Assessing evolutionary relationships among
... analysis (such as the identification of recent gene duplications [6•]). Best match approaches are limited, however, because sequence similarity is not a perfect indicator of evolutionary relatedness [15]. For example, the high level of similarity between thermophilic Bacteria and Archaea could be du ...
... analysis (such as the identification of recent gene duplications [6•]). Best match approaches are limited, however, because sequence similarity is not a perfect indicator of evolutionary relatedness [15]. For example, the high level of similarity between thermophilic Bacteria and Archaea could be du ...
Comparative mapping in cattle of genes located on human
... TTR, using somatic cell genetics and linkage analysis in the International Bovine Reference Panel (IBRP). Oligonucleotide primers for PCR were designed on the basis of the published nucleotide sequences of sheep or cattle genes ADCYAP1, CDH2, CYB5, DSC2, FECH, NDUFV2 and TTR, and were used to amplif ...
... TTR, using somatic cell genetics and linkage analysis in the International Bovine Reference Panel (IBRP). Oligonucleotide primers for PCR were designed on the basis of the published nucleotide sequences of sheep or cattle genes ADCYAP1, CDH2, CYB5, DSC2, FECH, NDUFV2 and TTR, and were used to amplif ...
Chapter 12 Section 12_1 DNA
... Molecular Cause of Transformation • In 1944, a group of scientists led by Oswald Avery wanted to learn which ...
... Molecular Cause of Transformation • In 1944, a group of scientists led by Oswald Avery wanted to learn which ...
Human Genome Project
... Human Genome Project Goals: ■ identify all the approximate 30,000 genes in human DNA, ■ determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA, ■ store this information in databases, ■ improve tools for data analysis, ■ transfer related technologies to the private secto ...
... Human Genome Project Goals: ■ identify all the approximate 30,000 genes in human DNA, ■ determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA, ■ store this information in databases, ■ improve tools for data analysis, ■ transfer related technologies to the private secto ...
Document
... Human Genome Project Goals: ■ identify all the approximate 30,000 genes in human DNA, ■ determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA, ■ store this information in databases, ■ improve tools for data analysis, ■ transfer related technologies to the private secto ...
... Human Genome Project Goals: ■ identify all the approximate 30,000 genes in human DNA, ■ determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA, ■ store this information in databases, ■ improve tools for data analysis, ■ transfer related technologies to the private secto ...
Nedchromosnotes2jan2014NED 20 KB
... condition refer to what? Important terms you need to and should know but I do not have time to redefine because they should be hardwired by now are haploid, diploid, nucleosome, chromatin, histone, centromere, telomere, homologues, chromatids. Bacterial genomes = 4.6 Mb = 4.6 x 10^6 bp Human genome ...
... condition refer to what? Important terms you need to and should know but I do not have time to redefine because they should be hardwired by now are haploid, diploid, nucleosome, chromatin, histone, centromere, telomere, homologues, chromatids. Bacterial genomes = 4.6 Mb = 4.6 x 10^6 bp Human genome ...
Shark Fin Forensics
... fins. To do this, open the first unknown sequence (click on the ATCG icon), click on the sequence to highlight it, then right-click and select "copy data." Now, open the great white sequence, click in the empty white space below the sequence, and then right-click (or ctrl-click) "paste" to paste the ...
... fins. To do this, open the first unknown sequence (click on the ATCG icon), click on the sequence to highlight it, then right-click and select "copy data." Now, open the great white sequence, click in the empty white space below the sequence, and then right-click (or ctrl-click) "paste" to paste the ...
File
... 2. understand why the stop codons in vertebrate mitochondrial protein-coding genes different than the stop codons found nuclear RNA 3. explain why it is necessary to translate all three reading frames of the COI amplicon when looking for stop codons 4. understand the following steps: a.
... 2. understand why the stop codons in vertebrate mitochondrial protein-coding genes different than the stop codons found nuclear RNA 3. explain why it is necessary to translate all three reading frames of the COI amplicon when looking for stop codons 4. understand the following steps: a.
