Faculty of Natural Sciences
... Crystal structures, Bravais lattices: basis, unit cell, reciprocal lattice, packing faction. Theory of diffraction: structural factor, atomic scattering factor. Noncrystalline solids, liquid crystals. Real crystals, classification of defects, thermodynamics of point defects. Lattice vibrations in ha ...
... Crystal structures, Bravais lattices: basis, unit cell, reciprocal lattice, packing faction. Theory of diffraction: structural factor, atomic scattering factor. Noncrystalline solids, liquid crystals. Real crystals, classification of defects, thermodynamics of point defects. Lattice vibrations in ha ...
Chapter 1
... assumptions were not just a matter of philosophical taste, and could be put to experimental test. [13] In his own discussion of the EPR argument, Bell maintained the assumption of locality ...
... assumptions were not just a matter of philosophical taste, and could be put to experimental test. [13] In his own discussion of the EPR argument, Bell maintained the assumption of locality ...
Nonlinear THz response of a one-dimensional superlattice * Avik W. Ghosh
... zeroth order Bessel function, the electron is predicted to execute bounded ac Bloch oscillations, else it drifts off. This behavior is easily understood in terms of a simple semiclassical picture;10 the electron continues to execute ac Bloch oscillations in phase with the incident field if it manage ...
... zeroth order Bessel function, the electron is predicted to execute bounded ac Bloch oscillations, else it drifts off. This behavior is easily understood in terms of a simple semiclassical picture;10 the electron continues to execute ac Bloch oscillations in phase with the incident field if it manage ...
On the formation of radiation fogs under heavily polluted
... crease the hygroscopicity of aerosol droplets and decrease the critical supersaturation at the droplet surface. It should be noted that there exists a precondition for the unactivated cloud formation, regardless of the pollution levels: the droplets must follow their equilibrium (Köhler) curves ver ...
... crease the hygroscopicity of aerosol droplets and decrease the critical supersaturation at the droplet surface. It should be noted that there exists a precondition for the unactivated cloud formation, regardless of the pollution levels: the droplets must follow their equilibrium (Köhler) curves ver ...
Chapter 8 - profpaz.com
... Heat is thermal energy change that is emitted or absorbed when a chemical reaction takes place. In chemistry, thermal energy at constant pressure (a common situation for most chemical reactions) is quantified by a function called enthalpy. ...
... Heat is thermal energy change that is emitted or absorbed when a chemical reaction takes place. In chemistry, thermal energy at constant pressure (a common situation for most chemical reactions) is quantified by a function called enthalpy. ...
Einstein`s impact on the physics of the twentieth century
... But who would want to read or write that? Einstein’s major, enduring contributions to physics were made during the first quarter of the 20th century. They can roughly be divided into four main branches: (1) statistical physics, (2) early quantum theory of light and matter, (3) Special Relativity, an ...
... But who would want to read or write that? Einstein’s major, enduring contributions to physics were made during the first quarter of the 20th century. They can roughly be divided into four main branches: (1) statistical physics, (2) early quantum theory of light and matter, (3) Special Relativity, an ...
Shannon Information Entropy in Position Space for Two
... is decreased below the critical value, the SEPS starts to increase in a rapid but moderate manner, and eventually it reaches to a saturated value and stay almost constant when the system is away from the shape resonance region. We have further observed that our moderate and gradual increase in SEPS ...
... is decreased below the critical value, the SEPS starts to increase in a rapid but moderate manner, and eventually it reaches to a saturated value and stay almost constant when the system is away from the shape resonance region. We have further observed that our moderate and gradual increase in SEPS ...
Enhancement of Tunneling from a Correlated 2D Electron System
... transferred to the entire WC, similar to the Mössbauer effect. This can be contrasted with the case of an electron confined inside the well but not under the barrier. Here the magnetic barrier is reduced by a factor of 2 compared to the free-electron case, but does not disappear [6]. We now apply th ...
