Identification and Structural Characterization of the ATP/ADP
... widely accepted that unlike Hsp70/DnaK and Hsp60/ GroEL, Hsp90 does not bind ATP. Although the structure of the intact Hsp90 molecule has not yet been determined, crystal structures of an amino-terminal domain identified by limited proteolysis have been determined for yeast (Prodromou et al., 1997) ...
... widely accepted that unlike Hsp70/DnaK and Hsp60/ GroEL, Hsp90 does not bind ATP. Although the structure of the intact Hsp90 molecule has not yet been determined, crystal structures of an amino-terminal domain identified by limited proteolysis have been determined for yeast (Prodromou et al., 1997) ...
Anaerobic Protist Metabolism Amitochondriate Biochemistry
... Oxidative phosphorylation - coupling of ATP formation to the respiratory chain (electron transport, membrane associated, O2 as final e- acceptor). As electrons move through complexes, a proton gradient is generated which drives ATP formation. Chemiosmotic theory - P. Mitchell, 1978. Substrate level ...
... Oxidative phosphorylation - coupling of ATP formation to the respiratory chain (electron transport, membrane associated, O2 as final e- acceptor). As electrons move through complexes, a proton gradient is generated which drives ATP formation. Chemiosmotic theory - P. Mitchell, 1978. Substrate level ...
Journal of Bacteriology
... aspartate residue that is phosphorylated during the reaction cycle, a conserved proline residue in a membrane domain that probably forms a portion of the ion translocation pathway, and consensus domains for ATP binding and energy transduction. The superfamily of P-type ATPases has five major branche ...
... aspartate residue that is phosphorylated during the reaction cycle, a conserved proline residue in a membrane domain that probably forms a portion of the ion translocation pathway, and consensus domains for ATP binding and energy transduction. The superfamily of P-type ATPases has five major branche ...
Lecture 10 Powerpoint Presentation
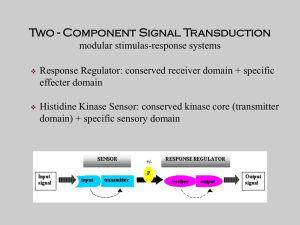
... Both PmrA and RcsB can bind and activate transcription from the ugd promoter. PmrD activates PmrA post-transcriptionally independently of PmrB in response to Mg++. The ugd gene is expressed in response to Mg++, Fe+++ OR cell envelope stress. ...
... Both PmrA and RcsB can bind and activate transcription from the ugd promoter. PmrD activates PmrA post-transcriptionally independently of PmrB in response to Mg++. The ugd gene is expressed in response to Mg++, Fe+++ OR cell envelope stress. ...
Chapter 5B Lecture
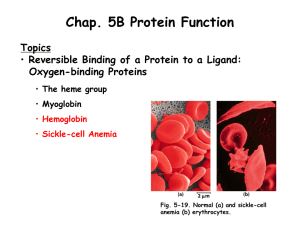
... Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless gas that is responsible for more than half of the annual poisoning deaths worldwide. CO has a 250-fold greater affinity for Hb than O2, and exposure to CO reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Symptoms of CO poisoning depend on the percent o ...
... Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless gas that is responsible for more than half of the annual poisoning deaths worldwide. CO has a 250-fold greater affinity for Hb than O2, and exposure to CO reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Symptoms of CO poisoning depend on the percent o ...
lecture 15
... Substrate is represented as a green circle to mark the expected position of contacts, but not as a direct indication of substrate size or structural details. The bulk of the substrate may, in fact, be variously extended outside of the Hsp90 clamp with chaperone:substrate contacts limited to a subdom ...
... Substrate is represented as a green circle to mark the expected position of contacts, but not as a direct indication of substrate size or structural details. The bulk of the substrate may, in fact, be variously extended outside of the Hsp90 clamp with chaperone:substrate contacts limited to a subdom ...
02_Murray - Sbkb.org
... Discriminate whether START domains bind cholesterol or PC (PI) or other ligands Provide leads for chemical library studies for function-interfering compounds Detailed computational analysis and function annotation Fine-grain structure analysis in the absence and presence of potential ligand Experime ...
... Discriminate whether START domains bind cholesterol or PC (PI) or other ligands Provide leads for chemical library studies for function-interfering compounds Detailed computational analysis and function annotation Fine-grain structure analysis in the absence and presence of potential ligand Experime ...
ATP, produced by glucose catabolized during cellular
... water is split, or lysed, and the resulting hydrogen atom (H+) and a hydroxyl group (OH) are added to the larger molecule. The hydrolysis of ATP produces ADP, together with an inorganic phosphateion (Pi ), and the release of free energy. To carry out life processes, ATP is continuously broken down ...
