Chapter 2
... a. genes that transcribe other parts of the DNA into the RNA that makes protein. b. the amino acids that compose certain genes over evolutionary time. c. a method for detailing change in microgenetics. d. a family of pleiotropic genes. 18. The fact that individuals with William’s syndrome have sympt ...
... a. genes that transcribe other parts of the DNA into the RNA that makes protein. b. the amino acids that compose certain genes over evolutionary time. c. a method for detailing change in microgenetics. d. a family of pleiotropic genes. 18. The fact that individuals with William’s syndrome have sympt ...
Microarrays = Gene Chips
... The chip has almost 30,000 pieces of genetic material taken from thousands of different viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites – represent all recognized 1,710 vertebrate viral species and 135 bacterial, 73 fungal, and 63 parasite genera. For each family or genus at least 3 separate genomic target r ...
... The chip has almost 30,000 pieces of genetic material taken from thousands of different viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites – represent all recognized 1,710 vertebrate viral species and 135 bacterial, 73 fungal, and 63 parasite genera. For each family or genus at least 3 separate genomic target r ...
Comparative Genomics Course
... The assignment is for you to explore thoroughly a genome browser of interest to you. If you are interested in genomes that are well-supported at UCSC and Ensembl, which includes genomes of most vertebrates, then use UCSC or Ensembl. As you noticed, I have emphasized the UCSC Genome Browser because o ...
... The assignment is for you to explore thoroughly a genome browser of interest to you. If you are interested in genomes that are well-supported at UCSC and Ensembl, which includes genomes of most vertebrates, then use UCSC or Ensembl. As you noticed, I have emphasized the UCSC Genome Browser because o ...
hox genes - WordPress.com
... Now that you understand the regulatory system that controls how genes are expressed, revisit the example of wing differentiation between Drosophila and Butterflies. Explain the genes and regulatory elements involved in the development of these wings: ...
... Now that you understand the regulatory system that controls how genes are expressed, revisit the example of wing differentiation between Drosophila and Butterflies. Explain the genes and regulatory elements involved in the development of these wings: ...
DNA - heredity2
... – Target specific sequences of DNA (often a stop codon or a repeated sequence of amino acids) – Cut the chromosome into fragments which can then be analysed by their mass and electronegativity ...
... – Target specific sequences of DNA (often a stop codon or a repeated sequence of amino acids) – Cut the chromosome into fragments which can then be analysed by their mass and electronegativity ...
Document
... 14.2 - Human Genetic Disorders From Molecule to Phenotype There is a molecular reason for genetic disorders. A change in DNA can alter an amino acid sequence, which can change a protein and therefore, the phenotype. Some common inherited disorders result from a change in DNA. They include: sickle ce ...
... 14.2 - Human Genetic Disorders From Molecule to Phenotype There is a molecular reason for genetic disorders. A change in DNA can alter an amino acid sequence, which can change a protein and therefore, the phenotype. Some common inherited disorders result from a change in DNA. They include: sickle ce ...
Lecture 17 - The Eukaryotic Genome
... then it is not enough to look at one gene. To do so, we have to have the whole picture. It's like saying you want to explore Valencia and the only thing you can see is this table. You see a little rust, but that tells you nothing about Valencia other than that the air is maybe salty. That's where we ...
... then it is not enough to look at one gene. To do so, we have to have the whole picture. It's like saying you want to explore Valencia and the only thing you can see is this table. You see a little rust, but that tells you nothing about Valencia other than that the air is maybe salty. That's where we ...
comp - Imtech - Institute of Microbial Technology
... – Paralogous: duplication of gene within genome have usually different functions – Xenologous: That are related by an interspecies (horizontal gene transfer) of the genetic material, have similar function ...
... – Paralogous: duplication of gene within genome have usually different functions – Xenologous: That are related by an interspecies (horizontal gene transfer) of the genetic material, have similar function ...
Uses of Genomic Information in the Diagnosis of Disease
... distal portion of their DNA during prophase 1 of meiosis. The two homologous chromosomes break and reconnect to the different end piece. If they break at the same place in the base pair sequence, the result is an exchange of genes called genetic recombination. It could be as often as several times p ...