... transferred to the entire WC, similar to the Mössbauer effect. This can be contrasted with the case of an electron confined inside the well but not under the barrier. Here the magnetic barrier is reduced by a factor of 2 compared to the free-electron case, but does not disappear [6]. We now apply th ...
Stoichiometry - Mr Field's Chemistry Class
... For example: a sample of a compound contains 20% hydrogen and 80% carbon by mass. C: ...
... For example: a sample of a compound contains 20% hydrogen and 80% carbon by mass. C: ...
12.4 Momentum and Impulse
... your hand? Why not? Unless you're Superman, you probably don't want to try stopping a moving car by holding out your hand. It's too big, and it's moving way too fast. Attempting such a feat would result in a number of physics demonstrations upon your body, all of which would hurt. ...
... your hand? Why not? Unless you're Superman, you probably don't want to try stopping a moving car by holding out your hand. It's too big, and it's moving way too fast. Attempting such a feat would result in a number of physics demonstrations upon your body, all of which would hurt. ...
Stoichiometry File
... model for the combustion of gasoline. The use of octane to represent all of the hydrocarbons in gasoline is mainly for simplicity. If we chose to, it would not be very difficult to write similar combustion equations for each hydrocarbon that is actually present. But the assumption of complete combus ...
... model for the combustion of gasoline. The use of octane to represent all of the hydrocarbons in gasoline is mainly for simplicity. If we chose to, it would not be very difficult to write similar combustion equations for each hydrocarbon that is actually present. But the assumption of complete combus ...
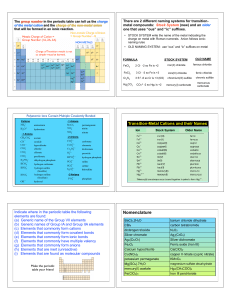
Document
... frequency of light (ΔE=hf), which is in the visible region of electromagnetic spectrum. Therefore, when white light passes through a metal complex, light of particular frequency is absorbed and an electron is promoted from a lower energy orbital to a higher energy orbital. From this issue, phenomeno ...
... frequency of light (ΔE=hf), which is in the visible region of electromagnetic spectrum. Therefore, when white light passes through a metal complex, light of particular frequency is absorbed and an electron is promoted from a lower energy orbital to a higher energy orbital. From this issue, phenomeno ...
Comparing field ionization models in simulations of laser
... Atomic units (AU) form a unit system which aims to simplify the equations describing atomic processes on their respective time-, length- or energy scale. At the same time they give a feeling for how the characteristics that are considered relate to atomic scales. They allow to assess if a process is ...
... Atomic units (AU) form a unit system which aims to simplify the equations describing atomic processes on their respective time-, length- or energy scale. At the same time they give a feeling for how the characteristics that are considered relate to atomic scales. They allow to assess if a process is ...
CHAPTER 1 Solutions Manual
... Strategy: The problem may be stated as ? lb 28.3 g A relationship between pounds and grams is given on the end sheet of your text (1 lb 453.6 g). This relationship will allow conversion from grams to pounds. If we can convert from g to grams, we can then convert from grams to pounds. Recall th ...
... Strategy: The problem may be stated as ? lb 28.3 g A relationship between pounds and grams is given on the end sheet of your text (1 lb 453.6 g). This relationship will allow conversion from grams to pounds. If we can convert from g to grams, we can then convert from grams to pounds. Recall th ...
Chemical Properties of Alkenes and Alkynes from - (BORA)
... The field of electron spectroscopy has evolved extensively the last couple of decades. On one hand, the technology at the synchrotron radiation facilities and of electron analyzers has improved, providing experimental data with more information about the sample. On the other, new and powerful computa ...
... The field of electron spectroscopy has evolved extensively the last couple of decades. On one hand, the technology at the synchrotron radiation facilities and of electron analyzers has improved, providing experimental data with more information about the sample. On the other, new and powerful computa ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.