Chemistry Standards and Frameworks
... Most periodic tables have a heavy stepped line running from boron to astatine. Elements to the immediate right and left of this line, excluding the metal aluminum, are semimetals and have properties that are intermediate between metals and nonmetals. Elements further to the left are metals. Those fu ...
... Most periodic tables have a heavy stepped line running from boron to astatine. Elements to the immediate right and left of this line, excluding the metal aluminum, are semimetals and have properties that are intermediate between metals and nonmetals. Elements further to the left are metals. Those fu ...
Honors-Final-Review-2014
... _____ boiling point _____ surfactant _____ viscosity _____ solution _____ surface tension ...
... _____ boiling point _____ surfactant _____ viscosity _____ solution _____ surface tension ...
oscillations_01
... force, net (resultant) force, Newton’s Second Law), Hooke’s Law, spring constant (spring stiffness), equilibrium, velocity, acceleration, work, kinetic energy, potential energy (reference point), gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, total energy, conservation of energy, ISEE, so ...
... force, net (resultant) force, Newton’s Second Law), Hooke’s Law, spring constant (spring stiffness), equilibrium, velocity, acceleration, work, kinetic energy, potential energy (reference point), gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, total energy, conservation of energy, ISEE, so ...
Slide 1
... force, net (resultant) force, Newton’s Second Law), Hooke’s Law, spring constant (spring stiffness), equilibrium, velocity, acceleration, work, kinetic energy, potential energy (reference point), gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, total energy, conservation of energy, ISEE, so ...
... force, net (resultant) force, Newton’s Second Law), Hooke’s Law, spring constant (spring stiffness), equilibrium, velocity, acceleration, work, kinetic energy, potential energy (reference point), gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, total energy, conservation of energy, ISEE, so ...
Chemistry EOC Review Spring 2013
... Directions: The following is an End-Of-Course Review Guide designed to assist you as prepare for your EOC. It is imperative that you complete this guide to the best of your ability. This will help you to achieve a higher average on your second quarter grade. Unit 1 & 2 Lab Safety, Introduction to Ch ...
... Directions: The following is an End-Of-Course Review Guide designed to assist you as prepare for your EOC. It is imperative that you complete this guide to the best of your ability. This will help you to achieve a higher average on your second quarter grade. Unit 1 & 2 Lab Safety, Introduction to Ch ...
Solving for time-varying and static cube roots in real and complex
... Online solution of time-varying cube root in the form of x3(t) - a(t) = 0 and/or static (or termed, constant, timeinvariant) cube root in the form of x3 - a = 0 is considered to be a basic problem arising in science and engineering fields, for example, computer graphics [1–3], scientific computing [ ...
... Online solution of time-varying cube root in the form of x3(t) - a(t) = 0 and/or static (or termed, constant, timeinvariant) cube root in the form of x3 - a = 0 is considered to be a basic problem arising in science and engineering fields, for example, computer graphics [1–3], scientific computing [ ...
Final review free response ch 1-4
... 5. If you have 4 g NaOH, and 10 g HBr, what is the limiting reagent and how much salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
... 5. If you have 4 g NaOH, and 10 g HBr, what is the limiting reagent and how much salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood (Pages 735
... c. some MATTER exists in elemental form [(e.g.) gold [Au] = not chemically REACTIVE)] *d. ELEMENTS individually or combined form everything in the universe including HUMANS *1. Human body’s most abundant ELEMENTS: carbon [C], oxygen [O], hydrogen [H], and nitrogen [N]; for teeth & BONES = calcium [C ...
... c. some MATTER exists in elemental form [(e.g.) gold [Au] = not chemically REACTIVE)] *d. ELEMENTS individually or combined form everything in the universe including HUMANS *1. Human body’s most abundant ELEMENTS: carbon [C], oxygen [O], hydrogen [H], and nitrogen [N]; for teeth & BONES = calcium [C ...
Wk-11-14
... C and D. Problem is: we may not necessarily agree! Western cultures (and chemists of all cultures) try to manipulate equilibrium, as if it is our manifest destiny to do so! ...
... C and D. Problem is: we may not necessarily agree! Western cultures (and chemists of all cultures) try to manipulate equilibrium, as if it is our manifest destiny to do so! ...
