Animal Phyla Lab - Biology Junction
... water-vascular system ending in tube feet. Sea stars use their tube feet to slowly pry open clams, mussels, or other prey. Some sea stars can even extrude their stomachs from their bodies and insert them into the tiny openings between the two shells of bivalves and digest the soft parts ...
... water-vascular system ending in tube feet. Sea stars use their tube feet to slowly pry open clams, mussels, or other prey. Some sea stars can even extrude their stomachs from their bodies and insert them into the tiny openings between the two shells of bivalves and digest the soft parts ...
study guide - SchoolNotes
... The pair of eyespots that detect light. The side flaps that function mainly for smell. o Movement flatworms can move in several ways: They use cilia on its ventral surface to slide about in search for food. They have muscles that enable it to twist and turn. o Examples planarians, tapewo ...
... The pair of eyespots that detect light. The side flaps that function mainly for smell. o Movement flatworms can move in several ways: They use cilia on its ventral surface to slide about in search for food. They have muscles that enable it to twist and turn. o Examples planarians, tapewo ...
Identify the features that animals have in common. • Distinguish
... a. The bodies of all other animals show bilateral symmetry, a body design in which there are distinct right and left halves. b. A plane passing through the animal’s midline divides the animal into mirror image halves. c. Most bilaterally symmetrical animals have evolved an anterior concentration of ...
... a. The bodies of all other animals show bilateral symmetry, a body design in which there are distinct right and left halves. b. A plane passing through the animal’s midline divides the animal into mirror image halves. c. Most bilaterally symmetrical animals have evolved an anterior concentration of ...
MTC8: Introduction to Anatomy 28/09/07
... The mediastinum is a protective partition oriented along the median plane and contains the heart, oesophagus and trachea, among others. The pleural cavities lie laterally on either side of the mediastinum and so are completely separated from one another, covering the inside of the ribs (reaching abo ...
... The mediastinum is a protective partition oriented along the median plane and contains the heart, oesophagus and trachea, among others. The pleural cavities lie laterally on either side of the mediastinum and so are completely separated from one another, covering the inside of the ribs (reaching abo ...
Phylum Cnidaria
... A germ layer, is a primary layer of cells that form during embryogenesis. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans, (animals more complex than the sponge) produce two or three primary germ layers. Animals with radial symmetry, like cnidarians, produc ...
... A germ layer, is a primary layer of cells that form during embryogenesis. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans, (animals more complex than the sponge) produce two or three primary germ layers. Animals with radial symmetry, like cnidarians, produc ...
Lab Exercise 10
... Oral Cavity: The tongue often protrudes from the anterior opening of the oral cavity. The tongue is a highly manipulative, muscular structure that contributes to chewing, swallowing, and sensing food. Chemical sensation occurs at sensory papillae, visible on the tongue. Taste cells within buds of t ...
... Oral Cavity: The tongue often protrudes from the anterior opening of the oral cavity. The tongue is a highly manipulative, muscular structure that contributes to chewing, swallowing, and sensing food. Chemical sensation occurs at sensory papillae, visible on the tongue. Taste cells within buds of t ...
Human Body Systems - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... We need enzymes in digestion because they break down the food for us to absorb the nutrients. Physical digestion is when the food actually passes through all the different segments of the digestive system. Chemical digestion is when our bodies digests the nutrients of the food. Carbohydrate digestio ...
... We need enzymes in digestion because they break down the food for us to absorb the nutrients. Physical digestion is when the food actually passes through all the different segments of the digestive system. Chemical digestion is when our bodies digests the nutrients of the food. Carbohydrate digestio ...
AP Biology Summer Assignment
... We know the words “summer assignment” tends to send chills down any high school student’s spine, but these assignments will be beneficial to you as we start the school year. The reason we are giving you a summer assignment is to keep your mind sharp so you are ready to hit the ground running! It is ...
... We know the words “summer assignment” tends to send chills down any high school student’s spine, but these assignments will be beneficial to you as we start the school year. The reason we are giving you a summer assignment is to keep your mind sharp so you are ready to hit the ground running! It is ...
Kingdom Animalia - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Amphibians change form, through metamorphosis, from an aquatic larval form to an adult terrestrial form, which may spend much of its time in water. Larval amphibians breathe through gills while adults breathe with lungs and through their skin. Eggs lack a protective shell and must be laid in water t ...
