Gluteal Region, Posterior Thigh and Popliteal Fossa
... What might happen to a person who has this variation and hypertrophies his/her piriformis because of repeated lateral rotation? Say, for example, from playing a lot of racketball. ...
... What might happen to a person who has this variation and hypertrophies his/her piriformis because of repeated lateral rotation? Say, for example, from playing a lot of racketball. ...
Full Article - Medical Ultrasonography
... do not have a basement membrane, join together to form larger lymphatic vessels. These vessels have valves that direct the lymphatic circulation in a one-way, centripetal, manner. The central nervous system, the bone marrow and the non-vascularized tissues (cornea, epidermis and cartilage) have no l ...
... do not have a basement membrane, join together to form larger lymphatic vessels. These vessels have valves that direct the lymphatic circulation in a one-way, centripetal, manner. The central nervous system, the bone marrow and the non-vascularized tissues (cornea, epidermis and cartilage) have no l ...
21 Hip Disarticulation
... are now identified. The large circumflex femoral vessels are nearby and should be avoided. The semimembranosus, semitendinosus, and long head of the biceps muscle are transected from their origin on the ischial tuberosity while preserving the quadratus femoris muscle and sciatic nerve. ...
... are now identified. The large circumflex femoral vessels are nearby and should be avoided. The semimembranosus, semitendinosus, and long head of the biceps muscle are transected from their origin on the ischial tuberosity while preserving the quadratus femoris muscle and sciatic nerve. ...
Lesson 1: What Is The Anatomy Of The Human Voice?
... are located where the pharynx splits between the trachea and esophagus. Vocal cords: twin membranes that stretch horizontally across the larynx. They are smaller than a nickel. They are open during inhalation, closed when you hold your breath and vibrate when you speak or sing. Glottis: the combin ...
... are located where the pharynx splits between the trachea and esophagus. Vocal cords: twin membranes that stretch horizontally across the larynx. They are smaller than a nickel. They are open during inhalation, closed when you hold your breath and vibrate when you speak or sing. Glottis: the combin ...
Educator`s Guide - Perot Museum of Nature and Science
... plastinates. This was when I began to think of anato- ...
... plastinates. This was when I began to think of anato- ...
Chapter 13
... • The vestibular region is located inside the nostrils and contains the coarse nasal hairs that act as the first line of defense for the respiratory system. • These hairs, called vibrissae, are covered with sebum, a greasy substance secreted by the sebaceous glands of the nose. • Sebum helps trap pa ...
... • The vestibular region is located inside the nostrils and contains the coarse nasal hairs that act as the first line of defense for the respiratory system. • These hairs, called vibrissae, are covered with sebum, a greasy substance secreted by the sebaceous glands of the nose. • Sebum helps trap pa ...
Superficial Facial Musculature March 2012
... orbicularis oculi muscles. These muscle fibers are intertwined and there are no attachments to bone. It inserts into the galea aponeurosis and innervated by the temporal branch of the facial nerve. Its function is to furrow the forehead, raise the eyebrows and widen the eyes. The frontalis muscle ca ...
... orbicularis oculi muscles. These muscle fibers are intertwined and there are no attachments to bone. It inserts into the galea aponeurosis and innervated by the temporal branch of the facial nerve. Its function is to furrow the forehead, raise the eyebrows and widen the eyes. The frontalis muscle ca ...
HERE - Faculty
... You must be able to distinguish between C1, C2, and the other cervical vertebrae Identify the transverse foramen Thoracic Look for articulations for ribs Lumbar Notice the lack of articulations for ribs Sacral 5 fused bones Note the sacral promontory Anterior/Posterior Sacral Foramina median sacral ...
... You must be able to distinguish between C1, C2, and the other cervical vertebrae Identify the transverse foramen Thoracic Look for articulations for ribs Lumbar Notice the lack of articulations for ribs Sacral 5 fused bones Note the sacral promontory Anterior/Posterior Sacral Foramina median sacral ...