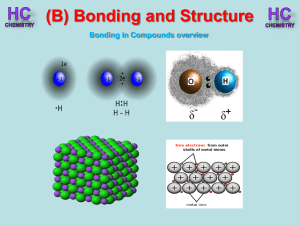
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... Silicon, like carbon, can form giant covalent networks. Silicon carbide exist in a similar structure to diamond. Tetrahedral shape ...
... Silicon, like carbon, can form giant covalent networks. Silicon carbide exist in a similar structure to diamond. Tetrahedral shape ...
01 Intro Chemistry
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
02Ch02chemistry2005
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
Chapter 2 Chemistry
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
Main Title 32pt
... • Support IBM’s call for research in RL TS – caveat requires 3 orders of magnitude reduction in clock • Search for more real world problems suitable for solution on a QC RL surprised by length of list • Demonstrate ways of using nano technologies (by researching architectures-- including quirks and ...
... • Support IBM’s call for research in RL TS – caveat requires 3 orders of magnitude reduction in clock • Search for more real world problems suitable for solution on a QC RL surprised by length of list • Demonstrate ways of using nano technologies (by researching architectures-- including quirks and ...
Final Exam Study Guide Page 1 Quiz
... a. Is completely used up in the reaction b. Will have some amount unchanged, or leftover, after the reaction c. Cannot be calculated without performing the reaction d. Has no effect in the amount of product formed ...
... a. Is completely used up in the reaction b. Will have some amount unchanged, or leftover, after the reaction c. Cannot be calculated without performing the reaction d. Has no effect in the amount of product formed ...
Unit 1 Review, pages 138–145
... 33. The contribution to the periodic table made by Dobereiner was his early attempt to classify small groups of elements according to their properties. 34. If an atom has high ionization energy, its electron affinity is also high. 35. (a) An electrolyte is a compound that conducts an electric curren ...
... 33. The contribution to the periodic table made by Dobereiner was his early attempt to classify small groups of elements according to their properties. 34. If an atom has high ionization energy, its electron affinity is also high. 35. (a) An electrolyte is a compound that conducts an electric curren ...
chapter3 - AlvarezHChem
... a. sum all atoms of each type on a side, even if an element is in more than one substance b. work from left to right to stay organized c. if a polyatomic ion is present in the same form on both sides it can be counted as a unit rather than as individual elements d. look to balance H’s and O’s last i ...
... a. sum all atoms of each type on a side, even if an element is in more than one substance b. work from left to right to stay organized c. if a polyatomic ion is present in the same form on both sides it can be counted as a unit rather than as individual elements d. look to balance H’s and O’s last i ...
Chemical reactions unit
... RATES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS There are 6 factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions: 1. Increase in temperature: Why? The particles are moving faster and have more chances to collide into each other to make a reaction. 2. Increase in Surface area: Why? More of the substance is exposed, so th ...
... RATES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS There are 6 factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions: 1. Increase in temperature: Why? The particles are moving faster and have more chances to collide into each other to make a reaction. 2. Increase in Surface area: Why? More of the substance is exposed, so th ...
Chemical reactions unit
... RATES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS There are 6 factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions: 1. Increase in temperature: Why? The particles are moving faster and have more chances to collide into each other to make a reaction. 2. Increase in Surface area: Why? More of the substance is exposed, so th ...
... RATES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS There are 6 factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions: 1. Increase in temperature: Why? The particles are moving faster and have more chances to collide into each other to make a reaction. 2. Increase in Surface area: Why? More of the substance is exposed, so th ...
Moles x (conversion factor) = new unit
... If decimals are present, multiply all numbers to create integers ...
... If decimals are present, multiply all numbers to create integers ...
Practice Final Chem1a
... indicating geometry around central atoms, hybridization, bond angles, and whether the species is polar or not. (20 pts) geometry Lewis structure around each each central atom chemical formula (include bond angles) central atom? hybridization? polar? CO32- ...
... indicating geometry around central atoms, hybridization, bond angles, and whether the species is polar or not. (20 pts) geometry Lewis structure around each each central atom chemical formula (include bond angles) central atom? hybridization? polar? CO32- ...
Chapter 3: Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Describe the energy changes that take place in processes of boiling, melting and sublimation. Define what is meant by the vapor pressure of a liquid or solid. Explain the relationship between vapor pressure, volatility, boiling point, and the strength of the forces holding particles together. ...
... Describe the energy changes that take place in processes of boiling, melting and sublimation. Define what is meant by the vapor pressure of a liquid or solid. Explain the relationship between vapor pressure, volatility, boiling point, and the strength of the forces holding particles together. ...