
Final review packet
... f. combustion of a hydrocarbon 6. What are the 4 driving forces in a reaction in aqueous solution? 7. Using the solubility rules, tell which of these compounds are soluble: (S) = Soluble or (I) = Insoluble in water _____ a. magnesium hydroxide ...
... f. combustion of a hydrocarbon 6. What are the 4 driving forces in a reaction in aqueous solution? 7. Using the solubility rules, tell which of these compounds are soluble: (S) = Soluble or (I) = Insoluble in water _____ a. magnesium hydroxide ...
Final Exam Practice Problems: R = 0.0821 Latm/molK NA = 6.022
... A) Li+ (aq) + SO42-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + Li+(aq) + NO3-(aq) B) Li+ (aq) + S-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + LiNO3(aq) C) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 LiNO3(s) D) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) ...
... A) Li+ (aq) + SO42-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + Li+(aq) + NO3-(aq) B) Li+ (aq) + S-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + LiNO3(aq) C) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 LiNO3(s) D) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) ...
Glossary
... Measurable quantity − a quantity that can be measured and expressed as the product of a numerical value and a basic unit of measurement. Measurements − acts and results of determining measurable quantities. Mechanics − the science of the structure and motion of physical objects. Mechanism − the brea ...
... Measurable quantity − a quantity that can be measured and expressed as the product of a numerical value and a basic unit of measurement. Measurements − acts and results of determining measurable quantities. Mechanics − the science of the structure and motion of physical objects. Mechanism − the brea ...
Chapter 9 Stoichiometry
... 5. Calculate the mass of a reactant or product from the mass of a different reactant or product. 6. Describe a method for determining which of two reactants is a limiting reactant. 7. Calculate the amount in moles of a product produced, given the amounts in moles of two reactants, one of which is in ...
... 5. Calculate the mass of a reactant or product from the mass of a different reactant or product. 6. Describe a method for determining which of two reactants is a limiting reactant. 7. Calculate the amount in moles of a product produced, given the amounts in moles of two reactants, one of which is in ...
Stoichiometry 2
... Worked Example: If 5.00 g of Propane (C3H8(l)) is combusted in excess oxygen gas, what mass of water is expected to be formed? What mass and volume of CO2 (g) (at STP) would you expect to collect? Step 1. Write a balanced Chemical Equation and ...
... Worked Example: If 5.00 g of Propane (C3H8(l)) is combusted in excess oxygen gas, what mass of water is expected to be formed? What mass and volume of CO2 (g) (at STP) would you expect to collect? Step 1. Write a balanced Chemical Equation and ...
BITSAT Chemistry
... A mixture of C6H6 and excess H2 has a pressure of 60 mm of Hg in an unknown volume. After the gas had been passed over a nickel catalyst and all the benzene converted to cyclohexane, the pressure of the gas was 30 mm of Hg in the same volume at ...
... A mixture of C6H6 and excess H2 has a pressure of 60 mm of Hg in an unknown volume. After the gas had been passed over a nickel catalyst and all the benzene converted to cyclohexane, the pressure of the gas was 30 mm of Hg in the same volume at ...
2007 - Thompson Rivers University
... The contest consists of 25 multiple choice questions. You have 60 minutes to complete the test. All questions are of equal value, there is no particular order to the questions and there is no penalty for incorrect answers. Please answer on the Scantron Answer Sheet. In the top right hand corner of t ...
... The contest consists of 25 multiple choice questions. You have 60 minutes to complete the test. All questions are of equal value, there is no particular order to the questions and there is no penalty for incorrect answers. Please answer on the Scantron Answer Sheet. In the top right hand corner of t ...
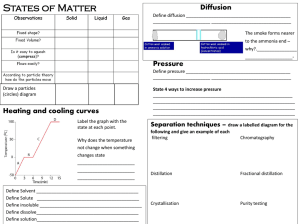
IGCSE Revision document
... Why are they stored under oil? _______________________________________ Why does reactivity increase down the group? _______________________________________ _______________________________________ Write the equation for sodium with water produces sodium hydroxide and hydrogen ________________________ ...
... Why are they stored under oil? _______________________________________ Why does reactivity increase down the group? _______________________________________ _______________________________________ Write the equation for sodium with water produces sodium hydroxide and hydrogen ________________________ ...
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry
... Reactants --> Products, Atoms rearrange to produce new substance(s) by breaking and forming new bonds. Mass and atoms are conserved in a chemical reaction. Subscripts and Coefficients: 4 CH4 represents 4 molecules of CH4, 4 C atoms and 16 H atoms. Coefficients represent relative numbers (moles, mole ...