... Amphibians change form, through metamorphosis, from an aquatic larval form to an adult terrestrial form, which may spend much of its time in water. Larval amphibians breathe through gills while adults breathe with lungs and through their skin. Eggs lack a protective shell and must be laid in water t ...
ch26a - Otterville R
... Characteristics of the Phylum Arthropoda The segmented bodies are arranged into regions, called tagmata (e.g., head, thorax, abdomen). The paired appendages (e.g., legs, antennae) are jointed. They posses a chitinous exoskeletion that must be shed during growth. They have bilateral symmetry. The ne ...
... Characteristics of the Phylum Arthropoda The segmented bodies are arranged into regions, called tagmata (e.g., head, thorax, abdomen). The paired appendages (e.g., legs, antennae) are jointed. They posses a chitinous exoskeletion that must be shed during growth. They have bilateral symmetry. The ne ...
Homeostasis 3.4
... They depend on different body systems or organs working together to determine when the control system needs to be switched on/off. These require the following components: ...
... They depend on different body systems or organs working together to determine when the control system needs to be switched on/off. These require the following components: ...
Arthropods - Biology Junction
... Characteristics of the Phylum Arthropoda The segmented bodies are arranged into regions, called tagmata (e.g., head, thorax, abdomen). The paired appendages (e.g., legs, antennae) are jointed. They posses a chitinous exoskeletion that must be shed during growth. They have bilateral symmetry. The ne ...
... Characteristics of the Phylum Arthropoda The segmented bodies are arranged into regions, called tagmata (e.g., head, thorax, abdomen). The paired appendages (e.g., legs, antennae) are jointed. They posses a chitinous exoskeletion that must be shed during growth. They have bilateral symmetry. The ne ...
Human Torso Model Activity
... 3. The heart is ___________________ to the lungs. The lungs are ________________ to the heart. (Fill with anterior, posterior, inferior, superior, medial, or lateral) 4. What body system does the brain belong to? Is the brain cranial or caudal to the cecum? *Turn the torso model over to the posterio ...
... 3. The heart is ___________________ to the lungs. The lungs are ________________ to the heart. (Fill with anterior, posterior, inferior, superior, medial, or lateral) 4. What body system does the brain belong to? Is the brain cranial or caudal to the cecum? *Turn the torso model over to the posterio ...
Biology\Arthropod Unit
... Phylum: Arthropoda (jointed feet) Characteristics * - jointed appendages (extensions of the body, including legs, arms, antennae) - segmented body (like annelids), segments are often fused (joined) *- exoskeleton (external or “outside” skeleton) provides protection & support. It’s secreted by the ep ...
... Phylum: Arthropoda (jointed feet) Characteristics * - jointed appendages (extensions of the body, including legs, arms, antennae) - segmented body (like annelids), segments are often fused (joined) *- exoskeleton (external or “outside” skeleton) provides protection & support. It’s secreted by the ep ...
RAD 251 - Advanced Cross-Sectional Anatomy
... Identifies relationship of basic facts and states general principles and can determine step-by-step procedures for Moderate doing the competency. Knowledge and Performs most parts of the competency. Needs help only Proficiency on hardest parts. Requires limited supervision. Analyzes facts an ...
... Identifies relationship of basic facts and states general principles and can determine step-by-step procedures for Moderate doing the competency. Knowledge and Performs most parts of the competency. Needs help only Proficiency on hardest parts. Requires limited supervision. Analyzes facts an ...
The circulatory system
... The first profession is heart surgeon – when someone has a heart attack they might need surgery! So a heart surgeon is called in and might have to operate. This person would work at a hospital. The second profession is cardiac and vascular surgeonsometimes medication can slow the progress of hea ...
... The first profession is heart surgeon – when someone has a heart attack they might need surgery! So a heart surgeon is called in and might have to operate. This person would work at a hospital. The second profession is cardiac and vascular surgeonsometimes medication can slow the progress of hea ...
Ch.26 - Jamestown School District
... Complex animals tend to have high levels of cell specialization & internal body organization, bilateral body symmetry, a front end or head with sense organs, & a body cavity ...
... Complex animals tend to have high levels of cell specialization & internal body organization, bilateral body symmetry, a front end or head with sense organs, & a body cavity ...
