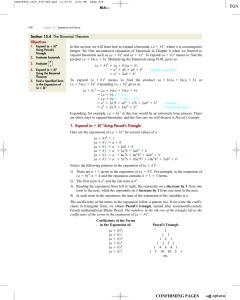
The binomial theorem
... • the expansion of (a + b)2 has three terms and in each term the sum of the indices is 2 • the expansion of (a + b)3 has four terms and in each term the sum of the indices is 3 • the expansion of (a + b)4 has five terms and in each term the sum of the indices is 4. We conjecture that the expansion o ...
... • the expansion of (a + b)2 has three terms and in each term the sum of the indices is 2 • the expansion of (a + b)3 has four terms and in each term the sum of the indices is 3 • the expansion of (a + b)4 has five terms and in each term the sum of the indices is 4. We conjecture that the expansion o ...
Full text
... all equal to −1, 0 or 1. We shall give a short proof of this fact, and a very simple recursive description of the coefficients of A(x). Following the notation of [4], let a(m) be the coefficient of xm in A(x). It is clear that a(m) = rE (m) − rO (m), where rE (m) is equal to the number of partitions ...
... all equal to −1, 0 or 1. We shall give a short proof of this fact, and a very simple recursive description of the coefficients of A(x). Following the notation of [4], let a(m) be the coefficient of xm in A(x). It is clear that a(m) = rE (m) − rO (m), where rE (m) is equal to the number of partitions ...