Chapter 25
... E. Mouth (Oral Cavity or Buccal Cavity) (p. 770) 1. The mouth is formed by the following structures: i. cheeks that form the lateral walls; they consist of skeletal muscles covered externally by skin and internally by nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium ii. superior and inferior lips (labi ...
... E. Mouth (Oral Cavity or Buccal Cavity) (p. 770) 1. The mouth is formed by the following structures: i. cheeks that form the lateral walls; they consist of skeletal muscles covered externally by skin and internally by nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium ii. superior and inferior lips (labi ...
03. face,N&vessels
... As it comes out from its exit of the skull ( stylomastoid foramen ) it gives rise to the posterior auricular nerve which ascends behind the ear & supplies the posterior & superior auricular muscles & the occipital belly of occipitofrontalis.Then It runs forward within the substance of the parotid sa ...
... As it comes out from its exit of the skull ( stylomastoid foramen ) it gives rise to the posterior auricular nerve which ascends behind the ear & supplies the posterior & superior auricular muscles & the occipital belly of occipitofrontalis.Then It runs forward within the substance of the parotid sa ...
Clinical and Functional Significance of the Anomalous Insertion of
... coronoid process of the ulna. Hatice Tuba et al [4], in his MRI study on cadaveric upper limbs, described the two heads of origin of the brachialis, the superficial and deep and all the specimens showed their insertion into the ulnar tuberosity and into the coronoid process of the ulna. There was no ...
... coronoid process of the ulna. Hatice Tuba et al [4], in his MRI study on cadaveric upper limbs, described the two heads of origin of the brachialis, the superficial and deep and all the specimens showed their insertion into the ulnar tuberosity and into the coronoid process of the ulna. There was no ...
Organization of the Skeleton
... –Supports the tongue and serves as an attachment for muscles that help move the tongue and function in ...
... –Supports the tongue and serves as an attachment for muscles that help move the tongue and function in ...
BIOL1151L - Clayton State University
... Epithelial Tissues ID Sheet Epithelial Tissues For this lab we will only be looking at one type of tissue. Epithelial tissues are found lining or covering various organs in the body. They can be recognized by the presence of a free surface, where the cells are in contact with spaces inside the body ...
... Epithelial Tissues ID Sheet Epithelial Tissues For this lab we will only be looking at one type of tissue. Epithelial tissues are found lining or covering various organs in the body. They can be recognized by the presence of a free surface, where the cells are in contact with spaces inside the body ...
articulators
... • Vowels have to form the vocal tract into a tube with one ([],[a, ]) or two (most other vowels) main cavities. For this the tongue dorsum (which comprises the mass of the tongue) is moved up and down, backwards & forwards, • Consonants have to form an obstruction to the airflow. For this any cons ...
... • Vowels have to form the vocal tract into a tube with one ([],[a, ]) or two (most other vowels) main cavities. For this the tongue dorsum (which comprises the mass of the tongue) is moved up and down, backwards & forwards, • Consonants have to form an obstruction to the airflow. For this any cons ...
Bones (Ch7)
... – False ribs – Pairs 8–10 (vertebrochondral ribs) • Attach indirectly to sternum by joining costal cartilage of rib above ...
... – False ribs – Pairs 8–10 (vertebrochondral ribs) • Attach indirectly to sternum by joining costal cartilage of rib above ...
Accessory Head of Flexor Pollicis Longus Muscle and its
... Manipal, we observed an accessory belly, which took its origin from the under surface of flexor digitorum superficialis muscle just digital to the origin of this muscle from medial epicondyle. On further dissection we have noticed that, the accessory belly was running downwards to the medial aspect ...
... Manipal, we observed an accessory belly, which took its origin from the under surface of flexor digitorum superficialis muscle just digital to the origin of this muscle from medial epicondyle. On further dissection we have noticed that, the accessory belly was running downwards to the medial aspect ...
beauty and facial esthetic treatments
... can improve the longevity of this approach utilizing better cellular nutrition. For example, supplementing with 3-5 thousand mg. of vitamin C will help improve collagen density. Without sufficient vitamin C, the chemical process of collagen formation cannot occur with any degree of density. To arriv ...