... water is split, or lysed, and the resulting hydrogen atom (H+) and a hydroxyl group (OH) are added to the larger molecule. The hydrolysis of ATP produces ADP, together with an inorganic phosphateion (Pi ), and the release of free energy. To carry out life processes, ATP is continuously broken down ...
Question #1 - Jordan
... Cross-bridge cycling forms the basis for movement and force production in muscle cells. Each cycle of myosin binding to actin and movement of the thin filament involves the hydrolysis of one ATP molecule. A myosin cross-bridge attaches to actin. ATP binding causes the dissociation of myosin from act ...
... Cross-bridge cycling forms the basis for movement and force production in muscle cells. Each cycle of myosin binding to actin and movement of the thin filament involves the hydrolysis of one ATP molecule. A myosin cross-bridge attaches to actin. ATP binding causes the dissociation of myosin from act ...
How ATP Packs Energy
... by compressing a spring. The tightly coiled spring has potential energy. When the compressed spring relaxes, its potential energy is released. The spring's kinetic energy can be used to perform work such as pushing a block attached to one end of the spring. The phosphate bonds are symbolized by spri ...
... by compressing a spring. The tightly coiled spring has potential energy. When the compressed spring relaxes, its potential energy is released. The spring's kinetic energy can be used to perform work such as pushing a block attached to one end of the spring. The phosphate bonds are symbolized by spri ...
Dephosphorylation of the Calcium Pump Coupled to Counterion
... at the N-terminal end of the protein Contains the Thr-Gly-Glu-Ser (TGES) sequence, amino acids 181-184 (main article). This sequence is highly conserved in Ptype ATPases, and plays an important role in the dephosphorylation of the E2-P phosphoenzyme. Links the changes at the phosphorylation site of ...
... at the N-terminal end of the protein Contains the Thr-Gly-Glu-Ser (TGES) sequence, amino acids 181-184 (main article). This sequence is highly conserved in Ptype ATPases, and plays an important role in the dephosphorylation of the E2-P phosphoenzyme. Links the changes at the phosphorylation site of ...
Introduction Part1
... Neck linker of leading head “zips up” agains catalytic core trailing head is thrown forward (trailing head has bound ADP and reduced affinity to microtubule): Trailing head swings by ~ 160 Å, net movement of dimeric kinesin is ~ 80 Å = length of one microtubule dimer ATP in new trailing head is hydr ...
... Neck linker of leading head “zips up” agains catalytic core trailing head is thrown forward (trailing head has bound ADP and reduced affinity to microtubule): Trailing head swings by ~ 160 Å, net movement of dimeric kinesin is ~ 80 Å = length of one microtubule dimer ATP in new trailing head is hydr ...
lecture 21
... Dr. Lynne Quarmby in MBB studies Katanin Katanin is part of the large AAA ATPase family heterodimer consisting of 60 kDa microtubule-stimulated ATPase that requires ATP hydrolysis to disassemble microtubules, and 80 kDa subunit that targets the complex to the centrosome and regulates the activit ...
... Dr. Lynne Quarmby in MBB studies Katanin Katanin is part of the large AAA ATPase family heterodimer consisting of 60 kDa microtubule-stimulated ATPase that requires ATP hydrolysis to disassemble microtubules, and 80 kDa subunit that targets the complex to the centrosome and regulates the activit ...
Structures of GRP94-Nucleotide Complexes Reveal Mechanistic
... are created, protein-protein recognition surfaces are formed, and the chemistry of life is set in motion. Although in principle the precise three-dimensional structure for each protein is encoded in its linear chain of amino acids, in practice it is often difficult or impossible for a protein to ach ...
... are created, protein-protein recognition surfaces are formed, and the chemistry of life is set in motion. Although in principle the precise three-dimensional structure for each protein is encoded in its linear chain of amino acids, in practice it is often difficult or impossible for a protein to ach ...
Substrate targeting mechanisms
... - The ability to select a restricted set of substrates in the cell any one time -15,000+ proteins in the genome - each with many phosphorylatable sites (ser/thr, tyr) ...
... - The ability to select a restricted set of substrates in the cell any one time -15,000+ proteins in the genome - each with many phosphorylatable sites (ser/thr, tyr) ...
Asp P
... linked to histidine kinases or diguanylate cyclases (obligate anaerobes) or methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins (obligate anaerobes). Uncovering the biological function of these H-NOX domains is currently an area of intense investigation in our lab. (A) Structural features of Tt H-NOX. (B) Heme bin ...
