PDF - Anatomy Journal of Africa
... found in the GP and GDP respectively. The branches of left and right gastric vessels were also found in the superior aspect of GP ligament, the splenic artery also run in the inferior aspect of the GP ligament. Portal triad is mainly contained within the hepatoduodenal ligament but in this case the ...
... found in the GP and GDP respectively. The branches of left and right gastric vessels were also found in the superior aspect of GP ligament, the splenic artery also run in the inferior aspect of the GP ligament. Portal triad is mainly contained within the hepatoduodenal ligament but in this case the ...
lateral - Personal
... • Attach the upper limbs to the axial skeleton • Provide attachment sites for muscles that move the upper limbs ...
... • Attach the upper limbs to the axial skeleton • Provide attachment sites for muscles that move the upper limbs ...
Left lower lobe collapse
... The appearance depends on the location of the lesion. 1.The more central lesions may merely appear as a bulky hilum, representing the tumor and local nodal involvement the lesion is irregular in outline have spiky or sun ray spiculation . 2.Lobar collapse may be seen due to obstruction of a bronchus ...
... The appearance depends on the location of the lesion. 1.The more central lesions may merely appear as a bulky hilum, representing the tumor and local nodal involvement the lesion is irregular in outline have spiky or sun ray spiculation . 2.Lobar collapse may be seen due to obstruction of a bronchus ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... 84. A sagittal plane is a vertical line that divides the body into right and left parts. ...
... 84. A sagittal plane is a vertical line that divides the body into right and left parts. ...
Chapter 94: Larynx - Anatomy
... The cartilage of the epiglottis is a leaflike structure composed primarily of elastic cartilage. The mucosa covering its anterior surface is composed of stratified squamous epithelium. Posteriorly, near the inlet of the larynx, the epithelium is pseudostratified, ciliated, and columnar. The inferior ...
... The cartilage of the epiglottis is a leaflike structure composed primarily of elastic cartilage. The mucosa covering its anterior surface is composed of stratified squamous epithelium. Posteriorly, near the inlet of the larynx, the epithelium is pseudostratified, ciliated, and columnar. The inferior ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... B. Left lower quadrant (LLQ) C. Right hypochondriac region D. Left hypochondriac region E. Right lower quadrant (RLQ) 73. These figures show a frontal view of the abdominopelvic cavities. Which number indicates the left iliac region? ...
... B. Left lower quadrant (LLQ) C. Right hypochondriac region D. Left hypochondriac region E. Right lower quadrant (RLQ) 73. These figures show a frontal view of the abdominopelvic cavities. Which number indicates the left iliac region? ...
Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy and Digestive System
... skin and muscles according to the diagram. Do not remove the umbilical cord. In the first section, you will only examine the abdominal cavity (the area below the ribcage). After completing the cuts, locate the umbilical vein that leads from the umbilical cord to the liver. You will need to cut this ...
... skin and muscles according to the diagram. Do not remove the umbilical cord. In the first section, you will only examine the abdominal cavity (the area below the ribcage). After completing the cuts, locate the umbilical vein that leads from the umbilical cord to the liver. You will need to cut this ...
Full file at http://testbanksolution.eu/Test-Bank-Bank-for
... 84. A sagittal plane is a vertical line that divides the body into right and left parts. ...
... 84. A sagittal plane is a vertical line that divides the body into right and left parts. ...
Anatomy of the Thoracic Wall, Axilla and Breast
... runs along the upper margin of this muscle, penetrates the clavipectoral fascia and divides into pectoralis, acromialis, clavicularis and deltoideus branches. Thoracica lateralis artery: This follows the lower margin of the pectoralis minor muscle as far as the thoracic wall, and irrigates the pecto ...
... runs along the upper margin of this muscle, penetrates the clavipectoral fascia and divides into pectoralis, acromialis, clavicularis and deltoideus branches. Thoracica lateralis artery: This follows the lower margin of the pectoralis minor muscle as far as the thoracic wall, and irrigates the pecto ...
Triangles of the neck
... It is bounded superiorly by the lower border of the mandible (the base), posteriorly by anterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle and medially by the midline of the neck. It is covered by the skin, superficial fascia, platysma and investing layer of deep fascia. ...
... It is bounded superiorly by the lower border of the mandible (the base), posteriorly by anterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle and medially by the midline of the neck. It is covered by the skin, superficial fascia, platysma and investing layer of deep fascia. ...
pdf
... The submandibular area is limited by the platysma (pt) The submandibular duct (1) go forward up against the medial surface of the sub lingual to the ostium near the lingual frenulum. It is undercrossed by the lingual nerve (2). It passes between the mylohyoid and hyoglossus muscles medial to subling ...
... The submandibular area is limited by the platysma (pt) The submandibular duct (1) go forward up against the medial surface of the sub lingual to the ostium near the lingual frenulum. It is undercrossed by the lingual nerve (2). It passes between the mylohyoid and hyoglossus muscles medial to subling ...
Fetal anatomy of the upper pharyngeal muscles with special
... branches of the glossopharyngeal nerve, exhibited a curved or recurrent course; they originated from the nerve trunks at the supero-inferior level including the hyoid bone, turned upward, and reached the superior level, including the pharyngotympanic tube. The nerves were located in the deeper side ...