... can improve the longevity of this approach utilizing better cellular nutrition. For example, supplementing with 3-5 thousand mg. of vitamin C will help improve collagen density. Without sufficient vitamin C, the chemical process of collagen formation cannot occur with any degree of density. To arriv ...
Nerve supply
... a powerful extensor of the knee joint. Some of the tendinous fibers of the vastus lateralis and vastus medialis form bands, or retinacula, that join the capsule of the knee joint and strengthen it. The lowest muscle fibers of the vastus medialis are almost horizontal and prevent the patella from bei ...
... a powerful extensor of the knee joint. Some of the tendinous fibers of the vastus lateralis and vastus medialis form bands, or retinacula, that join the capsule of the knee joint and strengthen it. The lowest muscle fibers of the vastus medialis are almost horizontal and prevent the patella from bei ...
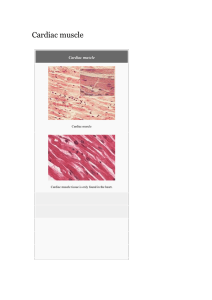
Cardiac muscle File
... cardiac connection fibres.[4] Electrical resistance through intercalated discs is very low, thus allowing free diffusion of ions. The ease of ion movement along cardiac muscle fibers axes is such that action potentials are able to travel from one cardiac muscle cell to the next, facing only slight ...
... cardiac connection fibres.[4] Electrical resistance through intercalated discs is very low, thus allowing free diffusion of ions. The ease of ion movement along cardiac muscle fibers axes is such that action potentials are able to travel from one cardiac muscle cell to the next, facing only slight ...
36-2 Internal Frog Anatomy INVESTIGATION Introduction
... ,. Using a scaJpel, cut the ventral muscle waJI from the anus to the throat. Be careful not to cut too dttply or you will damage the internal organs. 2. Make a lateral cut from shoulder to shoulder and down either side. Finish making a square, as in the diagram, so that the chest ar.d ab· dominal mu ...
... ,. Using a scaJpel, cut the ventral muscle waJI from the anus to the throat. Be careful not to cut too dttply or you will damage the internal organs. 2. Make a lateral cut from shoulder to shoulder and down either side. Finish making a square, as in the diagram, so that the chest ar.d ab· dominal mu ...
Bones and Muscles - OYR Raiders Ice Hockey
... mourning.(The lacrimal bone forms half of the receptacle, which holds the lacrimal sac, a structure that receives the tears and directs them into the nasal cavity. That explains why we blow our noses in cold weather, or when we cry, we are blowing out the tears that have drained into the cavity. The ...
... mourning.(The lacrimal bone forms half of the receptacle, which holds the lacrimal sac, a structure that receives the tears and directs them into the nasal cavity. That explains why we blow our noses in cold weather, or when we cry, we are blowing out the tears that have drained into the cavity. The ...
Axillary Aug Video Clip Legends
... pectoralis that are lateral to the main body of pectoralis origins (these origins often have a tendinous appearing attachment to the ribs, illustrated by the muscle origin in the center of the frame). The surgeon should never divide the main body of pectoralis origins along the sternum, even partial ...
... pectoralis that are lateral to the main body of pectoralis origins (these origins often have a tendinous appearing attachment to the ribs, illustrated by the muscle origin in the center of the frame). The surgeon should never divide the main body of pectoralis origins along the sternum, even partial ...
Course Outline - Pima Community College
... Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to do the following: 1. Identify the roles of the three types of word parts in forming medical terms. 2. Define anatomy and physiology and use anatomic reference systems to identify the anatomic position, body planes, directions, and cavities. ...
... Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to do the following: 1. Identify the roles of the three types of word parts in forming medical terms. 2. Define anatomy and physiology and use anatomic reference systems to identify the anatomic position, body planes, directions, and cavities. ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.