centripetal force - Batesville Community School
... moving in a circle also have a rotational or angular velocity, which is the rate angular position changes. Rotational velocity is measured in degrees/second, rotations/minute (rpm), etc. Common symbol, w (Greek letter omega) ...
... moving in a circle also have a rotational or angular velocity, which is the rate angular position changes. Rotational velocity is measured in degrees/second, rotations/minute (rpm), etc. Common symbol, w (Greek letter omega) ...
11. Two blocks of masses m and 3m are placed on a frictionless
... 75. Two gliders are set in motion on a horizontal air track. A spring of force constant k is attached to the back end of the second glider. As shown in Figure P9.75, the first glider, of mass m1, moves to the right with speed υ1, and the second glider, of mass m2, moves more slowly to the right with ...
... 75. Two gliders are set in motion on a horizontal air track. A spring of force constant k is attached to the back end of the second glider. As shown in Figure P9.75, the first glider, of mass m1, moves to the right with speed υ1, and the second glider, of mass m2, moves more slowly to the right with ...
AIM: Force and Motion Ideas An object`s position can be described
... The distance an object travels is the length of the actual path it takes from its starting position to its ending position. Objects may travel different distances between the same starting and ending points. The average speed of an object (as opposed to its speed at a particular instant) is defi ...
... The distance an object travels is the length of the actual path it takes from its starting position to its ending position. Objects may travel different distances between the same starting and ending points. The average speed of an object (as opposed to its speed at a particular instant) is defi ...
Physics - The Crowned Anarchist Literature and Science Fiction
... and velocity of a body are given, subsequent positions and velocities can be computed, although the force may vary with time or position; in the latter case, Newton's calculus must be applied. This simple law contained another important aspect: Each body has an ...
... and velocity of a body are given, subsequent positions and velocities can be computed, although the force may vary with time or position; in the latter case, Newton's calculus must be applied. This simple law contained another important aspect: Each body has an ...
vectors and motion
... from a height we know that its speed increases as it falls. • The increase in speed is due to the acceleration gravity, g = 9.8 m/sec2. ...
... from a height we know that its speed increases as it falls. • The increase in speed is due to the acceleration gravity, g = 9.8 m/sec2. ...
net force
... • It is the law which explains how things move • If a net force is applied to an object it will accelerate – change its velocity • It includes the law of inertia if there is no force F = 0, then accel = 0 the velocity doesn’t change no force is needed to keep an object moving with constant vel ...
... • It is the law which explains how things move • If a net force is applied to an object it will accelerate – change its velocity • It includes the law of inertia if there is no force F = 0, then accel = 0 the velocity doesn’t change no force is needed to keep an object moving with constant vel ...
Chapter 2: Two Dimensional Motion
... 14) A Corey in danger of drowning in a river is being carried downstream by a current that flows uniformly with a speed of 5 km/h. Corey is 0.12 km from shore and 0.16 km upstream of a hovercraft landing when a rescue hovercraft sets out. (a) If the rescue hovercraft proceeds at its maximum speed of ...
... 14) A Corey in danger of drowning in a river is being carried downstream by a current that flows uniformly with a speed of 5 km/h. Corey is 0.12 km from shore and 0.16 km upstream of a hovercraft landing when a rescue hovercraft sets out. (a) If the rescue hovercraft proceeds at its maximum speed of ...
The main difference between scalars and
... ● Free fall is vertical (up and/or down) motion of a body where gravitational force is the only force acting upon it. (when air resistance can be ignored). Gravitational force gives all bodies regardless of mass or shape, the same acceleration when air resistance can be ignored. For an object in fre ...
... ● Free fall is vertical (up and/or down) motion of a body where gravitational force is the only force acting upon it. (when air resistance can be ignored). Gravitational force gives all bodies regardless of mass or shape, the same acceleration when air resistance can be ignored. For an object in fre ...
Physics - USM-Rocks
... velocity of a body are given, subsequent positions and velocities can be computed, although the force may vary with time or position; in the latter case, Newton's calculus must be applied. This simple law contained another important aspect: Each body has an inherent property, its inertial mass, whic ...
... velocity of a body are given, subsequent positions and velocities can be computed, although the force may vary with time or position; in the latter case, Newton's calculus must be applied. This simple law contained another important aspect: Each body has an inherent property, its inertial mass, whic ...
Document
... Of the three graphs, the velocity-time graph is the most versatile because each main feature holds special significance: the area beneath the graph represents the change in displacement the tangent at any point on the graph gives the instantaneous acceleration. 1. A ball, thrown vertically upwar ...
... Of the three graphs, the velocity-time graph is the most versatile because each main feature holds special significance: the area beneath the graph represents the change in displacement the tangent at any point on the graph gives the instantaneous acceleration. 1. A ball, thrown vertically upwar ...
Unit 6: Motion and Forces
... Analyze the motion of an object in terms of its position, velocity and acceleration as functions of time Solve problems involving distance, velocity, speed and acceleration Create and interpret graphs ...
... Analyze the motion of an object in terms of its position, velocity and acceleration as functions of time Solve problems involving distance, velocity, speed and acceleration Create and interpret graphs ...
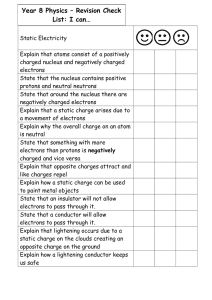
Year 8 Physics Revision Checklist1.02 MB
... Explain why air is a good insulator Explain why air will not prevent heat transfer via radiation Calculating the speed of an EM wave: A laser (red light) is shone up to a satellite that is orbiting 35786km above the Earth, and the time taken for the laser to reflect back onto a receiver on Earth is ...
... Explain why air is a good insulator Explain why air will not prevent heat transfer via radiation Calculating the speed of an EM wave: A laser (red light) is shone up to a satellite that is orbiting 35786km above the Earth, and the time taken for the laser to reflect back onto a receiver on Earth is ...
Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
... • Newtons Law of Universal Gravitation: If two particles with masses m1 and m2 are separated by a distance r, then a gravitational force acts along a line joining them with the magnitude : F=G( m1m2/ r2) G=6.673x10-11kg-1m3s-2 is constant of universal gravitation F- always an attractive force ...
... • Newtons Law of Universal Gravitation: If two particles with masses m1 and m2 are separated by a distance r, then a gravitational force acts along a line joining them with the magnitude : F=G( m1m2/ r2) G=6.673x10-11kg-1m3s-2 is constant of universal gravitation F- always an attractive force ...
Motion - ILM.COM.PK
... If acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects, regardless of mass, then all objects should fall at the same rate. Does a leaf fall as fast as an acorn? ...
... If acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects, regardless of mass, then all objects should fall at the same rate. Does a leaf fall as fast as an acorn? ...