Just inside the compact bone is a layer of spongy bone, which has many small spaces within it. ...
Lymph nodes
... vessels drain interstitial fluid (cells and large macromolecules) from tissues to venous blood. They begin as "porous" blind-ended lymphatic capillaries in tissues of the body and converge to form a number of larger vessels, which ultimately connect with large veins in the root of the neck. ...
... vessels drain interstitial fluid (cells and large macromolecules) from tissues to venous blood. They begin as "porous" blind-ended lymphatic capillaries in tissues of the body and converge to form a number of larger vessels, which ultimately connect with large veins in the root of the neck. ...
ARTHROPOD/ENIGMATICS LABORATORIES Phylum Arthropoda
... which terminates in a telson. The prosoma is composed of eight fused segments and carries the walking legs and chelicera. On its dorsal surface examine the simple and compound eyes. The opisthosoma houses the reproductive organs and book gills. The telson is used to right the body when overturned an ...
... which terminates in a telson. The prosoma is composed of eight fused segments and carries the walking legs and chelicera. On its dorsal surface examine the simple and compound eyes. The opisthosoma houses the reproductive organs and book gills. The telson is used to right the body when overturned an ...
preparing for icd-10-cm anatomy and pathophysiology training
... The epidermis is the most superficial layer of the skin that covers almost the entire body surface. The epidermis rests upon and protects the deeper and thicker dermis layer of the skin. Structurally, the epidermis is only about a tenth of a millimeter thick but is made of 40 to 50 rows of stacked s ...
... The epidermis is the most superficial layer of the skin that covers almost the entire body surface. The epidermis rests upon and protects the deeper and thicker dermis layer of the skin. Structurally, the epidermis is only about a tenth of a millimeter thick but is made of 40 to 50 rows of stacked s ...
Digestive system
... At the posterior edge of the liver, find a long, flat, smooth, brown organ on the left side of the abdominal cavity that superficially resembles the liver, but is not attached to the liver. This structure is the spleen, which functions in the storage, destruction, and production of red blood cells. ...
... At the posterior edge of the liver, find a long, flat, smooth, brown organ on the left side of the abdominal cavity that superficially resembles the liver, but is not attached to the liver. This structure is the spleen, which functions in the storage, destruction, and production of red blood cells. ...
The Thorax
... O: Superior border of rib below I: Inferior border of rib above Fibers run at RIGHT ANGLES to external intercostals Aid in forced expiration (depress ribcage, decrease dimensions) ...
... O: Superior border of rib below I: Inferior border of rib above Fibers run at RIGHT ANGLES to external intercostals Aid in forced expiration (depress ribcage, decrease dimensions) ...
The Thorax
... O: Superior border of rib below I: Inferior border of rib above Fibers run at RIGHT ANGLES to external intercostals Aid in forced expiration (depress ribcage, decrease dimensions) ...
... O: Superior border of rib below I: Inferior border of rib above Fibers run at RIGHT ANGLES to external intercostals Aid in forced expiration (depress ribcage, decrease dimensions) ...
Invertebrates Ch. 26-28
... Although capable of attaining a bell diameter of 2.5 m (8 feet), these jellyfish can greatly vary in size, those found in lower latitudes are much smaller than their far northern counterparts with bells about 50 cm (20 inches) in diameter. The tentacles of larger specimens may trail as long as 30 m ...
... Although capable of attaining a bell diameter of 2.5 m (8 feet), these jellyfish can greatly vary in size, those found in lower latitudes are much smaller than their far northern counterparts with bells about 50 cm (20 inches) in diameter. The tentacles of larger specimens may trail as long as 30 m ...
The Anatomical Position
... Outline of Human Anatomy for medical students from foreign nationality ...
... Outline of Human Anatomy for medical students from foreign nationality ...
Femur Tibia Fibula Patella Lateral Meniscus
... Within the knee, the surfaces of the bones are covered with a layer of articular cartilage. This tough, smooth tissue protects the bones. It allows them to glide smoothly as the knee flexes and extends. Menisci Between the tibia and femur are two thick pads called "menisci." Each one individually is ...
... Within the knee, the surfaces of the bones are covered with a layer of articular cartilage. This tough, smooth tissue protects the bones. It allows them to glide smoothly as the knee flexes and extends. Menisci Between the tibia and femur are two thick pads called "menisci." Each one individually is ...
Human Body Systems DR. I MCSNEER
... hard and dense, but not solid. Small canals run through the compact bone, carrying blood vessels and nerves from the bone’s surface to the living cells within the bone. Just inside the compact bone is a layer of spongy bone, which has many small spaces within it. ...
... hard and dense, but not solid. Small canals run through the compact bone, carrying blood vessels and nerves from the bone’s surface to the living cells within the bone. Just inside the compact bone is a layer of spongy bone, which has many small spaces within it. ...
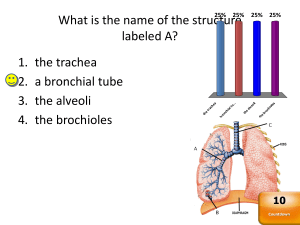
What is the name of the structure labeled A? 1. the trachea 2. a
... 1. The corn leaf must be able to produce food from air and water. 2. The corn leaf is more complex than the oak leaf. 3. The two leaves are nearly identical. 4. The leaves have a similar function but different structures. ...
... 1. The corn leaf must be able to produce food from air and water. 2. The corn leaf is more complex than the oak leaf. 3. The two leaves are nearly identical. 4. The leaves have a similar function but different structures. ...
United States Navy Hospital Corpsman NAVEDTRA
... the nostrils, bronchial tubes, and trachea), this tissue has a crown of microscopic hairlike processes known as cilia. These cilia provide motion to move secretions ...
... the nostrils, bronchial tubes, and trachea), this tissue has a crown of microscopic hairlike processes known as cilia. These cilia provide motion to move secretions ...
ARTHROPOD LABORATORY Phylum Arthropoda Subphylum
... groups that have evolved during this long period. We will have time today to study very few examples, but these will hopefully provide a brief introduction to some of the major patterns of arthropod adaptation. Classically, two major groups of living arthropods are generally recognized: the MANDIBUL ...
... groups that have evolved during this long period. We will have time today to study very few examples, but these will hopefully provide a brief introduction to some of the major patterns of arthropod adaptation. Classically, two major groups of living arthropods are generally recognized: the MANDIBUL ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.