Clinical anatomy of the superior cluneal nerve in relation
... difficult to palpate and may not correspond to the area where the trigger point is experienced. Facet syndromes have been described as originating from the cutaneous dorsal rami from the thoracolumbar junction and radiographic abnormalities have led to the incorrect diagnosis of LBP. These three dia ...
... difficult to palpate and may not correspond to the area where the trigger point is experienced. Facet syndromes have been described as originating from the cutaneous dorsal rami from the thoracolumbar junction and radiographic abnormalities have led to the incorrect diagnosis of LBP. These three dia ...
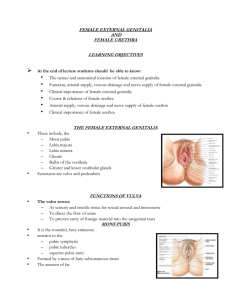
Female Ext Genitalia and urethra
... A thin anular fold of mucous membrane immediately within the vaginal orifice surrounding the lumen After its rupture, only remnants of the hymen, hymenal caruncles (tags), are visible The hymen has no established physiological function. It is considered primarily a ...
... A thin anular fold of mucous membrane immediately within the vaginal orifice surrounding the lumen After its rupture, only remnants of the hymen, hymenal caruncles (tags), are visible The hymen has no established physiological function. It is considered primarily a ...
FEMALE EXTERNAL GENITALIA
... A thin anular fold of mucous membrane immediately within the vaginal orifice surrounding the lumen After its rupture, only remnants of the hymen, hymenal caruncles (tags), are visible The hymen has no established physiological function. It is considered primarily a ...
... A thin anular fold of mucous membrane immediately within the vaginal orifice surrounding the lumen After its rupture, only remnants of the hymen, hymenal caruncles (tags), are visible The hymen has no established physiological function. It is considered primarily a ...
An autonomic pathway from the central nervous system to the
... C. is traversed by venous channels that drain into the pterygoid plexus. D. is located lateral to the posterior end of the nasal cavity. E. is traversed by fibers whose cell bodies are located in the trigeminal ganglion. Answer = B A patient with a gradual occlusion of the bifurcation of the left co ...
... C. is traversed by venous channels that drain into the pterygoid plexus. D. is located lateral to the posterior end of the nasal cavity. E. is traversed by fibers whose cell bodies are located in the trigeminal ganglion. Answer = B A patient with a gradual occlusion of the bifurcation of the left co ...
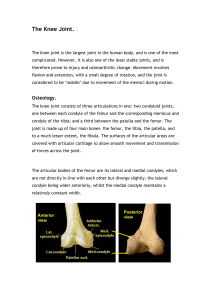
The Knee Joint - Judith Brown CPD
... The joint allows flexion and extension about a virtual transverse axis, together with some medial and lateral rotation about the axis of the lower leg in the flexed position. The centre of the transverse axis of the is located where both collateral ligaments and both cruciate ligaments intersect. Th ...
... The joint allows flexion and extension about a virtual transverse axis, together with some medial and lateral rotation about the axis of the lower leg in the flexed position. The centre of the transverse axis of the is located where both collateral ligaments and both cruciate ligaments intersect. Th ...
Parotid gland
... The buccal fat is one of several encapsulated fat masses in the cheek. It is a deep fat pad located on either side of the face between the buccinators muscle and several more superficial muscles ( including the masseter, the zygomaticus major, and the zygomaticus minor). The inferior portion of the ...
... The buccal fat is one of several encapsulated fat masses in the cheek. It is a deep fat pad located on either side of the face between the buccinators muscle and several more superficial muscles ( including the masseter, the zygomaticus major, and the zygomaticus minor). The inferior portion of the ...
Anatomy of Selected Synovial Joints
... downward motion of the condyle and mandibular depression. The temporomandibular joint is supported by an extrinsic ligament that anchors the mandible to the skull. This ligament spans the distance between the base of the skull and the lingula on the medial side of the mandibular ramus. Dislocation o ...
... downward motion of the condyle and mandibular depression. The temporomandibular joint is supported by an extrinsic ligament that anchors the mandible to the skull. This ligament spans the distance between the base of the skull and the lingula on the medial side of the mandibular ramus. Dislocation o ...