Microbial Diversity in Prince Edward County`s Soil Microbiome
... thousands of types of microbial bacteria that inhabit many different habitats and environments. New types of microbial bacteria are often discovered, so there is a lot about it that scientists are unsure of. Microbial bacteria play an important role in the ecosystems they inhabit, as well as indicat ...
... thousands of types of microbial bacteria that inhabit many different habitats and environments. New types of microbial bacteria are often discovered, so there is a lot about it that scientists are unsure of. Microbial bacteria play an important role in the ecosystems they inhabit, as well as indicat ...
221_exam_5_2003
... ____ Newly discovered antibiotics are tested for inhibitory activity against different types of microorganisms because A. B. C. D. ...
... ____ Newly discovered antibiotics are tested for inhibitory activity against different types of microorganisms because A. B. C. D. ...
learning_goals_objectives
... 2. understand why the stop codons in vertebrate mitochondrial protein-coding genes different than the stop codons found nuclear RNA 3. explain why it is necessary to translate all three reading frames of the COI amplicon when looking for stop codons 4. understand the following steps: a.
... 2. understand why the stop codons in vertebrate mitochondrial protein-coding genes different than the stop codons found nuclear RNA 3. explain why it is necessary to translate all three reading frames of the COI amplicon when looking for stop codons 4. understand the following steps: a.
(P) BioSafety Policy - Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences
... modification and genetic engineering. Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) are organisms in which the DNA from another genus (or higher taxonomic level) has been inserted into an organism in a laboratory. Genetically Engineered (GE) organisms are strains which have been genetically-altered in the l ...
... modification and genetic engineering. Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) are organisms in which the DNA from another genus (or higher taxonomic level) has been inserted into an organism in a laboratory. Genetically Engineered (GE) organisms are strains which have been genetically-altered in the l ...
Matlab Bioinfo Toolbox QuickGuide
... MathWorks. It features a family of add-on application-specific solutions called toolboxes (i.e., comprehensive collections of functions) that extend the MATLAB environment to solve particular classes of problems. Bioinformatics Toolbox offers an integrated software environment for genome and proteom ...
... MathWorks. It features a family of add-on application-specific solutions called toolboxes (i.e., comprehensive collections of functions) that extend the MATLAB environment to solve particular classes of problems. Bioinformatics Toolbox offers an integrated software environment for genome and proteom ...
Horizontal gene transfer of antimicrobial
... bacteria exchange AMR genes with other bacteria by horizontal gene transfer mechanisms – “bacterial sex”. Our recent studies have suggested that the important AMR pathogen methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) acquires AMR genes at very high frequency as it colonizes the host, but also ...
... bacteria exchange AMR genes with other bacteria by horizontal gene transfer mechanisms – “bacterial sex”. Our recent studies have suggested that the important AMR pathogen methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) acquires AMR genes at very high frequency as it colonizes the host, but also ...
LEQ: How do we splice new genes into DNA?
... transcriptase & fluorescent nucleotides are added cDNA is made from RNA cDNA is applied to well that contain DNA from a cell; cDNA will bind to DNA that is complementary in the wells Rinse unbound cDNA – fluorescent spots show DNA that is being expressed by the cell; no glow = unexpressed DNA ...
... transcriptase & fluorescent nucleotides are added cDNA is made from RNA cDNA is applied to well that contain DNA from a cell; cDNA will bind to DNA that is complementary in the wells Rinse unbound cDNA – fluorescent spots show DNA that is being expressed by the cell; no glow = unexpressed DNA ...
Microbial Genetics
... Mediated by a bacterial virus (bacteriophage or phage) DNA from the donor is transferred to the recipient inside the phage particle Two types of transduction ...
... Mediated by a bacterial virus (bacteriophage or phage) DNA from the donor is transferred to the recipient inside the phage particle Two types of transduction ...
Microbial Ecology: Where are we now?
... Consequently, focus was turned towards development of molecular approaches for understanding these complex communities, eliminating the need for culturing beforehand. Dawn of a new era began with the innovation of NGS technologies, which revolutionized the existing gold standard techniques of microb ...
