Regents Chemistry Review Questions
... What is the chemical formula for ammonia? Is it an acid or a base? Write and balance the chemical equation for the neutralization reaction between carbonic acid and magnesium hydroxide. Name the salt that is produced in this reaction. Write and balance the chemical equation for the neutralization re ...
... What is the chemical formula for ammonia? Is it an acid or a base? Write and balance the chemical equation for the neutralization reaction between carbonic acid and magnesium hydroxide. Name the salt that is produced in this reaction. Write and balance the chemical equation for the neutralization re ...
7 - Mona Shores Blogs
... 34. Which of the following metals cannot displace hydrogen from water? a. Mg b. Ba c. Li d. Ag 35. Copper does not react with hydrochloric acid whereas manganese does? This means that a. copper is more active than hydrogen b. manganese is less active than hydrogen c. chloride ion will react with cop ...
... 34. Which of the following metals cannot displace hydrogen from water? a. Mg b. Ba c. Li d. Ag 35. Copper does not react with hydrochloric acid whereas manganese does? This means that a. copper is more active than hydrogen b. manganese is less active than hydrogen c. chloride ion will react with cop ...
Honors Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 81. How many lone pairs of electrons are in the Lewis dot structure for H2O? 82. Draw the Lewis dot structures for the following: CO, CO2, N2, and O2. 83. Define intermolecular forces and intramolecular forces. 84. Define London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole attractions, and hydrogen bonding. 85. ...
... 81. How many lone pairs of electrons are in the Lewis dot structure for H2O? 82. Draw the Lewis dot structures for the following: CO, CO2, N2, and O2. 83. Define intermolecular forces and intramolecular forces. 84. Define London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole attractions, and hydrogen bonding. 85. ...
Chapter 8
... Determine the Empirical Formula of Acetic Anhydride if its Percent Composition is 47% Carbon, 47% Oxygen and 6.0% Hydrogen 4. If any of the ratios is not a whole number, multiply all the ratios by a factor to make it a whole number – If ratio is ?.5 then multiply by 2; if ?.33 or ?.67 then multiply ...
... Determine the Empirical Formula of Acetic Anhydride if its Percent Composition is 47% Carbon, 47% Oxygen and 6.0% Hydrogen 4. If any of the ratios is not a whole number, multiply all the ratios by a factor to make it a whole number – If ratio is ?.5 then multiply by 2; if ?.33 or ?.67 then multiply ...
Energy and Chemical Change Can changes be reversed
... Mass is also conserved during chemical changes. Antoine Lavoisier, a French chemist, discovered this in the 1700s. The masses of two substances that will chemically react can be measured and added together. After the two substances react to form new substances, the total mass after the reaction can ...
... Mass is also conserved during chemical changes. Antoine Lavoisier, a French chemist, discovered this in the 1700s. The masses of two substances that will chemically react can be measured and added together. After the two substances react to form new substances, the total mass after the reaction can ...
Lectures 1-2 - U of L Class Index
... MO diagrams relate the energies of molecular orbitals to the atomic orbitals from which they were derived. If the total energy of the electrons is lower using molecular orbitals (the middle column), the molecule forms. If the total energy of the electrons is lower using atomic orbitals (the two outs ...
... MO diagrams relate the energies of molecular orbitals to the atomic orbitals from which they were derived. If the total energy of the electrons is lower using molecular orbitals (the middle column), the molecule forms. If the total energy of the electrons is lower using atomic orbitals (the two outs ...
Lectures 1-2
... MO diagrams relate the energies of molecular orbitals to the atomic orbitals from which they were derived. If the total energy of the electrons is lower using molecular orbitals (the middle column), the molecule forms. If the total energy of the electrons is lower using atomic orbitals (the two outs ...
... MO diagrams relate the energies of molecular orbitals to the atomic orbitals from which they were derived. If the total energy of the electrons is lower using molecular orbitals (the middle column), the molecule forms. If the total energy of the electrons is lower using atomic orbitals (the two outs ...
Wave Mechanics
... • Describing is very complex… we will not go into detail… we will look at the solutions. • Atom is 3D; also +ve charge (protons) must be considered (I.e. electrostatic attraction of protons and electrons) Schrödinger Equation: ...
... • Describing is very complex… we will not go into detail… we will look at the solutions. • Atom is 3D; also +ve charge (protons) must be considered (I.e. electrostatic attraction of protons and electrons) Schrödinger Equation: ...
