Bio 520
... blood vessels. Use a dropper to inflate the lung with air (you might not be able to do this). 2. Locate the heart. The heart is a complex organ made out of one of the three classes of muscle: cardiac muscle (the others are: smooth muscle, which makes up the tubing, like blood vessels and intestines; ...
... blood vessels. Use a dropper to inflate the lung with air (you might not be able to do this). 2. Locate the heart. The heart is a complex organ made out of one of the three classes of muscle: cardiac muscle (the others are: smooth muscle, which makes up the tubing, like blood vessels and intestines; ...
Greek Jeopardy - mastrianascience
... I hold your body parts in. I have pores so sweat can escape your body. I am filled with nerves that help you sense temperature and feel things around you. Who am I? ...
... I hold your body parts in. I have pores so sweat can escape your body. I am filled with nerves that help you sense temperature and feel things around you. Who am I? ...
32696 Circ Resp Dig Uri CDROM
... bronchial tubes: Tubes within the lungs that help to filter out dirt and germs from the air. capillary: Small blood vessel that transports oxygen to the cells of the body and removes waste from those cells. carbon dioxide: Gas formed from animal respiration. cilia: Small hairs within the lungs that ...
... bronchial tubes: Tubes within the lungs that help to filter out dirt and germs from the air. capillary: Small blood vessel that transports oxygen to the cells of the body and removes waste from those cells. carbon dioxide: Gas formed from animal respiration. cilia: Small hairs within the lungs that ...
PowerPoint Lecture 12
... The horizontal fissure begins posterolaterally at the oblique fissure and passes deep to the 5th rib. Note positions of scapulae and costal recess relative to lungs. ...
... The horizontal fissure begins posterolaterally at the oblique fissure and passes deep to the 5th rib. Note positions of scapulae and costal recess relative to lungs. ...
Chapter 1
... Intro to the Human Body 1. Chemical – Atoms, small units of matter that participate in chemical reactions, and molecules, two or more atoms joined together. ...
... Intro to the Human Body 1. Chemical – Atoms, small units of matter that participate in chemical reactions, and molecules, two or more atoms joined together. ...
Full Text PDF - Edorium™ Journal of Anatomy and Embryology
... branching, and form the respiratory tree through the terminal bronchioles by the end of the canalicular stage. During the sacular stage, the bronchioles divide into the respiratory bronchioles and eventually into the terminal sacs (also termed primitive alveoli). Around week 36, the terminal sacs be ...
... branching, and form the respiratory tree through the terminal bronchioles by the end of the canalicular stage. During the sacular stage, the bronchioles divide into the respiratory bronchioles and eventually into the terminal sacs (also termed primitive alveoli). Around week 36, the terminal sacs be ...
Ch 9
... synovial membrane (which secretes a lubricating and jointnourishing synovial fluid) (Figure 9.3). • The flexibility of the fibrous capsule permits considerable movement at a joint, whereas its great tensile strength helps prevent bones from dislocating. • Other capsule features include ligaments and ...
... synovial membrane (which secretes a lubricating and jointnourishing synovial fluid) (Figure 9.3). • The flexibility of the fibrous capsule permits considerable movement at a joint, whereas its great tensile strength helps prevent bones from dislocating. • Other capsule features include ligaments and ...
morphometric study of pterion
... approaches towards important pathologies of this region [4, 6, 9, 18]. Additionally, the pterion is a primary region during surgical interventions of the sphenoid ridge and optic canal [5, 6]. In skulls with an epipteric bone a. Sphenoparietal type; b. Frontotemporal type ; c. Stel- variation, the l ...
... approaches towards important pathologies of this region [4, 6, 9, 18]. Additionally, the pterion is a primary region during surgical interventions of the sphenoid ridge and optic canal [5, 6]. In skulls with an epipteric bone a. Sphenoparietal type; b. Frontotemporal type ; c. Stel- variation, the l ...
Groups
... Due to the intricate connections between these two body systems, it is impossible to view each totally separately. Therefore, be aware that your dissections and investigations need to continuously go back and forth between these body structures. The dissection of blood vessels is delicate where curi ...