Anatomy and Biology Catalog
... The head is sectioned to expose half the brain. In addition, the neck is dissected to expose muscular, neural, vascular and glandular structures. The thorax and abdomen are completely open, providing an unrestricted view of all internal features. Significant structures are numbered and referenced on ...
... The head is sectioned to expose half the brain. In addition, the neck is dissected to expose muscular, neural, vascular and glandular structures. The thorax and abdomen are completely open, providing an unrestricted view of all internal features. Significant structures are numbered and referenced on ...
15-final Vasculature of lower limb
... List the main arterial anastomosis. List the sites where you feel the arterial pulse. Differentiate the veins of LL into superficial & deep Describe their origin, course & termination and tributaries ...
... List the main arterial anastomosis. List the sites where you feel the arterial pulse. Differentiate the veins of LL into superficial & deep Describe their origin, course & termination and tributaries ...
Prevalence of Laryngeal Cartilage Calcifications in Mangalore
... Similar studies7,8 done in the past have reported that ossifications are first seen in the thyroid, followed by cricoid and the arytenoids. In both males and females, the ossification began at the age of 18 to 20 years in the posterior part of the thyroid cartilage, same as our study. There is a gen ...
... Similar studies7,8 done in the past have reported that ossifications are first seen in the thyroid, followed by cricoid and the arytenoids. In both males and females, the ossification began at the age of 18 to 20 years in the posterior part of the thyroid cartilage, same as our study. There is a gen ...
Body Mechanics - Learn Muscles
... the talus; and because the extended knee joint also does not allow rotation, the femur medially rotates with the tibia. Therefore, hip joint lateral rotation musculature can support the arch by acting to brake/prevent medial rotation of the femur/tibia/talus. Hip joint lateral rotation musculature i ...
... the talus; and because the extended knee joint also does not allow rotation, the femur medially rotates with the tibia. Therefore, hip joint lateral rotation musculature can support the arch by acting to brake/prevent medial rotation of the femur/tibia/talus. Hip joint lateral rotation musculature i ...
superficial veins, lymphatics and lymph nodes
... • From the dense plexus of the palm, vessels pass in different directions, viz., upward toward the wrist, downward to join the digital vessels, medialward to join the vessels on the ulnar border of the hand, and lateralward to those on the thumb. • Several vessels from the central part of the plexu ...
... • From the dense plexus of the palm, vessels pass in different directions, viz., upward toward the wrist, downward to join the digital vessels, medialward to join the vessels on the ulnar border of the hand, and lateralward to those on the thumb. • Several vessels from the central part of the plexu ...
View PDF
... the suprascapular artery proper as opposed to the main artery itself; they suggested that an anterior approach, rather than a lateral approach, may be preferable for better visualization of the suprascapular ...
... the suprascapular artery proper as opposed to the main artery itself; they suggested that an anterior approach, rather than a lateral approach, may be preferable for better visualization of the suprascapular ...
Scapular, Clavicular, Acromioclavicular and Sternoclavicular Joint
... the capsular ligaments and the upper sternum. The costoclavicular or rhomboid ligament runs from the first rib to the rhomboid fossa at the inferior side of the medial clavicular metaphysis. This fossa should not be mistaken for a tumor when seen on radiographs. The SC joint is freely movable and fun ...
... the capsular ligaments and the upper sternum. The costoclavicular or rhomboid ligament runs from the first rib to the rhomboid fossa at the inferior side of the medial clavicular metaphysis. This fossa should not be mistaken for a tumor when seen on radiographs. The SC joint is freely movable and fun ...
Tongue Anatomy and Glossectomy
... keratinization is determined by the amount of physical force place on it ...
... keratinization is determined by the amount of physical force place on it ...
CARCINOMA OF THE RECTUM
... The inferior mesenteric artery is ligated below the left colic branch. Posterior mobilization is done carefully preserving the presacral nerves and without breaching the presacral fascia. Damage to the presacral fascia can lead to severe haemorrhage from the presacral veins. The anterior plan ...
... The inferior mesenteric artery is ligated below the left colic branch. Posterior mobilization is done carefully preserving the presacral nerves and without breaching the presacral fascia. Damage to the presacral fascia can lead to severe haemorrhage from the presacral veins. The anterior plan ...
