Reflected wave
... simplification which is not always valid: it was considered that the surface density of electrons was so high that light was emitted only forward and backward, but not at different angles because there the fields emitted by the charges left or right, up or down were compensated by equal fields out o ...
... simplification which is not always valid: it was considered that the surface density of electrons was so high that light was emitted only forward and backward, but not at different angles because there the fields emitted by the charges left or right, up or down were compensated by equal fields out o ...
12.1 Powerpoint
... According to Planck's hypothesis, thermal oscillators can only absorb or emit light in chunks which are whole-number multiples of E. Max Planck received the Nobel Prize in 1918 for his quantum hypothesis, which was used successfully to unravel other problems that could not be explained classically ...
... According to Planck's hypothesis, thermal oscillators can only absorb or emit light in chunks which are whole-number multiples of E. Max Planck received the Nobel Prize in 1918 for his quantum hypothesis, which was used successfully to unravel other problems that could not be explained classically ...
Shell Structures and Level Statistics of a Quantum Dot
... Among different (N+ , N− ) with N = N+ + N− the ground state is chosen to be the one which gives the lowest value of E(N+ , N− ). In such a state the Fermi levels for spin-up and -down electrons match. Our basis set consists of the 120 lowest energy states of a noninteracting single-particle. An ato ...
... Among different (N+ , N− ) with N = N+ + N− the ground state is chosen to be the one which gives the lowest value of E(N+ , N− ). In such a state the Fermi levels for spin-up and -down electrons match. Our basis set consists of the 120 lowest energy states of a noninteracting single-particle. An ato ...
Electric Field
... A positively-charged piece of plastic exerts an attractive force on an electrically neutral piece of paper. This is because A. electrons are less massive than atomic nuclei. B. the electric force between charged particles decreases with increasing distance. C. an atomic nucleus occupies only a small ...
... A positively-charged piece of plastic exerts an attractive force on an electrically neutral piece of paper. This is because A. electrons are less massive than atomic nuclei. B. the electric force between charged particles decreases with increasing distance. C. an atomic nucleus occupies only a small ...
Physics 214b-2008 Walter F
... IMPORTANT: This exam will be truly cumulative, i.e. it will cover material from the entire semester. For example, it will cover material such as the quantum nature of light that we discussed back in chapter 1. However, there will be some extra emphasis on the material since exam 2, since you’ve not ...
... IMPORTANT: This exam will be truly cumulative, i.e. it will cover material from the entire semester. For example, it will cover material such as the quantum nature of light that we discussed back in chapter 1. However, there will be some extra emphasis on the material since exam 2, since you’ve not ...
Slide
... -Series expansion in U is often divergent, or, even worse, asymptotic. Does it makes sense to have more terms calculated? Yes! (i) Unbiased resummation techniques (ii) there are interesting cases with convergent series (Hubbard model at finite-T, resonant fermions) ...
... -Series expansion in U is often divergent, or, even worse, asymptotic. Does it makes sense to have more terms calculated? Yes! (i) Unbiased resummation techniques (ii) there are interesting cases with convergent series (Hubbard model at finite-T, resonant fermions) ...
No Slide Title - Wake Forest Student, Faculty and Staff Web Pages
... Nucleus consists of protons and neutrons Protons are positively charged Atomic number = number of protons Number protons unequivocally determines element (e.g. 6 protons = carbon) Number or neutrons is about equal to number of protons, but it can vary for any given atom different isotopes ...
... Nucleus consists of protons and neutrons Protons are positively charged Atomic number = number of protons Number protons unequivocally determines element (e.g. 6 protons = carbon) Number or neutrons is about equal to number of protons, but it can vary for any given atom different isotopes ...
Solved Problems on Quantum Mechanics in One
... •For the case E < U , obtain solutions to the Schrödinger equation Eq. (20) inside the well (0 ≤ x ≤ L) and in the region beyond (x > L) that satisfy the appropriate boundary conditons at x = 0 and at x = ∞. •Enforce the proper matching conditions at x = L to find an equation for the allowed energi ...
... •For the case E < U , obtain solutions to the Schrödinger equation Eq. (20) inside the well (0 ≤ x ≤ L) and in the region beyond (x > L) that satisfy the appropriate boundary conditons at x = 0 and at x = ∞. •Enforce the proper matching conditions at x = L to find an equation for the allowed energi ...
View PDF - CiteSeerX
... The third point stems from the fact that historically the Periodic Law was formulated based on empirical data before physics was capable of approaching the problem on the microlevel. The power of physical (and, more generally, scientific) approach to the world is manifested most convincingly when pr ...