... Due to the intricate connections between these two body systems, it is impossible to view each totally separately. Therefore, be aware that your dissections and investigations need to continuously go back and forth between these body structures. The dissection of blood vessels is delicate where curi ...
Today:
... can be separated into two groups based on symmetry Radial symmetry = Radiata Bilateral Symmetry = Bilateria ...
... can be separated into two groups based on symmetry Radial symmetry = Radiata Bilateral Symmetry = Bilateria ...
Human Body Systems Webquest
... You are now beginning a study of the human body. It is important that we understand how our bodies work so that we will be able to take good care of them. Your body is covered by your largest organ and it’s supported from within by your foundation, your skeletal system! All of your body systems have ...
... You are now beginning a study of the human body. It is important that we understand how our bodies work so that we will be able to take good care of them. Your body is covered by your largest organ and it’s supported from within by your foundation, your skeletal system! All of your body systems have ...
NAME: CLASS:______ Fetal Pig Dissection Pigs are placental
... 2. Liver. This structure is lobed and is the largest organ in the body. The liver is responsible for making bile for digestion. 3. Gall bladder. This greenish organ is located underneath the liver; the bile duct attaches the gall bladder to the duodenum. The gall bladder stores bile and sends it to ...
... 2. Liver. This structure is lobed and is the largest organ in the body. The liver is responsible for making bile for digestion. 3. Gall bladder. This greenish organ is located underneath the liver; the bile duct attaches the gall bladder to the duodenum. The gall bladder stores bile and sends it to ...
The Orbit
... the orbit is pyramidal in shaped cavity with its base in front & its apex behind . the orbital margin is formed above by the frontal bone, which is notched or canalized for the passage of the superaorbital nerve and vessels . the lateral margin is formed by the processes of the frontal and zygomatic ...
... the orbit is pyramidal in shaped cavity with its base in front & its apex behind . the orbital margin is formed above by the frontal bone, which is notched or canalized for the passage of the superaorbital nerve and vessels . the lateral margin is formed by the processes of the frontal and zygomatic ...
MAN AWESOMELY AND WONDERFULLY MADE
... Use this simple diagram to explain the circulatory system (G322V) Do this Circulatory system activity (G322A) to help understand how the blood moves around the body and delivers oxygen (and nutrients) to the body. Relay races: Include a range of cardiovascular activities in the races (run, jump, hop ...
... Use this simple diagram to explain the circulatory system (G322V) Do this Circulatory system activity (G322A) to help understand how the blood moves around the body and delivers oxygen (and nutrients) to the body. Relay races: Include a range of cardiovascular activities in the races (run, jump, hop ...
Prenatal Development Vocabulary - Bowdle FACS
... • This would be the very beginning of prenatal ...
... • This would be the very beginning of prenatal ...
Regional Government Kordstan/ Iraq The Ministry of Higher
... will be discussed and discussed and the application of certain lab tests physiological sports and some recent studies . Know ledge of the physiological functions of the organs of the body . Know ledge of the physical components of the systems in the human body . knowledge of the functional relations ...
... will be discussed and discussed and the application of certain lab tests physiological sports and some recent studies . Know ledge of the physiological functions of the organs of the body . Know ledge of the physical components of the systems in the human body . knowledge of the functional relations ...
Liver Segmental Anatomy Robin Smithuis Liver anatomy can be
... In the Couinaud classification little attention is given to the high prevalence of anatomic al variations which occur, especially in the right hemiliver. Using volumetric acquisition techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging or spiral co mputed tomography scanning, detailed insight into the ind ...
... In the Couinaud classification little attention is given to the high prevalence of anatomic al variations which occur, especially in the right hemiliver. Using volumetric acquisition techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging or spiral co mputed tomography scanning, detailed insight into the ind ...
Head, Facial, & Neck Trauma
... Changes in ICP result in compensation Increased ICP = Increased BP • This causes ICP to rise higher and BP to rise Brain injury and death become imminent ...
... Changes in ICP result in compensation Increased ICP = Increased BP • This causes ICP to rise higher and BP to rise Brain injury and death become imminent ...
Answer Key: What Did You Learn
... The fibula is a laterally placed bone in the leg that does not bear any weight, but serves as a site for the attachment of several muscles. Additionally, its distal tip, called the lateral malleolus extends laterally to the ankle joint where it provides lateral stability to the ankle. ...