File
... A cold or nasal inflammation often causes the lacrimal mucosa to become inflamed and swell. This impairs the drainage of tears from the eye surface, causing “watery” eyes. Leave ~ 7 – 10 lines for a diagram. ...
... A cold or nasal inflammation often causes the lacrimal mucosa to become inflamed and swell. This impairs the drainage of tears from the eye surface, causing “watery” eyes. Leave ~ 7 – 10 lines for a diagram. ...
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
... • Coronal refers to a cut or plane dividing the body into equal or non equal parts front and back as in taking the face off. • Sagittal refers to a cut or plane made from front to back dividing the body unequally as in slicing the arm or leg longitudinally ...
... • Coronal refers to a cut or plane dividing the body into equal or non equal parts front and back as in taking the face off. • Sagittal refers to a cut or plane made from front to back dividing the body unequally as in slicing the arm or leg longitudinally ...
Earthworm Dissection Lab report
... Internal Anatomy 1. Place the specimen in the dissecting pan DORSAL(top) side up. (The Dorsal side does NOT have a break in the clitellum.) 2. Locate the clitellum and insert the tip of the scissors about 3 cm posterior (behind) to it. 3. Cut carefully all the way up to the anterior (front) end. Try ...
... Internal Anatomy 1. Place the specimen in the dissecting pan DORSAL(top) side up. (The Dorsal side does NOT have a break in the clitellum.) 2. Locate the clitellum and insert the tip of the scissors about 3 cm posterior (behind) to it. 3. Cut carefully all the way up to the anterior (front) end. Try ...
Chapter 9 THE BODY AND ITS MOVEMENT
... Protection – the bones protect the soft organs of our body . The brain is protected by the skull ; the heart and the lungs by the thin long bones in your chest called the ribs . c) Movement – though the individual bones are hard , several of them move at places where they are joined to other bones. ...
... Protection – the bones protect the soft organs of our body . The brain is protected by the skull ; the heart and the lungs by the thin long bones in your chest called the ribs . c) Movement – though the individual bones are hard , several of them move at places where they are joined to other bones. ...
The Animal Kingdom - Tri-County Technical College
... larval stages bilaterally symmetrical adults radially symmetrical water vascular system--tube feet endoskeleton under spiny skin starfish and sea urchins ...
... larval stages bilaterally symmetrical adults radially symmetrical water vascular system--tube feet endoskeleton under spiny skin starfish and sea urchins ...
Reptilian Groups
... Appeared in Triassic, 200 mya Shells have dorsal carapace and ventral plastron; outer horny layer and inner layer of bone Limbs and limb girdles far from ribs No teeth; use horny plates to rip food ...
... Appeared in Triassic, 200 mya Shells have dorsal carapace and ventral plastron; outer horny layer and inner layer of bone Limbs and limb girdles far from ribs No teeth; use horny plates to rip food ...
Frog Dissection Guide
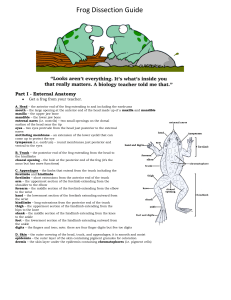
... use scissors to cut along the center of the body from the cloaca to the lip. Turn back the skin, cut toward the side at each leg, and pin the skin flat. The diagram above shows how to make these cuts Lift and cut through the muscles and breast bone to open up the body cavity. If your frog is a femal ...
... use scissors to cut along the center of the body from the cloaca to the lip. Turn back the skin, cut toward the side at each leg, and pin the skin flat. The diagram above shows how to make these cuts Lift and cut through the muscles and breast bone to open up the body cavity. If your frog is a femal ...
total
... structures: lungs, kidneys, urinary bladder, ureter, urethra, liver, and skin. Nervous: Describe the path a nerve impulse takes through your body when it goes from stimulus to response. Required organs and structures: brain, spinal cord, nerves, and neurons. Respiratory: Explain the “breathing” ...
... structures: lungs, kidneys, urinary bladder, ureter, urethra, liver, and skin. Nervous: Describe the path a nerve impulse takes through your body when it goes from stimulus to response. Required organs and structures: brain, spinal cord, nerves, and neurons. Respiratory: Explain the “breathing” ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.