... The third point stems from the fact that historically the Periodic Law was formulated based on empirical data before physics was capable of approaching the problem on the microlevel. The power of physical (and, more generally, scientific) approach to the world is manifested most convincingly when pr ...
IGCSE Revision Question Booklet Mark Scheme
... 14.(a) ideas that hydrogen is in a group / is with the halogens only seven groups / no group O / no noble gases / fewer elements halogens are in the first group / Group 1 other elements are in one group higher (or example) modern table only has two elements in the top row / period modern ...
... 14.(a) ideas that hydrogen is in a group / is with the halogens only seven groups / no group O / no noble gases / fewer elements halogens are in the first group / Group 1 other elements are in one group higher (or example) modern table only has two elements in the top row / period modern ...
The Mole & Stoicheometry
... 3. Divide each by the smallest number of moles to obtain the simplest whole number ratio. 4. If whole numbers are not obtained* in step 3), multiply through by the smallest number that will give all whole numbers * Be ...
... 3. Divide each by the smallest number of moles to obtain the simplest whole number ratio. 4. If whole numbers are not obtained* in step 3), multiply through by the smallest number that will give all whole numbers * Be ...
Why is the proton mass interesting?
... within the cluster and obtained a value at least 400 times greater than expected from their luminosity, which means that most of the matter must be dark ...
... within the cluster and obtained a value at least 400 times greater than expected from their luminosity, which means that most of the matter must be dark ...
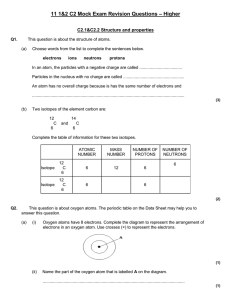
Year 11 C2 Mock Exam Revision Questions
... Draw a ring around the correct answer in each box to explain why propane evaporates easily. ...
... Draw a ring around the correct answer in each box to explain why propane evaporates easily. ...
Chemical Synthesis (sat6)
... A1: MgO and H2 -> Mg and H2O; A2: C and O2 -> CO2; A3: CO2 and H2O -> H2CO3; A4: MgO and H2 and O2 and C; minimize obj: H2CO3; Write(’Yes, H2CO3 is produced’); Write(’No, H2CO3 is not produced’); ...
... A1: MgO and H2 -> Mg and H2O; A2: C and O2 -> CO2; A3: CO2 and H2O -> H2CO3; A4: MgO and H2 and O2 and C; minimize obj: H2CO3; Write(’Yes, H2CO3 is produced’); Write(’No, H2CO3 is not produced’); ...
the PDF - JILA Science - University of Colorado Boulder
... for lattice sites containing exactly one Rb atom and one K atom (11). In addition, previous measurements of inelastic collisional loss rates for Feshbach molecules with K or Rb atoms (8, 34) suggest that having an extra atom on a lattice site will be detrimental to molecule production at that site. ...
... for lattice sites containing exactly one Rb atom and one K atom (11). In addition, previous measurements of inelastic collisional loss rates for Feshbach molecules with K or Rb atoms (8, 34) suggest that having an extra atom on a lattice site will be detrimental to molecule production at that site. ...
Chapter 12 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... 3. Make a simple redox table similar to Table 12.1 that contains all the metal atoms and metal ions that you analyzed in this investigation. Note that the ion that was able to oxidize all other metal atoms is placed at the top of the left column. In the next row, place the ion that oxidized all but ...
... 3. Make a simple redox table similar to Table 12.1 that contains all the metal atoms and metal ions that you analyzed in this investigation. Note that the ion that was able to oxidize all other metal atoms is placed at the top of the left column. In the next row, place the ion that oxidized all but ...
ch6 - ChemistryVCE
... a Metals and ionic solids both contain positive ions in a regular arrangement. b In metals and ionic solids, there is attraction between one particle and all the neighbouring particles of opposite charge. c In metals and ionic solids, there will be forces of repulsion between particles with like cha ...
... a Metals and ionic solids both contain positive ions in a regular arrangement. b In metals and ionic solids, there is attraction between one particle and all the neighbouring particles of opposite charge. c In metals and ionic solids, there will be forces of repulsion between particles with like cha ...
Week 2
... - Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements unite in fixed proportions. That is, one atom of A to one of B in AB, two atoms of A to one of B in A2B and so on. - A chemical reaction involves a rearrangement of atoms to produce new compounds. No atoms are created, destroyed, or broken apar ...
... - Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements unite in fixed proportions. That is, one atom of A to one of B in AB, two atoms of A to one of B in A2B and so on. - A chemical reaction involves a rearrangement of atoms to produce new compounds. No atoms are created, destroyed, or broken apar ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.