FUNDAMENTALS OF WATER
... COMMERCIAL ELECTRICAL (Additional information) Overcurrent protection device (OCPD) ...
... COMMERCIAL ELECTRICAL (Additional information) Overcurrent protection device (OCPD) ...
Kirchhoff`s Laws - Edvantage Science
... Using Ohm’s Law I = V/R, and knowing that the potential difference is the same in a parallel circuit the equivalent resistance in a parallel circuit can be determined by: ...
... Using Ohm’s Law I = V/R, and knowing that the potential difference is the same in a parallel circuit the equivalent resistance in a parallel circuit can be determined by: ...
REVIEW SHEET – ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
... 12. a) How is an ammeter connected into a circuit? b) How much internal resistance does an ideal ammeter have? c) How is a voltmeter connected into a circuit? d) How much internal resistance does an ideal voltmeter have? 13. What are some common uses of variable resistors? ...
... 12. a) How is an ammeter connected into a circuit? b) How much internal resistance does an ideal ammeter have? c) How is a voltmeter connected into a circuit? d) How much internal resistance does an ideal voltmeter have? 13. What are some common uses of variable resistors? ...
Electical Circuits - World of Teaching
... When the switch is closed, the lamp lights up. This is because there is a continuous path of metal for the electric current to flow around. ...
... When the switch is closed, the lamp lights up. This is because there is a continuous path of metal for the electric current to flow around. ...
Circuit Breaker Types.doc
... All circuit breakers have common features in their operation, although details vary substantially depending on the voltage class, current rating and type of the circuit breaker. The circuit breaker must detect a fault condition; in low-voltage circuit breakers this is usually done within the breaker ...
... All circuit breakers have common features in their operation, although details vary substantially depending on the voltage class, current rating and type of the circuit breaker. The circuit breaker must detect a fault condition; in low-voltage circuit breakers this is usually done within the breaker ...
Circuit Defects
... The sum of the branch circuit currents is equal to the total circuit current The voltage drop across each branch circuit is the same The current in each branch circuit is different if the resistance values are different. ...
... The sum of the branch circuit currents is equal to the total circuit current The voltage drop across each branch circuit is the same The current in each branch circuit is different if the resistance values are different. ...
Physics 536 - Assignment #8 - Due April 7
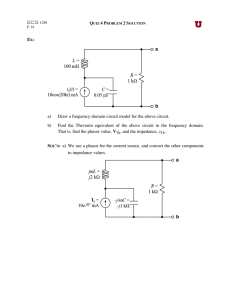
... (c) What is the advantage of using the circuit on the left when a load applied to the current source changes at a high frequency? (d) What is the advantage of using the circuit on the right when the current IC0 is constant but the temperature of the circuit changes? ...
... (c) What is the advantage of using the circuit on the left when a load applied to the current source changes at a high frequency? (d) What is the advantage of using the circuit on the right when the current IC0 is constant but the temperature of the circuit changes? ...
SNC1D1 10.2 Current Electricity and Electric Circuits
... 1. An energy source – “energizes” the electrons, ex. battery, photoelectric cell in calculator 2. a conducting wire (connector) – provides a path for current to flow 3. A load which is a device that converts electrical energy to another form of energy, ex. light bulb Many electric circuits also in ...
... 1. An energy source – “energizes” the electrons, ex. battery, photoelectric cell in calculator 2. a conducting wire (connector) – provides a path for current to flow 3. A load which is a device that converts electrical energy to another form of energy, ex. light bulb Many electric circuits also in ...
Rectification - Animated Science
... – Contain diodes • Semiconductor • Thermionic – Power rating • Supply current to circuits ...
... – Contain diodes • Semiconductor • Thermionic – Power rating • Supply current to circuits ...
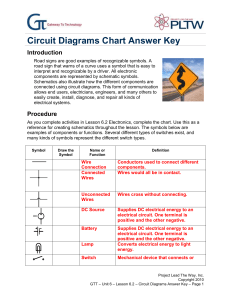
Circuit Diagrams Chart Answer Key
... Supplies DC electrical energy to an electrical circuit. One terminal is positive and the other negative. Converts electrical energy to light energy. ...
... Supplies DC electrical energy to an electrical circuit. One terminal is positive and the other negative. Converts electrical energy to light energy. ...
4 Electricity - Home Distribution
... POSSIBLE FAULTS: Overloading a circuit: In parallel circuits, the total current flowing in the circuit is the sum of the individual currents through the devices. Too many appliance operating on a single power circuit will produce a large current. The conducting wires get hot and melt their insul ...
... POSSIBLE FAULTS: Overloading a circuit: In parallel circuits, the total current flowing in the circuit is the sum of the individual currents through the devices. Too many appliance operating on a single power circuit will produce a large current. The conducting wires get hot and melt their insul ...
Use the equations for electric power to
... is high enough, the power will increase and the wires can become hot enough to start a fire. To avoid this, we use fuses or circuit breakers, which disconnect when the current goes above a predetermined value. ...
... is high enough, the power will increase and the wires can become hot enough to start a fire. To avoid this, we use fuses or circuit breakers, which disconnect when the current goes above a predetermined value. ...
Student Handout #2 Extract - AS 440-221, Safe Laboratory
... become “hot” by itself being in contact with an energized wire, while the person is in contact with the circuit ground. It is possible to receive a shock by touching only the energized wire, or an energized metallic part, and the ground because of the nature of an electric circuit. An electric circu ...
... become “hot” by itself being in contact with an energized wire, while the person is in contact with the circuit ground. It is possible to receive a shock by touching only the energized wire, or an energized metallic part, and the ground because of the nature of an electric circuit. An electric circu ...
Investigating Components having Non-Linear Characteristics 6EM
... Try to calculate the current, I which flows in the circuit and the voltage, V across the diode. It will soon become clear that you can not calculate these answers without knowing the detailed characteristics of the diode (make sure you understand why this is the case). Let us assume that the diode i ...
... Try to calculate the current, I which flows in the circuit and the voltage, V across the diode. It will soon become clear that you can not calculate these answers without knowing the detailed characteristics of the diode (make sure you understand why this is the case). Let us assume that the diode i ...
Commonly used electrical symbols
... The symbol is a combination of a fuse and a disconnect switch with the switch in the open position. The symbol is a combination of a normally open contact (switch), overload relay, motor, and disconnect device. The symbol is a combination of a drawout fuse, normally open contact (switch), and motor. ...
... The symbol is a combination of a fuse and a disconnect switch with the switch in the open position. The symbol is a combination of a normally open contact (switch), overload relay, motor, and disconnect device. The symbol is a combination of a drawout fuse, normally open contact (switch), and motor. ...
Circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and interrupt current flow. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation. Circuit breakers are made in varying sizes, from small devices that protect an individual household appliance up to large switchgear designed to protect high voltage circuits feeding an entire city.