... The fibula is a laterally placed bone in the leg that does not bear any weight, but serves as a site for the attachment of several muscles. Additionally, its distal tip, called the lateral malleolus extends laterally to the ankle joint where it provides lateral stability to the ankle. ...
Ch 15 Pseudocoelomate Animals
... 1. Phyla related based on anatomy, pseudocoelom, cuticle, muscular pharynx, and adhesive glands. 2. Phyla not related, thus are polyphyletic absence in single unique feature independent evolution a. similarities result of convergent evolution in similar environments. ...
... 1. Phyla related based on anatomy, pseudocoelom, cuticle, muscular pharynx, and adhesive glands. 2. Phyla not related, thus are polyphyletic absence in single unique feature independent evolution a. similarities result of convergent evolution in similar environments. ...
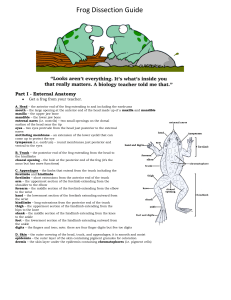
Frog Dissection Guide
... the side at each leg, and pin the skin flat. The diagram above shows how to make these cuts Lift and cut through the muscles and breast bone to open up the body cavity. If your frog is a female, the abdominal cavity may be filled with dark-colored eggs. If so, remove the eggs on one side so you can ...
... the side at each leg, and pin the skin flat. The diagram above shows how to make these cuts Lift and cut through the muscles and breast bone to open up the body cavity. If your frog is a female, the abdominal cavity may be filled with dark-colored eggs. If so, remove the eggs on one side so you can ...
Whitman-Hanson Regional High School provides all students with a
... *Can you explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system? *Can you name the structures of the PNS and CNS? Nervous Tissue Structure and Function: *Can you state the functions of neurons and neuroglia? *Can you describe the general structure of a neuron? *Can you describe ...
... *Can you explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system? *Can you name the structures of the PNS and CNS? Nervous Tissue Structure and Function: *Can you state the functions of neurons and neuroglia? *Can you describe the general structure of a neuron? *Can you describe ...
Gummy Bear Lab
... (5) Use an ink pen to label (with arrows) the unsectioned Gummi Bear to show the cranial (cephalad) & caudal (caudad) directions. (6) Make sure that all the members of your lab group are listed at the top of the lab sheet under your group designation (Group A, Group B, etc). Return the completed lab ...
... (5) Use an ink pen to label (with arrows) the unsectioned Gummi Bear to show the cranial (cephalad) & caudal (caudad) directions. (6) Make sure that all the members of your lab group are listed at the top of the lab sheet under your group designation (Group A, Group B, etc). Return the completed lab ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Lab
... 18. Study the heart, major veins, and major arteries by carefully removing tissue as necessary to expose the vessels. This is best done by separating tissues with a blunt probe and by picking away connective tissue (CT) from the blood vessels with a forceps. In a fetus, the placenta is the source o ...
... 18. Study the heart, major veins, and major arteries by carefully removing tissue as necessary to expose the vessels. This is best done by separating tissues with a blunt probe and by picking away connective tissue (CT) from the blood vessels with a forceps. In a fetus, the placenta is the source o ...
Day 4 FETAL PIG DISSECTION HAND-IN
... 5. Lift the urinary bladder to find the urethra, the tube which carries urine out of the body. Follow the urethra to the urogenital opening on the outside of the pig's body. 6. Make sure that incision #6 extends all the way to the anus but be careful to not cut too deep and damage the internal organ ...
... 5. Lift the urinary bladder to find the urethra, the tube which carries urine out of the body. Follow the urethra to the urogenital opening on the outside of the pig's body. 6. Make sure that incision #6 extends all the way to the anus but be careful to not cut too deep and damage the internal organ ...
History of anatomy

The history of anatomy extends from the earliest examinations of sacrificial victims to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern scientists. It has been characterized, over time, by a continually developing understanding of the functions of organs and structures in the body. Human anatomy was the most prominent of the biological sciences of the 19th and early 20th centuries. Methods have also improved dramatically.