Curriculum Map Discipline: Science Course: Anatomy & Physiology
... Collect, organize and analyze data accurately and precisely. Formulate alternative hypotheses to explain unexpected results. Formulate hypotheses referencing prior research and knowledge. Describe the structures and organization of cells and tissues that underlie basic life functions including nutri ...
... Collect, organize and analyze data accurately and precisely. Formulate alternative hypotheses to explain unexpected results. Formulate hypotheses referencing prior research and knowledge. Describe the structures and organization of cells and tissues that underlie basic life functions including nutri ...
Q7 Describe the anatomy of the antecubital fossa
... perforates the brachial fascia above the medial epicondyle, joining the brachial veins to form the axillary vein. Favoured for PICC cannulation because it is usually of substantial size, with predictable anato ...
... perforates the brachial fascia above the medial epicondyle, joining the brachial veins to form the axillary vein. Favoured for PICC cannulation because it is usually of substantial size, with predictable anato ...
The Skeletal System
... The bottom layer, the stratum basale, has cells that are shaped like columns. In this layer the cells divide and push already formed cells into higher layers. As the cells move into the higher layers, they flatten and eventually die. The stratum basale is the bottom layer of keratinocytes in the ep ...
... The bottom layer, the stratum basale, has cells that are shaped like columns. In this layer the cells divide and push already formed cells into higher layers. As the cells move into the higher layers, they flatten and eventually die. The stratum basale is the bottom layer of keratinocytes in the ep ...
earthworm dissection
... earthworm takes in a mixture of soil and organic matter through its mouth, which is the beginning of the digestive tract. The mixture enters the pharynx, which is located in segments 1–6. The esophagus, in segments 6–13, acts as a passageway between the pharynx and the crop. The crop stores food tem ...
... earthworm takes in a mixture of soil and organic matter through its mouth, which is the beginning of the digestive tract. The mixture enters the pharynx, which is located in segments 1–6. The esophagus, in segments 6–13, acts as a passageway between the pharynx and the crop. The crop stores food tem ...
06 General information about the nervous system
... • 2 superior colliculi that control reflex movements of the eyes, head and neck in response to visual stimuli • 2 inferior colliculi that control reflex movements of the head, neck, and trunk in response to auditory stimuli ...
... • 2 superior colliculi that control reflex movements of the eyes, head and neck in response to visual stimuli • 2 inferior colliculi that control reflex movements of the head, neck, and trunk in response to auditory stimuli ...
Interesting Case Series Review of Facial Nerve Anatomy
... A review of the anatomy in the temporal region is a point to return to in many traumatic and elective surgical interventions due to the complexity of the facial planes enveloping the facial nerve. The facial nerve exits the cranium at the stylomastoid foramen just inferior and posterior to the auric ...
... A review of the anatomy in the temporal region is a point to return to in many traumatic and elective surgical interventions due to the complexity of the facial planes enveloping the facial nerve. The facial nerve exits the cranium at the stylomastoid foramen just inferior and posterior to the auric ...
Masticatory Anatomy Quiz: Friday March 30, 2007 8 South 1:15 p.m.
... History of Centric Relation “This position is independent of tooth contact. This position is ...
... History of Centric Relation “This position is independent of tooth contact. This position is ...
STUDENT - BODY WORLDS Vital
... break down, they are more likely to choose healthy lifestyles. They also hope it will inspire visitors to learn more about the life sciences. Knowledge about what the human body looks like and how it functions is basic life science information that should be available to everyone. ...
... break down, they are more likely to choose healthy lifestyles. They also hope it will inspire visitors to learn more about the life sciences. Knowledge about what the human body looks like and how it functions is basic life science information that should be available to everyone. ...
[ PDF ] - journal of evidence based medicine and
... Inclusion Criteria: All south Indian races included. Both male and female bodies were included. Exclusion Criteria: Euarcian, African, Mongolian races and paediatric age group less than 12 years excluded. Previous surgical scarring at axillae was excluded. RESULTS & OBSERVATIONS: During the routine ...
... Inclusion Criteria: All south Indian races included. Both male and female bodies were included. Exclusion Criteria: Euarcian, African, Mongolian races and paediatric age group less than 12 years excluded. Previous surgical scarring at axillae was excluded. RESULTS & OBSERVATIONS: During the routine ...
Which of the following places on the diaphragm are weak? a
... 8. The correct statement about the topography of the prostate is: a) Below the urinary bladder b) In the scrotum c) In the region of the bulb of the penis d) In the region of the spongy part of the urethra 9. The correct statement about the peritoneal relation of the ovarium is: a) Completely covere ...
... 8. The correct statement about the topography of the prostate is: a) Below the urinary bladder b) In the scrotum c) In the region of the bulb of the penis d) In the region of the spongy part of the urethra 9. The correct statement about the peritoneal relation of the ovarium is: a) Completely covere ...
Mussel dissection – Geukensia, Brachidontes or Mytilus – live
... and foot closer together on the ventral side. That’s how they got their name, Cephalopoda (head, foot). The mantle surrounds the visceral mass, and ancestrally a hard shell surrounded all of this to form an elongated cone-shaped shell with the head and foot poking out the open end. It was easier to ...
... and foot closer together on the ventral side. That’s how they got their name, Cephalopoda (head, foot). The mantle surrounds the visceral mass, and ancestrally a hard shell surrounded all of this to form an elongated cone-shaped shell with the head and foot poking out the open end. It was easier to ...
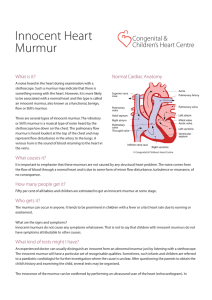
Innocent Heart Murmur - Congenital and Children`s Heart Centre
... the flow of blood through a normal heart and is due to some form of minor flow disturbance, turbulence or resonance, of no consequence. ...
