Sample Questions - C&G 2382 17th Edition paper C
... 5 oc3 When making an assessment of the frequency and quality of maintenance, a factor to be considered is that a power factor is monitored b protective measures for safety remain effective c starting currents are at a minimum d unbalanced loads need to be checked more frequently. 6 oc4 What is the r ...
... 5 oc3 When making an assessment of the frequency and quality of maintenance, a factor to be considered is that a power factor is monitored b protective measures for safety remain effective c starting currents are at a minimum d unbalanced loads need to be checked more frequently. 6 oc4 What is the r ...
Product data sheet 3RT1033-3AK60 CONTACTOR, AC-3 11 KW/400 V,
... Operating range factor control supply voltage rated value / of the magnet coil • at 50 Hz • for AC ...
... Operating range factor control supply voltage rated value / of the magnet coil • at 50 Hz • for AC ...
1 TRAINING SUPPORT PACKAGE (TSP) CF631R42 Series Circuits
... Along in BK&S Electrical Workbook, chapter 6. a. A basic electric circuit has a complete path through which electrons can flow from the negative terminal of the voltage source, through the connecting wires, through the load and back to the positive side of the voltage source. b. A series circuit is ...
... Along in BK&S Electrical Workbook, chapter 6. a. A basic electric circuit has a complete path through which electrons can flow from the negative terminal of the voltage source, through the connecting wires, through the load and back to the positive side of the voltage source. b. A series circuit is ...
Lecture_18
... A 500 MVA, 20 kV, 3 is operated with an internal voltage of 1.05 pu. Assume a solid 3 fault occurs on the generator's terminal and that the circuit breaker operates after three cycles. Determine the fault current. ...
... A 500 MVA, 20 kV, 3 is operated with an internal voltage of 1.05 pu. Assume a solid 3 fault occurs on the generator's terminal and that the circuit breaker operates after three cycles. Determine the fault current. ...
Lab #3 Linearity, Proportionality, and Superposition
... flying 100mph or 1000mph that the airplane would react the same way (effects of drag, etc. scaled of course). That is a linear system. It exhibits the same constant linear properties over any time frame and input. In reality, an airplane is a highly complex grouping of many linear and non-linear sys ...
... flying 100mph or 1000mph that the airplane would react the same way (effects of drag, etc. scaled of course). That is a linear system. It exhibits the same constant linear properties over any time frame and input. In reality, an airplane is a highly complex grouping of many linear and non-linear sys ...
Power System Protection
... A systematic study of current responsive devices in an electrical power system. ...
... A systematic study of current responsive devices in an electrical power system. ...
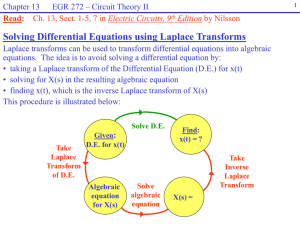
Chapter 13 – Circuit Analysis using Laplace Transforms
... Circuit Analysis using the Laplace-transformed circuit Although Laplace transforms can be used effectively to solve differential equations, this is not the preferred approach when analyzing circuits. Instead it is easier to analyze the circuit directly in the s-domain. Advantages to working directly ...
... Circuit Analysis using the Laplace-transformed circuit Although Laplace transforms can be used effectively to solve differential equations, this is not the preferred approach when analyzing circuits. Instead it is easier to analyze the circuit directly in the s-domain. Advantages to working directly ...
summary of requirements
... Protection of tap conductors in motor groups: The new 31.4.3 will require all motor tap conductors, i.e. conductors that carry current from a single motor, to have an ampacity, per Table 28.1, that is coordinated with the overall size (ampere rating) of the motor group. Manufacturers may need to mod ...
... Protection of tap conductors in motor groups: The new 31.4.3 will require all motor tap conductors, i.e. conductors that carry current from a single motor, to have an ampacity, per Table 28.1, that is coordinated with the overall size (ampere rating) of the motor group. Manufacturers may need to mod ...
NRD1-6_Rev.0110 - pes-psrc
... Metal oxide varistor (MOV). An assembly of metal oxide varistor units that limits overvoltages to a given value. In the context of series capacitor banks, the MOV is typically defined by its ability to divert fault current around the series capacitor units, limiting the voltage to a specified protec ...
... Metal oxide varistor (MOV). An assembly of metal oxide varistor units that limits overvoltages to a given value. In the context of series capacitor banks, the MOV is typically defined by its ability to divert fault current around the series capacitor units, limiting the voltage to a specified protec ...
Circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and interrupt current flow. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation. Circuit breakers are made in varying sizes, from small devices that protect an individual household appliance up to large switchgear designed to protect high voltage circuits feeding an entire city.