... Reactants --> Products, Atoms rearrange to produce new substance(s) by breaking and forming new bonds. Mass and atoms are conserved in a chemical reaction. Subscripts and Coefficients: 4 CH4 represents 4 molecules of CH4, 4 C atoms and 16 H atoms. Coefficients represent relative numbers (moles, mole ...
Notes matter energy
... A molecule is made up of two or more nonmetal atoms. A chemical formula tells the number and type of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) is the formula for a molecule because it consists of only nonmetals. The molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen a ...
... A molecule is made up of two or more nonmetal atoms. A chemical formula tells the number and type of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) is the formula for a molecule because it consists of only nonmetals. The molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen a ...
Balanced Chemical Equation
... 1. Write the skeleton equation. All reactants and products have their correct balanced formulas. 2. By inspection, find an element or polyatomic group that does not have equal amounts on both sides. 3. Add coefficients to make the number of atoms or groups equal on both sides of equation. ...
... 1. Write the skeleton equation. All reactants and products have their correct balanced formulas. 2. By inspection, find an element or polyatomic group that does not have equal amounts on both sides. 3. Add coefficients to make the number of atoms or groups equal on both sides of equation. ...
Matter Change
... The process by which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances Occurrence can be indicated by changes in temperature, color, odor, & physical state Also known as a chemical change Chemical properties can only be observed when a substance undergoes a chemical cha ...
... The process by which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances Occurrence can be indicated by changes in temperature, color, odor, & physical state Also known as a chemical change Chemical properties can only be observed when a substance undergoes a chemical cha ...
Overhead Notes Stoichiometry
... volumes of gas, at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of particles. Moles are numbers of particles You can treat reactions as if they happen liters at a time, as long as you keep the temperature and pressure the same. 1 mole = 22.4 L @ STP ...
... volumes of gas, at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of particles. Moles are numbers of particles You can treat reactions as if they happen liters at a time, as long as you keep the temperature and pressure the same. 1 mole = 22.4 L @ STP ...
2016-2017 Summer Assignment AP Chem 2017 Summer
... in mole percent, 10.0% O2, 10.0% N2 , and 80.0% He. a. Calculate the molar mass of this mixture. b. What is the ratio of the density of this gas to that of pure Oxygen? 56. When Hydrogen sulfide gas, H2S, reacts with oxygen, Sulfur dioxide gas and steam are ...
... in mole percent, 10.0% O2, 10.0% N2 , and 80.0% He. a. Calculate the molar mass of this mixture. b. What is the ratio of the density of this gas to that of pure Oxygen? 56. When Hydrogen sulfide gas, H2S, reacts with oxygen, Sulfur dioxide gas and steam are ...
Chemistry Lesson Plans #07 - Chemical Reactions
... formula of a substance. Check each atom or polyatomic ion to be sure that the equation is balanced. Finally, make sure all the coefficients are in the lowest possible ratio that balances Sample Problems Hydrogen and oxygen react to form water. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. First, writ ...
... formula of a substance. Check each atom or polyatomic ion to be sure that the equation is balanced. Finally, make sure all the coefficients are in the lowest possible ratio that balances Sample Problems Hydrogen and oxygen react to form water. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. First, writ ...
unit (4) calculations and chemical reactions
... reaction reactants (starting materials) are converted into products. Consider the reaction in which magnesium oxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form magnesium carbonate. We can represent the above “word description” by a “chemical equation”. Chemical equation: MgO + CO2 → MgCO3 Reactants Product W ...
... reaction reactants (starting materials) are converted into products. Consider the reaction in which magnesium oxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form magnesium carbonate. We can represent the above “word description” by a “chemical equation”. Chemical equation: MgO + CO2 → MgCO3 Reactants Product W ...
Chemistry 1A Final Exam December 12, 2001 Page 1 of 16 (Closed
... Chemical reactions are more favorable. Chemical reactions are less favorable. Equilibrium constants are smaller. Equilibrium constants are larger. Chemical reactions are sometimes more favorable. ...
... Chemical reactions are more favorable. Chemical reactions are less favorable. Equilibrium constants are smaller. Equilibrium constants are larger. Chemical reactions are sometimes more favorable. ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.











![[Mg] +2[ S ]-2](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014450548_1-468f3af464a09baae245d79fadf97d41-300x300.png)










