239 Lesson 5 . 2
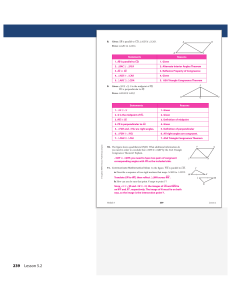
... so AE ≅ CE and BE ≅ DE by the definition of congruence. By the Vertical Angle Theorem, you also know that ∠AEB ≅ ∠CED. Two sides and the included angle of △AEB are congruent to two sides and the included angle of △CED. The triangles are congruent _ _ by the SAS Triangle Congruence Theorem. _ _ By CP ...
... so AE ≅ CE and BE ≅ DE by the definition of congruence. By the Vertical Angle Theorem, you also know that ∠AEB ≅ ∠CED. Two sides and the included angle of △AEB are congruent to two sides and the included angle of △CED. The triangles are congruent _ _ by the SAS Triangle Congruence Theorem. _ _ By CP ...
Ch 5 Properties AND Attributes of Triangles – HOLT Geom
... Ch 5 Properties AND Attributes of Triangles – HOLT Geom 5-1 Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors If a point is on the If perpendicular bisector of a segment, then it is A equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Then ...
... Ch 5 Properties AND Attributes of Triangles – HOLT Geom 5-1 Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors If a point is on the If perpendicular bisector of a segment, then it is A equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Then ...
Exceptional real Lucas sequences
... it suffices to take I > 0. For if (U) and (Uf) are generated by #2 — Iz + m and z2 + Iz + m, respectively, then Z7W = (—ly^Ul. In all that follows we therefore suppose I > 0. If i2 > 4m, (C7) will be called real. Birkhoff and Vandiver [1] have shown that when a and /3 are coprime rational integers t ...
... it suffices to take I > 0. For if (U) and (Uf) are generated by #2 — Iz + m and z2 + Iz + m, respectively, then Z7W = (—ly^Ul. In all that follows we therefore suppose I > 0. If i2 > 4m, (C7) will be called real. Birkhoff and Vandiver [1] have shown that when a and /3 are coprime rational integers t ...
Full Text Article - International Journal of Mathematics
... Theorem 3.10. Let f: (X, τ ) (Y, σ ) be a function. Then the following hold: 1. If f: (X, τ ) (Y, σ ) is b-continuous and (Y, σ) is almost regular, then f is almost strongly b-δcontinuous, 2.If f: (X, τ) (Y, σ) is almost strongly b-δ-continuous and (Y, σ) is semi regular, then f is strongly b- ...
... Theorem 3.10. Let f: (X, τ ) (Y, σ ) be a function. Then the following hold: 1. If f: (X, τ ) (Y, σ ) is b-continuous and (Y, σ) is almost regular, then f is almost strongly b-δcontinuous, 2.If f: (X, τ) (Y, σ) is almost strongly b-δ-continuous and (Y, σ) is semi regular, then f is strongly b- ...
The Weil representation in characteristic two
... 0001-8708/$ - see front matter ⃝ doi:10.1016/j.aim.2012.03.008 ...
... 0001-8708/$ - see front matter ⃝ doi:10.1016/j.aim.2012.03.008 ...
When does the Fell topology on a hyperspace of
... of MA under the map q which identifies limit points of all sequences from MA into the single point *, and that the map q is closed. Therefore, SA is a super-complete LaSnev space. It is easy to see that Ic(5’~) = IAl. Somewhat ...
... of MA under the map q which identifies limit points of all sequences from MA into the single point *, and that the map q is closed. Therefore, SA is a super-complete LaSnev space. It is easy to see that Ic(5’~) = IAl. Somewhat ...
covariant and contravariant approaches to topology
... (the 0-dimensional sphere or the simplest direte space which is not anti-discrete), 4. The unit interval I with the standard topology, 5. The real numbers R with the standard topology. Q c R are rationals. It is well known that connected spaces X are precisely those, so that all maps f X So are cons ...
... (the 0-dimensional sphere or the simplest direte space which is not anti-discrete), 4. The unit interval I with the standard topology, 5. The real numbers R with the standard topology. Q c R are rationals. It is well known that connected spaces X are precisely those, so that all maps f X So are cons ...
Brouwer fixed-point theorem

Brouwer's fixed-point theorem is a fixed-point theorem in topology, named after Luitzen Brouwer. It states that for any continuous function f mapping a compact convex set into itself there is a point x0 such that f(x0) = x0. The simplest forms of Brouwer's theorem are for continuous functions f from a closed interval I in the real numbers to itself or from a closed disk D to itself. A more general form than the latter is for continuous functions from a convex compact subset K of Euclidean space to itself.Among hundreds of fixed-point theorems, Brouwer's is particularly well known, due in part to its use across numerous fields of mathematics.In its original field, this result is one of the key theorems characterizing the topology of Euclidean spaces, along with the Jordan curve theorem, the hairy ball theorem and the Borsuk–Ulam theorem.This gives it a place among the fundamental theorems of topology. The theorem is also used for proving deep results about differential equations and is covered in most introductory courses on differential geometry.It appears in unlikely fields such as game theory. In economics, Brouwer's fixed-point theorem and its extension, the Kakutani fixed-point theorem, play a central role in the proof of existence of general equilibrium in market economies as developed in the 1950s by economics Nobel prize winners Kenneth Arrow and Gérard Debreu.The theorem was first studied in view of work on differential equations by the French mathematicians around Poincaré and Picard.Proving results such as the Poincaré–Bendixson theorem requires the use of topological methods.This work at the end of the 19th century opened into several successive versions of the theorem. The general case was first proved in 1910 by Jacques Hadamard and by Luitzen Egbertus Jan Brouwer.