... Consequently, focus was turned towards development of molecular approaches for understanding these complex communities, eliminating the need for culturing beforehand. Dawn of a new era began with the innovation of NGS technologies, which revolutionized the existing gold standard techniques of microb ...
3D structures of RNA
... RNA on the other hand, can have as diverse structures as proteins, as well as simple double helix of type A. The ability of being both informational and diverse in structure suggests that RNA was the prebiotic molecule that could function in both replication and ...
... RNA on the other hand, can have as diverse structures as proteins, as well as simple double helix of type A. The ability of being both informational and diverse in structure suggests that RNA was the prebiotic molecule that could function in both replication and ...
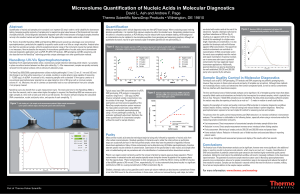
Microvolume Quantification of Nucleic Acids in Molecular Diagnostics
... The time and financial costs of failed sample analyses can be significant. QC of template quantity means that delays caused by failed nucleic acid extractions are limited to the time required to re-extract samples, which is typically less than an hour. However, if failed DNA extractions are not iden ...
... The time and financial costs of failed sample analyses can be significant. QC of template quantity means that delays caused by failed nucleic acid extractions are limited to the time required to re-extract samples, which is typically less than an hour. However, if failed DNA extractions are not iden ...
Promoter Analysis for Intestinally
... Cele_RSAT_filt_motifsampler.GIF c. Observations i. Lots of overlap between MotifSampler and RSAT predictions ii. RSAT finds all occurrences of a given sequence, while MotifSampler only finds some of them and ignores others ...
... Cele_RSAT_filt_motifsampler.GIF c. Observations i. Lots of overlap between MotifSampler and RSAT predictions ii. RSAT finds all occurrences of a given sequence, while MotifSampler only finds some of them and ignores others ...
Document
... Matt Pratola, Kelly Burkett, Mercedeh Ghadessi, Brad McNeney, Jinko Graham and Denise Daley ...
... Matt Pratola, Kelly Burkett, Mercedeh Ghadessi, Brad McNeney, Jinko Graham and Denise Daley ...
Gene Prediction Gene Prediction Genes Prokaryotic
... • Gene Desert - a region with no known, novel, or partial genes in a 500 kb ...
... • Gene Desert - a region with no known, novel, or partial genes in a 500 kb ...
omicsjcpresentation2-6
... whatever the classifier type, is that the samples used for validation must not have been used in any way before being tested. Most importantly, the outcome information of the tested samples must not have been used for developing the classifier or in steps before classifier development”. ...
... whatever the classifier type, is that the samples used for validation must not have been used in any way before being tested. Most importantly, the outcome information of the tested samples must not have been used for developing the classifier or in steps before classifier development”. ...
Chapter 3
... Exons are usually short, typically coding for 100 amino acids. Introns are short in lower eukaryotes, but range up to several 10s of kb in length in higher eukaryotes. The overall length of a gene is determined largely by its introns. ...
... Exons are usually short, typically coding for 100 amino acids. Introns are short in lower eukaryotes, but range up to several 10s of kb in length in higher eukaryotes. The overall length of a gene is determined largely by its introns. ...
Sequence Analysis
... Here we consider the access and analysis of data and information items rather than their generation, storage or annotation ...
... Here we consider the access and analysis of data and information items rather than their generation, storage or annotation ...
Metagenomics

Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental samples. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics or community genomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods. Recent studies use either ""shotgun"" or PCR directed sequencing to get largely unbiased samples of all genes from all the members of the sampled communities. Because of its ability to reveal the previously hidden diversity of microscopic life, metagenomics offers a powerful lens for viewing the microbial world that has the potential to revolutionize understanding of the entire living world. As the price of DNA sequencing continues to fall, metagenomics now allows microbial ecology to be investigated at a much greater scale and detail than before.