... distal portion of their DNA during prophase 1 of meiosis. The two homologous chromosomes break and reconnect to the different end piece. If they break at the same place in the base pair sequence, the result is an exchange of genes called genetic recombination. It could be as often as several times p ...
BB30055: Genes and genomes
... signal transduction and immune function) However, only 3 cases where a combination of 3 domain types shared by human & yeast proteins. e.g carbomyl-phosphate synthase (involved in the first 3 steps of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis) has 7 domain types, which occurs once in human and yeast but twice ...
... signal transduction and immune function) However, only 3 cases where a combination of 3 domain types shared by human & yeast proteins. e.g carbomyl-phosphate synthase (involved in the first 3 steps of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis) has 7 domain types, which occurs once in human and yeast but twice ...
RNA interference - Creighton University
... interacting with complementary sites in their 3’ untranslated regions (UTRs) • It was later appreciated that the stRNAs are processed by Dicer and thus function through related pathway • Disruption of the stRNAs, Dicer, or argonaute genes result in similar developmental abnormalities • With the subs ...
... interacting with complementary sites in their 3’ untranslated regions (UTRs) • It was later appreciated that the stRNAs are processed by Dicer and thus function through related pathway • Disruption of the stRNAs, Dicer, or argonaute genes result in similar developmental abnormalities • With the subs ...
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS
... most damage is removed and repaired, but some repair is inaccurate. ...
... most damage is removed and repaired, but some repair is inaccurate. ...
Systematic Implications of DNA variation in subfamily Opuntioideae
... - Possibly greater assurance of homology with molecular data (less likely to misinterpret characters) but homoplasy happens! - Principal advantages are the much greater number of molecular characters available & greater comparability across lineages ...
... - Possibly greater assurance of homology with molecular data (less likely to misinterpret characters) but homoplasy happens! - Principal advantages are the much greater number of molecular characters available & greater comparability across lineages ...
genome that an organism carries in its DNA. analysis of chromosomes.
... effort to sequence all 3 billion base pairs of human DNA. • Other important goals included sequencing the genomes of model organisms to compare to human DNA, developing technology to support the research, exploring gene functions, studying human variation, and training future scientists. • Today, mu ...
... effort to sequence all 3 billion base pairs of human DNA. • Other important goals included sequencing the genomes of model organisms to compare to human DNA, developing technology to support the research, exploring gene functions, studying human variation, and training future scientists. • Today, mu ...
Applying Our Knowledge of Genetics
... • Gene therapy involves the insertion of a properly working gene into a patient that has a faulty gene in hopes that the new, healthy gene could be used to cure the disorder. • A vector, or DNA delivery system, would need to be used to insert the “foreign” DNA into the patient’s cells. • Some vector ...
... • Gene therapy involves the insertion of a properly working gene into a patient that has a faulty gene in hopes that the new, healthy gene could be used to cure the disorder. • A vector, or DNA delivery system, would need to be used to insert the “foreign” DNA into the patient’s cells. • Some vector ...
slides
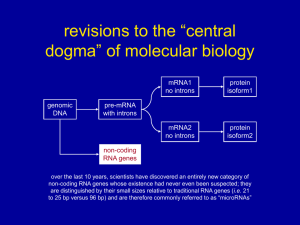
... – Introns (intervening sequences) are regions of the iniFal RNA transcript that are not expressed in the amino acid sequence of the protein. – Introns are removed by splicing and the exons (expressed) ar ...
... – Introns (intervening sequences) are regions of the iniFal RNA transcript that are not expressed in the amino acid sequence of the protein. – Introns are removed by splicing and the exons (expressed) ar ...
Voices - Indiana University Bloomington
... types and organisms. The picture that emerges from these studies elucidates the astounding degree to which our genome, including the repetitive regions derived from transposon elements, appears to be dynamically utilized for the purposes of gene regulation. The human ENCODE project alone mapped near ...