Energy and Matter
... elements bonded together. (ex: NaCl, H2O) Pure substances are elements & compounds. ...
... elements bonded together. (ex: NaCl, H2O) Pure substances are elements & compounds. ...
Lecture 1: Vector Algebra - McMaster University > ECE
... The atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its characteristics It consists of a central nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons (-) The nucleus consists of protons (+) and neutrons (neutral) ...
... The atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its characteristics It consists of a central nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons (-) The nucleus consists of protons (+) and neutrons (neutral) ...
Chap12_Multielectron Atoms_Notes_s10
... The Pauli exclusion principle extends to all quantum mechanical systems containing particles called fermions. (Fermions have half-integral spin.) An electron is a fermion. Other examples of fermions are neutrons, protons, and muons. Let us illustrate how the Pauli principle governs atomic structure ...
... The Pauli exclusion principle extends to all quantum mechanical systems containing particles called fermions. (Fermions have half-integral spin.) An electron is a fermion. Other examples of fermions are neutrons, protons, and muons. Let us illustrate how the Pauli principle governs atomic structure ...
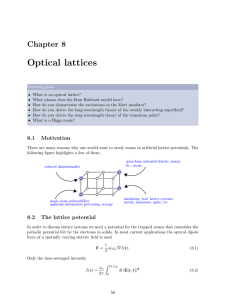
Optical lattices - Condensed Matter Theory and Quantum Optics
... We now have a good understanding of the phases of the Bose Hubbard model. For weak interactions we have a superfluid that is very similar to a free-space Bose Einstein condensate. For very strong interactions there is a series of insulating Mott lobes, one for each integer filling. Moreover, we know ...
... We now have a good understanding of the phases of the Bose Hubbard model. For weak interactions we have a superfluid that is very similar to a free-space Bose Einstein condensate. For very strong interactions there is a series of insulating Mott lobes, one for each integer filling. Moreover, we know ...
Periodic Table
... 3. Metalloids (Semimetals) = have properties of both metals and non-metals III. Trends or Patterns in the Periodic Table A. Certain properties of elements in the periodic table follow a predictable ...
... 3. Metalloids (Semimetals) = have properties of both metals and non-metals III. Trends or Patterns in the Periodic Table A. Certain properties of elements in the periodic table follow a predictable ...
Chemistry EOC Review Spring 2013
... 36. What is the energy associated with the photon in problem above? ...
... 36. What is the energy associated with the photon in problem above? ...
PART 1 Identical particles, fermions and bosons. Pauli exclusion
... the wave equation for a particle with spin 1/2 is of the first order in time derivative (see discussion of the Dirac equation later in the course). At the same time the wave equation for a particle with integer spin is of the second order in time derivative. An example: The vector potential in elect ...
... the wave equation for a particle with spin 1/2 is of the first order in time derivative (see discussion of the Dirac equation later in the course). At the same time the wave equation for a particle with integer spin is of the second order in time derivative. An example: The vector potential in elect ...
TOWNSEND`SFIRSTIONIZATIONCOEFFICIENT Consider a parallel
... insulating medium and separated by a distance d as shown in Fig.4.4. When no electric field is setup between the plates, a state of equilibrium exists between the state of electron and positive ion generation due to the decay processes. This state of equilibrium will be disturbed moment a high elect ...
... insulating medium and separated by a distance d as shown in Fig.4.4. When no electric field is setup between the plates, a state of equilibrium exists between the state of electron and positive ion generation due to the decay processes. This state of equilibrium will be disturbed moment a high elect ...
投影片 1
... The aim of this chapter is to understand how certain combinations of N neutrons and Z protons form bound states and to understand the masses, spins and parities of those states. 4.3.1 The Liquid-Drop Model One of the first nuclear models, proposed in 1935 by Bohr, is based on the short range of nucl ...
... The aim of this chapter is to understand how certain combinations of N neutrons and Z protons form bound states and to understand the masses, spins and parities of those states. 4.3.1 The Liquid-Drop Model One of the first nuclear models, proposed in 1935 by Bohr, is based on the short range of nucl ...
Document
... To formulate the theory employing methods developed for description of the electron scattering from large molecules. ...
... To formulate the theory employing methods developed for description of the electron scattering from large molecules. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.