... linked to histidine kinases or diguanylate cyclases (obligate anaerobes) or methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins (obligate anaerobes). Uncovering the biological function of these H-NOX domains is currently an area of intense investigation in our lab. (A) Structural features of Tt H-NOX. (B) Heme bin ...
ABSTRACT Cofactors are essential small molecules that
... Cofactors are essential small molecules that help catalyse a variety of enzymatic reactions. They are either inorganic (e.g., metal ions such as Mg2+, Mn2+, and Zn2+) or organic (e.g., NAD and ATP). Herein we have performed systematic studies on cofactor conformations from simple metal ions to compl ...
... Cofactors are essential small molecules that help catalyse a variety of enzymatic reactions. They are either inorganic (e.g., metal ions such as Mg2+, Mn2+, and Zn2+) or organic (e.g., NAD and ATP). Herein we have performed systematic studies on cofactor conformations from simple metal ions to compl ...
Overriding Imatinib Resistance with a Novel ABL Kinase
... To date 17 mutations, mostly within the kinase domain of BCR-ABL have been observed. ...
... To date 17 mutations, mostly within the kinase domain of BCR-ABL have been observed. ...
Anti-HSP70 Catalog# SPC- 1 78C/D Size: 25/100µg This product is
... displays multiple features of nucleotide binding proteins (4). All hsp70s, regardless of location, bind proteins, particularly unfolded ones. The molecular chaperones of the hsp70 family recognize and bind to nascent polypeptide chains as well as partially folded intermediates of proteins preventing ...
... displays multiple features of nucleotide binding proteins (4). All hsp70s, regardless of location, bind proteins, particularly unfolded ones. The molecular chaperones of the hsp70 family recognize and bind to nascent polypeptide chains as well as partially folded intermediates of proteins preventing ...
Document
... Complex II is not a proton pump. When electrons flow from FADH2 to oxygen, as catalyzed by complex II, complex III, and complex IV, fewer protons are pumped out of the matrix as compared to NADH. Thus, fewer ATP molecules are ultimately made ...
... Complex II is not a proton pump. When electrons flow from FADH2 to oxygen, as catalyzed by complex II, complex III, and complex IV, fewer protons are pumped out of the matrix as compared to NADH. Thus, fewer ATP molecules are ultimately made ...
Document
... bond to give mixed disulfide) 2) Protein SH attacks protein-PDI mixed S-S bond to give protein S-S bond 3) Continues until protein in native S-S configuration and PDI cannot bind to exposed hydrophobic patches on the protein ...
... bond to give mixed disulfide) 2) Protein SH attacks protein-PDI mixed S-S bond to give protein S-S bond 3) Continues until protein in native S-S configuration and PDI cannot bind to exposed hydrophobic patches on the protein ...
Helicase-Primase Inhibitors as Novel Anti-HSV
... LmrA contains an N-terminal membrane domain with six membrane-spanning segments followed by the ABC domain. LmrA is homologous to certain eukaryotic ABC transporters and is a halfmolecule version of the human multidrugresistance protein P-glycoprotein. To study the domain organization of LmrA, fusio ...
... LmrA contains an N-terminal membrane domain with six membrane-spanning segments followed by the ABC domain. LmrA is homologous to certain eukaryotic ABC transporters and is a halfmolecule version of the human multidrugresistance protein P-glycoprotein. To study the domain organization of LmrA, fusio ...
Neurotransmitter Transporter homologue A.Yamashita(RIKEN)
... neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft to the cytoplasm of neurons and glia catalyzed by specific transporters. Na+/Cl--dependent neurotransmitter transporters (also referred to as neurotransmitter sodium symporters; NSS) employ sodium and chloride electrochemical gradients to drive transport of ...
... neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft to the cytoplasm of neurons and glia catalyzed by specific transporters. Na+/Cl--dependent neurotransmitter transporters (also referred to as neurotransmitter sodium symporters; NSS) employ sodium and chloride electrochemical gradients to drive transport of ...
ATP-binding cassette transporter

ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC transporters) are members of a protein superfamily that is one of the largest and oldest families with representatives in all extant phyla from prokaryotes to humans. ABC transporters are transmembrane proteins that utilize the energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding and hydrolysis to carry out certain biological processes including translocation of various substrates across membranes and non-transport-related processes such as translation of RNA and DNA repair. They transport a wide variety of substrates across extra- and intracellular membranes, including metabolic products, lipids and sterols, and drugs. ABC transporters are classified as proteins based on the sequence and organization of their ATP-binding cassette (ABC) domain(s). ABC transporters are involved in tumor resistance, cystic fibrosis and a range of other inherited human diseases along with both prokaryotic and eukaryotic (including human) development of resistance to multiple drugs.