... types and organisms. The picture that emerges from these studies elucidates the astounding degree to which our genome, including the repetitive regions derived from transposon elements, appears to be dynamically utilized for the purposes of gene regulation. The human ENCODE project alone mapped near ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... A. alteration of chromatin structure in association with transcription. B. a process that only bacteria perform since they contain no nucleus. C. a process that is exclusively associated with transcription by RNA polymerase III in eukaryotes. D. alteration in chromatin structure to facilitate loadin ...
... A. alteration of chromatin structure in association with transcription. B. a process that only bacteria perform since they contain no nucleus. C. a process that is exclusively associated with transcription by RNA polymerase III in eukaryotes. D. alteration in chromatin structure to facilitate loadin ...
Recombination is the principal source of variation in asexually
... 60. Triploid watermelons are derived from crosses of tetraploid x diploid parents. a) T b) F 61. The cultivated banana is triploid and sterile. Which of the following is the most likely source of genetic variation in this species? a) Mutation b) Recombination 62. The fact that there can be up to fo ...
... 60. Triploid watermelons are derived from crosses of tetraploid x diploid parents. a) T b) F 61. The cultivated banana is triploid and sterile. Which of the following is the most likely source of genetic variation in this species? a) Mutation b) Recombination 62. The fact that there can be up to fo ...
scientists and philosophers find that gene has a multitude of meanings
... guanine, adenine, thymine and cytosine, which are read by the cell when genes are active. Intron A segment of a protein-coding gene that is edited out of an RNA transcript. Noncoding RNA Molecules of RNA produced from DNA that are not used to produce proteins. Protein A molecule (like collagen or he ...
... guanine, adenine, thymine and cytosine, which are read by the cell when genes are active. Intron A segment of a protein-coding gene that is edited out of an RNA transcript. Noncoding RNA Molecules of RNA produced from DNA that are not used to produce proteins. Protein A molecule (like collagen or he ...
Slide 1
... A construct that consists of chloroplast sequences (C and D) that flank two selectable marker genes is inserted into the chloroplast genome through homologous recombination, thereby transforming the native plastome into a TRANSPLASTOME (a). One of the selectable genes (aadA) is designed for exclusiv ...
... A construct that consists of chloroplast sequences (C and D) that flank two selectable marker genes is inserted into the chloroplast genome through homologous recombination, thereby transforming the native plastome into a TRANSPLASTOME (a). One of the selectable genes (aadA) is designed for exclusiv ...
lecture24_RnaInterfe.. - University of Alberta
... silencing was achieved by injecting C. elegans with ssRNAs, but potent and specific silencing was achieved by injecting a sense-antisense mixture; in other words it is the dsRNAs that matter ...
... silencing was achieved by injecting C. elegans with ssRNAs, but potent and specific silencing was achieved by injecting a sense-antisense mixture; in other words it is the dsRNAs that matter ...
Functional genomics and drug discovery: use of alternative model
... correlates of the patterns embedded in these sequences. Large number of studies have shown that protein sequences and their basic functions are conserved amongst various species of animals. The application of molecular genetics to study animal development has also revealed striking conservation of d ...
... correlates of the patterns embedded in these sequences. Large number of studies have shown that protein sequences and their basic functions are conserved amongst various species of animals. The application of molecular genetics to study animal development has also revealed striking conservation of d ...
Transposable element
A transposable element (TE or transposon) is a DNA sequence that can change its position within the genome, sometimes creating or reversing mutations and altering the cell's genome size. Transposition often results in duplication of the TE. Barbara McClintock's discovery of these jumping genes earned her a Nobel prize in 1983.TEs make up a large fraction of the C-value of eukaryotic cells. There are at least two classes of TEs: class I TEs generally function via reverse transcription, while class II TEs encode the protein transposase, which they require for insertion and excision, and some of these TEs also encode other proteins. It has been shown that TEs are important in genome function and evolution. In Oxytricha, which has a unique genetic system, they play a critical role in development. They are also very useful to researchers as a means to alter DNA inside a living organism.