chemical equation - HCC Learning Web
... • Writing chemical equations The law of conservation of mass dictates that the total number of atoms of each element on both sides of a chemical equation must match. The equation is then said to be balanced. ...
... • Writing chemical equations The law of conservation of mass dictates that the total number of atoms of each element on both sides of a chemical equation must match. The equation is then said to be balanced. ...
MATHEMATICAL THEORY OF PHYSICAL VACUUM
... The basis of modern conception of the world consists of two phenomenological theories (theory of quantum mechanics and theory of relativity), both largely inconsistent, but, in a number of cases, suitable for evaluation of experimental data. Both of these theories have one thing in common: their aut ...
... The basis of modern conception of the world consists of two phenomenological theories (theory of quantum mechanics and theory of relativity), both largely inconsistent, but, in a number of cases, suitable for evaluation of experimental data. Both of these theories have one thing in common: their aut ...
Introduction(s)
... Binary aqueous acid compounds (recognized because hydrogen is the first element that is combined with an ide ion) are named by using the pattern: hydro-(root word of negative element)-ic acid ...
... Binary aqueous acid compounds (recognized because hydrogen is the first element that is combined with an ide ion) are named by using the pattern: hydro-(root word of negative element)-ic acid ...
Memorization?
... Binary aqueous acid compounds (recognized because hydrogen is the first element that is combined with an ide ion) are named by using the pattern: hydro-(root word of negative element)-ic acid ...
... Binary aqueous acid compounds (recognized because hydrogen is the first element that is combined with an ide ion) are named by using the pattern: hydro-(root word of negative element)-ic acid ...
a non-perturbative approach for quantum field theory
... – A nonperturbative numerical approach to quantum field theory – Evaluate the structure and interaction of “elementary” particles – such as electrons and nucleons, from first principle – Alternative approach to Lattice Gauge Theory ...
... – A nonperturbative numerical approach to quantum field theory – Evaluate the structure and interaction of “elementary” particles – such as electrons and nucleons, from first principle – Alternative approach to Lattice Gauge Theory ...
the original file
... The Correspondence Principle describes how QM relates to physics in the classical limit. It connects QM to the macroscopic world by way of using a statistical interpretation. It states that the familiar observations of classical physics are supported by the expectation values of the quantum systems. ...
... The Correspondence Principle describes how QM relates to physics in the classical limit. It connects QM to the macroscopic world by way of using a statistical interpretation. It states that the familiar observations of classical physics are supported by the expectation values of the quantum systems. ...
Wave Theory
... of light and other quantum particles. A coherent light source illuminates a thin plate with two parallel slits cut in it, and the light passing through the slits strikes a screen behind them. The wave nature of light causes the light waves passing through both slits to interfere, creating an interfe ...
... of light and other quantum particles. A coherent light source illuminates a thin plate with two parallel slits cut in it, and the light passing through the slits strikes a screen behind them. The wave nature of light causes the light waves passing through both slits to interfere, creating an interfe ...
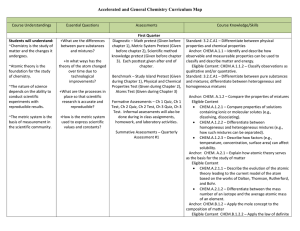
Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Anchor: CHEM.B.1.1 – Explain how the mole is a fundamental unit of chemistry. Eligible Content: CHEM.B.1.1.1 – Apply the mole concept to representative particles (e.g., counting, determining mass of atoms, ions, molecules, and/or formula units). Standard: 3.2.C.A5 – Models – Recognize discoveries fr ...
... Anchor: CHEM.B.1.1 – Explain how the mole is a fundamental unit of chemistry. Eligible Content: CHEM.B.1.1.1 – Apply the mole concept to representative particles (e.g., counting, determining mass of atoms, ions, molecules, and/or formula units). Standard: 3.2.C.A5 – Models – Recognize discoveries fr ...
Rubidium 87 D Line Data
... Some useful fundamental physical constants are given in Table 1. The values given are the 1998 CODATA recommended values, as listed in [1]. Some of the overall physical properties of 87 Rb are given in Table 2. 87 Rb has 37 electrons, only one of which is in the outermost shell. 87 Rb is not a stabl ...
... Some useful fundamental physical constants are given in Table 1. The values given are the 1998 CODATA recommended values, as listed in [1]. Some of the overall physical properties of 87 Rb are given in Table 2. 87 Rb has 37 electrons, only one of which is in the outermost shell. 87 Rb is not a stabl ...
22 Sept 08 - Seattle Central College
... • Since your least accurate value has two certain digits and one estimated digit, your calculated digit simply can't do any better, so it cannot have more than three significant figures. ...
... • Since your least accurate value has two certain digits and one estimated digit, your calculated digit simply can't do any better, so it cannot have more than three significant figures. ...
PPT
... The scattered intensity is the square of the (spatial) Fourier transform of the amplitude density of the target The conjugate variable is kx, better the transverse component of wave-vector the scattered particle (kT) If D</2 the total phase change Df induced by the target on its section D is small ...
... The scattered intensity is the square of the (spatial) Fourier transform of the amplitude density of the target The conjugate variable is kx, better the transverse component of wave-vector the scattered particle (kT) If D</2 the total phase change Df induced by the target on its section D is small ...
Calculation of the Energy Levels of Phosphorus Isotopes
... technique, wave functions with good angular momentum J and isospin T are constructed. The SDPN and SD model spaces consist of (0d5/2, 1s1/2 and 0d3/2) above the Z = 8 and N=8 closed shells for protons and neutrons. CW is an effective interaction that has been used with the SD model space, where the ...
... technique, wave functions with good angular momentum J and isospin T are constructed. The SDPN and SD model spaces consist of (0d5/2, 1s1/2 and 0d3/2) above the Z = 8 and N=8 closed shells for protons and neutrons. CW is an effective interaction that has been used with the SD model space, where the ...
Quantum states
... wave packet (= wave function). • A quantum state is characterized by a set of quantum numbers, such as the energy E. • Quantum numbers can be measured exactly. For example, the uncertainty E is zero for a stable state, where one can take an infinite time t for measuring the energy. ...
... wave packet (= wave function). • A quantum state is characterized by a set of quantum numbers, such as the energy E. • Quantum numbers can be measured exactly. For example, the uncertainty E is zero for a stable state, where one can take an infinite time t for measuring the energy. ...
Quantum `jump`
... wave packet (= wave function). • A quantum state is characterized by a set of quantum numbers, such as the energy E. • Quantum numbers can be measured exactly. For example, the uncertainty E is zero for a stable state, where one can take an infinite time t for measuring the energy. ...
... wave packet (= wave function). • A quantum state is characterized by a set of quantum numbers, such as the energy E. • Quantum numbers can be measured exactly. For example, the uncertainty E is zero for a stable state, where one can take an infinite time t for measuring the energy. ...
Aalborg Universitet Unification and CPH Theory Javadi, Hossein; Forouzbakhsh, Farshid
... photon, gravitons convert to negative and positive color charges and magnetic color too. These color charges and magnetic color form the electromagnetic energy. Electromagnetic energy converts to matter and anti-matter such as charged particles. Charged particles use gravitons and generate electroma ...
... photon, gravitons convert to negative and positive color charges and magnetic color too. These color charges and magnetic color form the electromagnetic energy. Electromagnetic energy converts to matter and anti-matter such as charged particles. Charged particles use gravitons and generate electroma ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.