... the flow of blood through a normal heart and is due to some form of minor flow disturbance, turbulence or resonance, of no consequence. ...
Module 4 - Australian College of Sport and Fitness
... Strength refers to the ability of muscles to generate force against physical objects and/or resistance. In the fitness world, this typically refers to things like how much weight you can lift or how many push ups you can do. This type of resistance can include dumbbells, barbells, res ...
... Strength refers to the ability of muscles to generate force against physical objects and/or resistance. In the fitness world, this typically refers to things like how much weight you can lift or how many push ups you can do. This type of resistance can include dumbbells, barbells, res ...
Lessons 3 and 4 Exercise and Heart Rate
... Your heart is really a muscle. It's located a little to the left of the middle of your chest, and it's about the size of your fist. The heart sends blood around your body. The blood provides your body with the oxygen and nutrients it needs. It also carries away waste. Your heart is sort of like a pu ...
... Your heart is really a muscle. It's located a little to the left of the middle of your chest, and it's about the size of your fist. The heart sends blood around your body. The blood provides your body with the oxygen and nutrients it needs. It also carries away waste. Your heart is sort of like a pu ...
Rat Dissection
... to help you waves into the ear opening out: Paired openings leading into the nose Nares Mesentery Organs of the thoracic and abdominal cavities Nares Viscera Peritoneum A partition or wall separating 2 cavities Septum Pinna A membrane which suspends the organs Mesentery Septum Vibrissae Shiny membra ...
... to help you waves into the ear opening out: Paired openings leading into the nose Nares Mesentery Organs of the thoracic and abdominal cavities Nares Viscera Peritoneum A partition or wall separating 2 cavities Septum Pinna A membrane which suspends the organs Mesentery Septum Vibrissae Shiny membra ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Lecture Outline Adapted from Martini
... regulating blood flow through the capillaries Histological Organization of Blood Vessels Capillary Beds (continued) In areas such as the brain, heart, and stomach, a continuous, rich flow of blood is required In these areas, more than one artery supplies a specific area These arteries (collateral ar ...
... regulating blood flow through the capillaries Histological Organization of Blood Vessels Capillary Beds (continued) In areas such as the brain, heart, and stomach, a continuous, rich flow of blood is required In these areas, more than one artery supplies a specific area These arteries (collateral ar ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 22 Martini Lecture Outline
... regulating blood flow through the capillaries Histological Organization of Blood Vessels Capillary Beds (continued) In areas such as the brain, heart, and stomach, a continuous, rich flow of blood is required In these areas, more than one artery supplies a specific area These arteries (collateral ar ...
... regulating blood flow through the capillaries Histological Organization of Blood Vessels Capillary Beds (continued) In areas such as the brain, heart, and stomach, a continuous, rich flow of blood is required In these areas, more than one artery supplies a specific area These arteries (collateral ar ...
Respiratory Membrane
... Extends from soft palate to the epiglottis Epithelium is stratified squamous epithelium Two types of tonsils in the oropharynx – Palatine tonsils – in the lateral walls of the fauces – Lingual tonsils – embedded in the posterior surface of the tongue ...
... Extends from soft palate to the epiglottis Epithelium is stratified squamous epithelium Two types of tonsils in the oropharynx – Palatine tonsils – in the lateral walls of the fauces – Lingual tonsils – embedded in the posterior surface of the tongue ...
Word format
... 3. Find the internal nasal openings on either side of the vomerine teeth. Air enters the mouth through these openings. Push a probe through the external nasal openings to show their connection to the inside of the mouth. The holes behind the sides of the upper jaw are the openings of the Eustachian ...
... 3. Find the internal nasal openings on either side of the vomerine teeth. Air enters the mouth through these openings. Push a probe through the external nasal openings to show their connection to the inside of the mouth. The holes behind the sides of the upper jaw are the openings of the Eustachian ...
Earthworm Dissection
... the worm’s setae, which are the minute bristle-like spines located on every segment except the first and last one. 5. Refer again to the diagram of the ventral view of the worm to locate and identify the external parts of its reproductive system. Find the pair of sperm grooves that extend from the c ...
... the worm’s setae, which are the minute bristle-like spines located on every segment except the first and last one. 5. Refer again to the diagram of the ventral view of the worm to locate and identify the external parts of its reproductive system. Find the pair of sperm grooves that extend from the c ...
Injury to the long thoracic nerve as a complication of neck dissection
... appearance indicated that it was a thick tumour. The patient was admitted for treatment by wide local excision and sentinel node biopsy. Lymphoscintigraphy showed ...
... appearance indicated that it was a thick tumour. The patient was admitted for treatment by wide local excision and sentinel node biopsy. Lymphoscintigraphy showed ...
Masticatory Anat CR
... History of Centric Relation “The most retruded relation of the mandible to the maxillae when the condyles are in the most unstrained position in the glenoid fossae from which lateral movement can be made, at any given degree of jaw separation.” The Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms, 1st Edition: The ...
... History of Centric Relation “The most retruded relation of the mandible to the maxillae when the condyles are in the most unstrained position in the glenoid fossae from which lateral movement can be made, at any given degree of jaw separation.” The Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms, 1st Edition: The ...
History of anatomy

The history of anatomy extends from the earliest examinations of sacrificial victims to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern scientists. It has been characterized, over time, by a continually developing understanding of the functions of organs and structures in the body. Human anatomy was the most prominent of the biological sciences of the 19th and early 20th centuries. Methods have also improved dramatically.






![[ PDF ] - journal of evidence based medicine and](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002548741_1-4e3c5f24230bf4ed03ac164770162a03-300x300.png)