Solutions
... have higher boiling points than pure solvents. This is true with solid solutes and heavier liquid solutes. Other liquid solutes may form azeotropes, which are mixtures with lower boiling points than either solute or solvent – example 95% ethanol/water.) Solutes raise the boiling point of liquids ...
... have higher boiling points than pure solvents. This is true with solid solutes and heavier liquid solutes. Other liquid solutes may form azeotropes, which are mixtures with lower boiling points than either solute or solvent – example 95% ethanol/water.) Solutes raise the boiling point of liquids ...
Kinetics
... ride and oxalate ion in hot aqueous solution is shown above. The reaction rate may be determined by meas- (b) A small increase in temperature causes a large inuring the initial rate of formation of chloride ion, at crease in the reaction rate. constant temperature, for various initial concentrations ...
... ride and oxalate ion in hot aqueous solution is shown above. The reaction rate may be determined by meas- (b) A small increase in temperature causes a large inuring the initial rate of formation of chloride ion, at crease in the reaction rate. constant temperature, for various initial concentrations ...
Equilibrium
... ______________ (the process of dissolving) equals the rate of _______________]. At this instance, ___________ equilibrium has been established. ...
... ______________ (the process of dissolving) equals the rate of _______________]. At this instance, ___________ equilibrium has been established. ...
1.ThermoStudentNotes
... because of the law of conservation of energy, the heat of reaction is the ______________ whether the reactants are converted to the products in a ______________________________________ or in a ______________________________________________________ ...
... because of the law of conservation of energy, the heat of reaction is the ______________ whether the reactants are converted to the products in a ______________________________________ or in a ______________________________________________________ ...
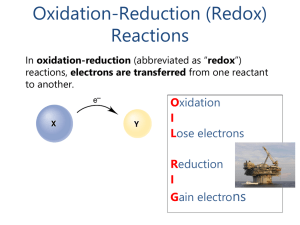
Worksheet 1 - Oxidation/Reduction Reactions Oxidation number
... changes, as seen in the previous example. However, there is an easier method, which involves breaking a redox reaction into two half- reactions. This is best shown by working an example. Hydrobromic acid will react with permanganate to form elemental bromine and the manganese(II) ion. The unbalanced ...
... changes, as seen in the previous example. However, there is an easier method, which involves breaking a redox reaction into two half- reactions. This is best shown by working an example. Hydrobromic acid will react with permanganate to form elemental bromine and the manganese(II) ion. The unbalanced ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
... Assigning Oxidation Numbers 1. The oxidation number of an element in its natural form is 0. Examples: the oxidation number is zero for each element in H2, O2, Cl2, P4, Na, etc. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the charge on the ion. Examples: Na3N, the ions are Na+ and N3–, so oxidatio ...
... Assigning Oxidation Numbers 1. The oxidation number of an element in its natural form is 0. Examples: the oxidation number is zero for each element in H2, O2, Cl2, P4, Na, etc. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the charge on the ion. Examples: Na3N, the ions are Na+ and N3–, so oxidatio ...
C:\D\Books\Cambridge University Press\CUP Problems\Problems.wpd
... 81. Consider the hydrological cycle shown in Figure 3.3. a What is the lifetime of water in the oceans with respect to evaporation? b According to the figure, the evaporation of water from the ocean uses 1 YJ/a. Show that this is correct. c Compare the energy released into the atmosphere through con ...
... 81. Consider the hydrological cycle shown in Figure 3.3. a What is the lifetime of water in the oceans with respect to evaporation? b According to the figure, the evaporation of water from the ocean uses 1 YJ/a. Show that this is correct. c Compare the energy released into the atmosphere through con ...
Molecular Modeling Activity for Carbohydrates
... Just as double sugars were formed from two single sugar molecules using a dehydration synthesis reaction, polysaccharides and water molecules are formed when many single sugars are chemically joined together. The prefix “poly-” means many. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are the three most common po ...
... Just as double sugars were formed from two single sugar molecules using a dehydration synthesis reaction, polysaccharides and water molecules are formed when many single sugars are chemically joined together. The prefix “poly-” means many. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are the three most common po ...
Changing Matter
... • Atoms that bond form molecules – May be the same type (nonmetals) of atom or, – Different types (metal + nonmetal) of atoms ...
... • Atoms that bond form molecules – May be the same type (nonmetals) of atom or, – Different types (metal + nonmetal) of atoms ...
Chapter 4-5
... 4. Multiply by two to remove the fractional coefficient 2 C6H14O4 (l) + 15 O2 (g)→ 12 CO2 (g) + 14 H2O(g) and check all elements. ...
... 4. Multiply by two to remove the fractional coefficient 2 C6H14O4 (l) + 15 O2 (g)→ 12 CO2 (g) + 14 H2O(g) and check all elements. ...
4.3 Reaction and Process Design
... Nowadays, reactions in unconventional media for sustainable organic synthesis focus on aqueous biphasic catalysis, supercritical media, fluorous biphasic catalysis, ionic liquids and biphasic combination. Several of these media, like fluorous and ionic liquids, allow intensified separation technolog ...
