Background Material
... the angular shapes of the spherical box problem are the same as in atomic structure because, in both cases, the potential is independent of and . As the orbital plots shown above indicate, the angular shapes of s, p, and d orbitals display varying number of nodal surfaces. The s orbitals have non ...
... the angular shapes of the spherical box problem are the same as in atomic structure because, in both cases, the potential is independent of and . As the orbital plots shown above indicate, the angular shapes of s, p, and d orbitals display varying number of nodal surfaces. The s orbitals have non ...
STUDY GUIDE
... other. For example, acids should not be stored near cyanides, sulfides and other chemicals that produce toxic gases when combined. Acids should also not be stored near bases or active metals. Reactions between acids and bases produce heat. Acids and active metals react to produce gases and heat. Aci ...
... other. For example, acids should not be stored near cyanides, sulfides and other chemicals that produce toxic gases when combined. Acids should also not be stored near bases or active metals. Reactions between acids and bases produce heat. Acids and active metals react to produce gases and heat. Aci ...
Chapter 3: Chemical Reactions and the Earth`s Composition
... Example 2: Everclear is a brand of grain alcohol that can be as high as 190 proof (or 95% ethanol, C2H5OH, by volume). Calculate the mass of carbon dioxide produced upon complete combustion of the ethanol in a 750 mL bottle of Everclear. Write the balanced chemical equation for the combustion of eth ...
... Example 2: Everclear is a brand of grain alcohol that can be as high as 190 proof (or 95% ethanol, C2H5OH, by volume). Calculate the mass of carbon dioxide produced upon complete combustion of the ethanol in a 750 mL bottle of Everclear. Write the balanced chemical equation for the combustion of eth ...
PDF corrected surface chemistry
... an alcoholic solution (true solution) of sulphur is added in excess of water, a colloidal solution of sulphur results. Sulphur is insoluble in water. 2. Passing vapours of an element into a liquid: When the vapours of an element are passed through a liquid, condensation takes place to give a colloid ...
... an alcoholic solution (true solution) of sulphur is added in excess of water, a colloidal solution of sulphur results. Sulphur is insoluble in water. 2. Passing vapours of an element into a liquid: When the vapours of an element are passed through a liquid, condensation takes place to give a colloid ...
here.
... • The physics of particles and fields deals with the fundamental constituents of matter and their interactions. This branch of physics is also called (elementary) particle physics or high energy physics and sometimes sub-atomic or sub-nuclear physics. Sub-atomic/nuclear means of size less than atomi ...
... • The physics of particles and fields deals with the fundamental constituents of matter and their interactions. This branch of physics is also called (elementary) particle physics or high energy physics and sometimes sub-atomic or sub-nuclear physics. Sub-atomic/nuclear means of size less than atomi ...
$doc.title
... Feshbach resonances, allow to realize systems with very large scattering length, in which the mean-field picture is no more applicable. Similarly, the realization of a Bosecondensed metastable Helium gas [10], with a potential to study higher order correlation functions of the system, demands an anal ...
... Feshbach resonances, allow to realize systems with very large scattering length, in which the mean-field picture is no more applicable. Similarly, the realization of a Bosecondensed metastable Helium gas [10], with a potential to study higher order correlation functions of the system, demands an anal ...
Midterm Review
... ____ 70. How are the frequency and wavelength of light related? a. They are inversely proportional to each other. b. Frequency equals wavelength divided by the speed of light. c. Wavelength is determined by dividing frequency by the speed of light. d. They are directly proportional to each other. _ ...
... ____ 70. How are the frequency and wavelength of light related? a. They are inversely proportional to each other. b. Frequency equals wavelength divided by the speed of light. c. Wavelength is determined by dividing frequency by the speed of light. d. They are directly proportional to each other. _ ...
Reactions and Balancing
... so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element in order to balance the equation. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios. (reduced) ...
... so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element in order to balance the equation. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios. (reduced) ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Physics 121, Lecture 12.
... determined by the external forces. Forces exerted by one part of the system on other parts of the system are called internal forces. According to Newton’s third law, the sum of all internal forces cancel out (for each interaction there are two forces acting on two parts: they are equal in magnitude ...
... determined by the external forces. Forces exerted by one part of the system on other parts of the system are called internal forces. According to Newton’s third law, the sum of all internal forces cancel out (for each interaction there are two forces acting on two parts: they are equal in magnitude ...
Chapter 2. Model Problems That Form Important Starting Points
... the angular shapes of the spherical box problem are the same as in atomic structure because, in both cases, the potential is independent of θ and φ. As the orbital plots shown above indicate, the angular shapes of s, p, and d orbitals display varying number of nodal surfaces. The s orbitals have non ...
... the angular shapes of the spherical box problem are the same as in atomic structure because, in both cases, the potential is independent of θ and φ. As the orbital plots shown above indicate, the angular shapes of s, p, and d orbitals display varying number of nodal surfaces. The s orbitals have non ...
Unit 5 Test Review
... Methane and oxygen are combined in a reaction vessel in amounts of 16 grams and 32 grams respectively. What amounts of reactants and products will be present in the reaction vessel once the reaction is complete? a. 0 grams CH4, 0 grams of O2, 44 grams of CO2, 36 grams of H2O b. 8 grams CH4, 0 grams ...
... Methane and oxygen are combined in a reaction vessel in amounts of 16 grams and 32 grams respectively. What amounts of reactants and products will be present in the reaction vessel once the reaction is complete? a. 0 grams CH4, 0 grams of O2, 44 grams of CO2, 36 grams of H2O b. 8 grams CH4, 0 grams ...
Product Instructions: Inclined Plane
... For a normal balance, the two masses would need to be the same in order for the system to be in equilibrium. However, only a component of the weight of 1 is acting to pull it down the incline, so the mass of 2 only need be equal and opposite to the component of 1 acting along the incline. ...
... For a normal balance, the two masses would need to be the same in order for the system to be in equilibrium. However, only a component of the weight of 1 is acting to pull it down the incline, so the mass of 2 only need be equal and opposite to the component of 1 acting along the incline. ...
Exercises in Statistical Mechanics
... frequency ω0 . The total angular momentum is ` = 0, 1, 2, .... The masses of the atoms are mA and mB , and they have spins SA and SB . (a) Explian what are the conditions that allow to ignore all the excited vibrational levels, so you can treat the molecule as a rigid body (”rotor”). (b) Calculate t ...
... frequency ω0 . The total angular momentum is ` = 0, 1, 2, .... The masses of the atoms are mA and mB , and they have spins SA and SB . (a) Explian what are the conditions that allow to ignore all the excited vibrational levels, so you can treat the molecule as a rigid body (”rotor”). (b) Calculate t ...
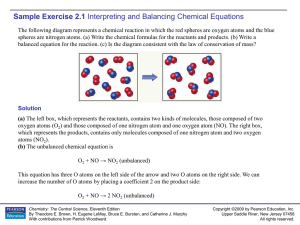
Sample Exercise 2.1
... Analyze We are given the number of moles and the name of a substance and asked to calculate the number of grams in the sample. Plan To convert moles to grams, we need the molar mass, which we can calculate using the chemical formula and atomic weights. Solve Because the calcium ion is Ca2+ and the n ...
... Analyze We are given the number of moles and the name of a substance and asked to calculate the number of grams in the sample. Plan To convert moles to grams, we need the molar mass, which we can calculate using the chemical formula and atomic weights. Solve Because the calcium ion is Ca2+ and the n ...
Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations How
... – CuSO4 • 6H2O is called copper sulfate hexahydrate. ...
... – CuSO4 • 6H2O is called copper sulfate hexahydrate. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.