EXTENSOR DIGITORUM - Medicine Batch 2013
... stem has given off its deep branch in front of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus ...
... stem has given off its deep branch in front of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus ...
Bones of the Upper Limb
... whose bones are weakened due to osteoporosis. Falls onto the hand or elbow, or direct blows to the arm, can result in fractures of the humerus (Figure 7 (Fractures of the Humerus and Radius )). Following a fall, fractures at the surgical neck, the region at which the expanded proximal end of the hum ...
... whose bones are weakened due to osteoporosis. Falls onto the hand or elbow, or direct blows to the arm, can result in fractures of the humerus (Figure 7 (Fractures of the Humerus and Radius )). Following a fall, fractures at the surgical neck, the region at which the expanded proximal end of the hum ...
Pdf - McMed International
... extensor carpi radialis longus inserts into the dorsal surface of the base of the second metacarpal bone on its radial side to extend and abduct the wrist. The extensor carpi radialis brevis inserts into the lateral dorsal surface of the base of the third metacarpal bone, with a few fibres inserting ...
... extensor carpi radialis longus inserts into the dorsal surface of the base of the second metacarpal bone on its radial side to extend and abduct the wrist. The extensor carpi radialis brevis inserts into the lateral dorsal surface of the base of the third metacarpal bone, with a few fibres inserting ...
Lower Extremities Homework 2 Nancy Nesyto
... Gluteus medius – O- gluteal surface of the ilium between the iliac crest and posterior and anterior gluteal lines – I Greater trochanter, A Abduct the hip, anterior fibers flex and medially rotate the hip, posterior fibers extend and laterally rotate the hip G. minimus – O- gluteal surface of th ...
... Gluteus medius – O- gluteal surface of the ilium between the iliac crest and posterior and anterior gluteal lines – I Greater trochanter, A Abduct the hip, anterior fibers flex and medially rotate the hip, posterior fibers extend and laterally rotate the hip G. minimus – O- gluteal surface of th ...
16-VASCULATURE OF UL2016-12
... Deep Veins of the Upper Limb Accompany the arteries of the same region and bear similar names. Venae commitantes: They are generally arranged in pairs, and are situated one on either side of the corresponding artery, and connected at intervals by short transverse branches. The superficial and ...
... Deep Veins of the Upper Limb Accompany the arteries of the same region and bear similar names. Venae commitantes: They are generally arranged in pairs, and are situated one on either side of the corresponding artery, and connected at intervals by short transverse branches. The superficial and ...
Anterior Knee pain
... posterior to the lateral facet (curved arrow). On a lateral radiograph the median ridge and lateral facet form two separate borders which appear slightly concave. ...
... posterior to the lateral facet (curved arrow). On a lateral radiograph the median ridge and lateral facet form two separate borders which appear slightly concave. ...
Anterior Thigh Flexors of the hip Pectineus Superior ramus of pubis
... Lateral condyle and superior half of lateral surface of tibia and interosseus membrane -> medial and inferior surfaces of medial cuneiform and base of 1st metatarsal Deep fibular nerve (L4, L5) Dorsiflexes ankle and inverts foot Extensor digitorum longus Lateral condyle of tibia and superi ...
... Lateral condyle and superior half of lateral surface of tibia and interosseus membrane -> medial and inferior surfaces of medial cuneiform and base of 1st metatarsal Deep fibular nerve (L4, L5) Dorsiflexes ankle and inverts foot Extensor digitorum longus Lateral condyle of tibia and superi ...
anterior cruciate ligament: history, anatomy, and reconstruction
... sort of contractile power. Galen wrote that ligaments were the supporting structures of diarthrodial joints. serving as stabilizers of these joints and limiting abnormal motion. Interest in the structure lapsed for the next 1.600 years as medical attention was drawn to infectious disease and major t ...
... sort of contractile power. Galen wrote that ligaments were the supporting structures of diarthrodial joints. serving as stabilizers of these joints and limiting abnormal motion. Interest in the structure lapsed for the next 1.600 years as medical attention was drawn to infectious disease and major t ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.