... Nowadays, reactions in unconventional media for sustainable organic synthesis focus on aqueous biphasic catalysis, supercritical media, fluorous biphasic catalysis, ionic liquids and biphasic combination. Several of these media, like fluorous and ionic liquids, allow intensified separation technolog ...
revised Chemical Kinetics
... Surface Area: If a chemical reaction takes place at a boundary between two phases, the surface area will affect the reaction rate. When we consider surface area, we are usually thinking of a solid reactant in contact with a liquid solution that contains another reactant. Certainly, other cases are a ...
... Surface Area: If a chemical reaction takes place at a boundary between two phases, the surface area will affect the reaction rate. When we consider surface area, we are usually thinking of a solid reactant in contact with a liquid solution that contains another reactant. Certainly, other cases are a ...
Section 3_Energetics
... ones formed in the products. Bond-breaking is energy absorbing, i.e. endothermic, whereas bond-forming is energy releasing, i.e. exothermic. Therefore, during the course of a chemical reaction, heat is either given out or taken in from the surroundings. Therefore, the total energy absorbed or releas ...
... ones formed in the products. Bond-breaking is energy absorbing, i.e. endothermic, whereas bond-forming is energy releasing, i.e. exothermic. Therefore, during the course of a chemical reaction, heat is either given out or taken in from the surroundings. Therefore, the total energy absorbed or releas ...
13. Condensed azines. Quinoline. Isoquinoline. Acridine. Diazines
... colorless liquid with a boiling point of 208 °C. Pyridazine has no household use. It is mainly used in research and industry as building block for more complex compounds. The pyridazine structure is found within a number of herbicides such as credazine, pyridafol and pyridate. It is also found withi ...
... colorless liquid with a boiling point of 208 °C. Pyridazine has no household use. It is mainly used in research and industry as building block for more complex compounds. The pyridazine structure is found within a number of herbicides such as credazine, pyridafol and pyridate. It is also found withi ...
Percent Purity - Mr. Lawson`s Website
... 3. Examine the picture CLOSELY and determine how many TOTAL atoms of silver make up Mr. Lawson’s net worth! 4. DO NOT OPEN THE CASE, Mr. Lawson is a new teacher and does not get paid very much… ...
... 3. Examine the picture CLOSELY and determine how many TOTAL atoms of silver make up Mr. Lawson’s net worth! 4. DO NOT OPEN THE CASE, Mr. Lawson is a new teacher and does not get paid very much… ...
Tro Chemistry a Molecular Approach, 3E
... moles of each of the substances involved in the reaction. In other words, from the equation, we know that 16 moles of CO2 are produced for every 2 moles of octane burned. The numerical relationships between chemical amounts in a balanced chemical equation are called reaction stoichiometry. Stoichiom ...
... moles of each of the substances involved in the reaction. In other words, from the equation, we know that 16 moles of CO2 are produced for every 2 moles of octane burned. The numerical relationships between chemical amounts in a balanced chemical equation are called reaction stoichiometry. Stoichiom ...
unit-3-atoms-and-nuclear - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... Nuclear Fission ■ Nuclear Fission = a very heavy nucleus splits into more stable nuclei or intermediate mass and releases large amounts of energy – Can occur spontaneously or when nuclei are bombarded with particles. – A chain reaction = a reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is ...
... Nuclear Fission ■ Nuclear Fission = a very heavy nucleus splits into more stable nuclei or intermediate mass and releases large amounts of energy – Can occur spontaneously or when nuclei are bombarded with particles. – A chain reaction = a reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is ...
Theoretical Competition - Austrian Chemistry Olympiad
... June 15th, 2012 The kinetics of gas reactions are usually followed by measuring the total pressure of the gas mixture, which changes with time. In this case the partial pressure of oxygen derives in the following way from the total pressure: ...
... June 15th, 2012 The kinetics of gas reactions are usually followed by measuring the total pressure of the gas mixture, which changes with time. In this case the partial pressure of oxygen derives in the following way from the total pressure: ...
Reaction and Process Design Vision Document
... Nowadays, reactions in unconventional media for sustainable organic synthesis focus on aqueous biphasic catalysis, supercritical media, fluorous biphasic catalysis, ionic liquids and biphasic combination. Several of these media, like fluorous and ionic liquids, allow intensified separation technolog ...
... Nowadays, reactions in unconventional media for sustainable organic synthesis focus on aqueous biphasic catalysis, supercritical media, fluorous biphasic catalysis, ionic liquids and biphasic combination. Several of these media, like fluorous and ionic liquids, allow intensified separation technolog ...
N5 Chemistry Summary notes 2017
... Everything is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Atoms are mostly empty space made up of smaller sub-atomic particles. At the centre of the atom is the nucleus. This contains two types of particles, called protons and neutrons. Spinning around the nucleus are very fast moving particles called e ...
... Everything is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Atoms are mostly empty space made up of smaller sub-atomic particles. At the centre of the atom is the nucleus. This contains two types of particles, called protons and neutrons. Spinning around the nucleus are very fast moving particles called e ...
+ H 2 O(l) - Cloudfront.net
... • Determining the concentration of an unknown solution. • Use a 2nd solution of known concentration (standard solution) that undergoes a reaction with the unknown solution. • Use the ratios in the balanced equation along with the M = mol/L equation to determine molarity of unknown. ...
... • Determining the concentration of an unknown solution. • Use a 2nd solution of known concentration (standard solution) that undergoes a reaction with the unknown solution. • Use the ratios in the balanced equation along with the M = mol/L equation to determine molarity of unknown. ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.