... branches of the glossopharyngeal nerve, exhibited a curved or recurrent course; they originated from the nerve trunks at the supero-inferior level including the hyoid bone, turned upward, and reached the superior level, including the pharyngotympanic tube. The nerves were located in the deeper side ...
handout - Arizona Osteopathic Medical Association
... Probe placement: Place probe on posterior shoulder in vertical position, just below scapular spine and lateral to view humeral head and infrapinatus tendon. From this position, move the probe inferior and slightly medial to visualize the humeral head (laterally) and glenoid fossa/labrum (medially). ...
... Probe placement: Place probe on posterior shoulder in vertical position, just below scapular spine and lateral to view humeral head and infrapinatus tendon. From this position, move the probe inferior and slightly medial to visualize the humeral head (laterally) and glenoid fossa/labrum (medially). ...
ppt - Mr. Gracias Homepage
... Every cell in the human body is both an independent unit and an interdependent part of a larger community—the entire organism. ...
... Every cell in the human body is both an independent unit and an interdependent part of a larger community—the entire organism. ...
sample
... lie in nearly a horizontal plane and are less stable. Although the spinal cord may be compressed, it may escape severe injury because of the large vertebral canal. Nevertheless, all movement of patients suspected of having a neck injury should be minimized until the cervical spine is properly stabil ...
... lie in nearly a horizontal plane and are less stable. Although the spinal cord may be compressed, it may escape severe injury because of the large vertebral canal. Nevertheless, all movement of patients suspected of having a neck injury should be minimized until the cervical spine is properly stabil ...
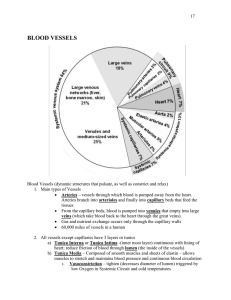
Circulatory System Part 3
... Major Veins in Systemic Circulation Veins are typically located in more superficial areas of the body but some some follow the course of the major arteries. With a few exceptions the naming of these veins is identical to that of the companion arteries Superior Vena Cava – veins draining the head and ...
... Major Veins in Systemic Circulation Veins are typically located in more superficial areas of the body but some some follow the course of the major arteries. With a few exceptions the naming of these veins is identical to that of the companion arteries Superior Vena Cava – veins draining the head and ...
Anatomical localization motor pathways
... CHAPTER V Movement disorders Part I: Anatomy and physiology of motor system ...
... CHAPTER V Movement disorders Part I: Anatomy and physiology of motor system ...
The Central Nervous System
... crisscross each other and become redistributed so that – Each branch of the plexus contains fibers from several different spinal nerves – Fibers from each ventral ramus travel to the body periphery via several different routes or branches ...
... crisscross each other and become redistributed so that – Each branch of the plexus contains fibers from several different spinal nerves – Fibers from each ventral ramus travel to the body periphery via several different routes or branches ...
Grasshopper lab - davis.k12.ut.us
... attached to the thorax, a single pair of antennae, mouthparts adapted for chewing and two pairs of wings. Grasshoppers, along with katydids and crickets belong to the order orthoptera, derived from the Greek "ortho" meaning straight and "ptera" meaning wing. External anatomy ...
... attached to the thorax, a single pair of antennae, mouthparts adapted for chewing and two pairs of wings. Grasshoppers, along with katydids and crickets belong to the order orthoptera, derived from the Greek "ortho" meaning straight and "ptera" meaning wing. External anatomy ...
HeadandNeckPracticeExam2011
... C. the epicranial aponeurosis and the loose areolar tissue D. the loose areolar tissue and the pericranium E. None of the above 17. _____ Which of the following arises from the second part of the Maxillary artery (as it passes superficial to or within the Lateral pterygoid muscle)? A. Buccal artery ...
... C. the epicranial aponeurosis and the loose areolar tissue D. the loose areolar tissue and the pericranium E. None of the above 17. _____ Which of the following arises from the second part of the Maxillary artery (as it passes superficial to or within the Lateral pterygoid muscle)? A. Buccal artery ...
Tongji Univesity School of Medicine 2011
... eventually experiences which of the following? (A) loss of wrist extension, leading to wrist drop (B) Weakness in pronating the forearm (C) Sensory loss over the ventral aspect of the base of the thumb (D) Inability to oppose the thumb (E) Inability to abduct the fingers 12 Which of the following is ...
... eventually experiences which of the following? (A) loss of wrist extension, leading to wrist drop (B) Weakness in pronating the forearm (C) Sensory loss over the ventral aspect of the base of the thumb (D) Inability to oppose the thumb (E) Inability to abduct the fingers 12 Which of the following is ...
knee-anatomy
... First, we will define some common anatomic terms as they relate to the knee. This will make it clearer as we talk about the structures later. Because many parts of the body have duplicates, it is common to describe parts of the body using terms that define where the part is in relation to an imagina ...
... First, we will define some common anatomic terms as they relate to the knee. This will make it clearer as we talk about the structures later. Because many parts of the body have duplicates, it is common to describe parts of the body using terms that define where the part is in relation to an imagina ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.