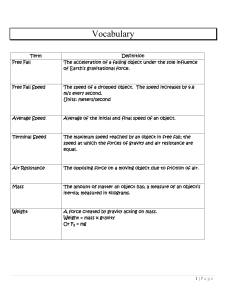
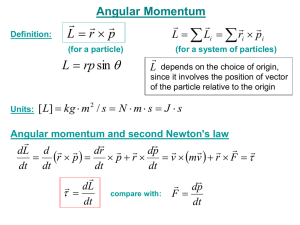
Sect. 7.4 - TTU Physics
... done on the particle in moving it from position 1 to position 2 in space is defined as the line integral (ds = differential path length) (assume mass m = constant) W12 ∫Fds (limits: from 1 to 2) • We also have the work-energy principle, which tells us that W12 ∫Fds T2 - T1 = T ...
... done on the particle in moving it from position 1 to position 2 in space is defined as the line integral (ds = differential path length) (assume mass m = constant) W12 ∫Fds (limits: from 1 to 2) • We also have the work-energy principle, which tells us that W12 ∫Fds T2 - T1 = T ...
Galileo Galili Essay, Research Paper email: triaxxxxx@aol
... time from different angles. One was pulled back about 5 degrees while the other was released from about 45 degrees. The pendulum pulled back five degrees was allowed to travel through thirty cycles, and the numbers of complete swings of the other pendulum during this time were counted.The pendulum w ...
... time from different angles. One was pulled back about 5 degrees while the other was released from about 45 degrees. The pendulum pulled back five degrees was allowed to travel through thirty cycles, and the numbers of complete swings of the other pendulum during this time were counted.The pendulum w ...
Horizontal Motion
... • a projectile is any object upon which the only force acting upon it is gravity, • projectiles travel with a parabolic trajectory due to the influence of gravity, • there are no horizontal forces acting upon projectiles and thus no horizontal acceleration, • the horizontal velocity of a projectile ...
... • a projectile is any object upon which the only force acting upon it is gravity, • projectiles travel with a parabolic trajectory due to the influence of gravity, • there are no horizontal forces acting upon projectiles and thus no horizontal acceleration, • the horizontal velocity of a projectile ...
Gravity, Not Mass Increases with Velocity
... harder it becomes to pull it toward earth. So the gravitational force required must be stronger. This, until an object recedes at a speed close to the velocity of light © where the force required is almost infinite. For an object approaching earth, its inertial force is in the same direction as the ...
... harder it becomes to pull it toward earth. So the gravitational force required must be stronger. This, until an object recedes at a speed close to the velocity of light © where the force required is almost infinite. For an object approaching earth, its inertial force is in the same direction as the ...
Acceleration Due to Gravity
... For a conservative system, the total amount of energy remains constant. In our setup, only forces in the vertical direction come into play (neglect air resistance). At the beginning of the experiment, the object is fixed at a specified distance above some base level (e.g. the ground). At the startin ...
... For a conservative system, the total amount of energy remains constant. In our setup, only forces in the vertical direction come into play (neglect air resistance). At the beginning of the experiment, the object is fixed at a specified distance above some base level (e.g. the ground). At the startin ...
3rd Six Weeks Review
... b) example: we pull down on a pulley and this makes the object easier to lift (uses less effort on our part) we apply. Rather than pulling up, we pull down. This makes it easier to lift an object. b) examples: A pulley helps us lift objects – raising a flag on a flag pole, raising or lowering window ...
... b) example: we pull down on a pulley and this makes the object easier to lift (uses less effort on our part) we apply. Rather than pulling up, we pull down. This makes it easier to lift an object. b) examples: A pulley helps us lift objects – raising a flag on a flag pole, raising or lowering window ...
Document
... A gun carrier M moves on a frictionless incline, its speed reduces from v to 0 after shooting a canon-ball m in the horizontal direction. Is the total momentum of system (M and m) conserved in this process, and why? Find out the speed of canon-ball. ...
... A gun carrier M moves on a frictionless incline, its speed reduces from v to 0 after shooting a canon-ball m in the horizontal direction. Is the total momentum of system (M and m) conserved in this process, and why? Find out the speed of canon-ball. ...
Induction Generators
... The interaction of the magnetic flux of the stator and the magnetic flux of the rotor produce a “countertorque” that opposes the driving torque of the prime mover. Increasing the speed of the rotor increases the countertorque and the power delivered to the system by the generator. The maximum value ...
... The interaction of the magnetic flux of the stator and the magnetic flux of the rotor produce a “countertorque” that opposes the driving torque of the prime mover. Increasing the speed of the rotor increases the countertorque and the power delivered to the system by the generator. The maximum value ...
Lecture Three (Powerpoint format)
... The Darker Side of Isaac Newton Newton was a highly complex individual -- besides his fundamental work on motion and optics, he also pursued extensive research in alchemy and bible studies. As President of the Royal Society, he has the Royal Astronomer Flamsteed’s star catalog seized and publis ...
... The Darker Side of Isaac Newton Newton was a highly complex individual -- besides his fundamental work on motion and optics, he also pursued extensive research in alchemy and bible studies. As President of the Royal Society, he has the Royal Astronomer Flamsteed’s star catalog seized and publis ...
centripetal force
... What will be the rotational and tangential speed of a penny placed at 3 cm away from the center? ...
... What will be the rotational and tangential speed of a penny placed at 3 cm away from the center? ...
Chapter 7
... The escape speed is the speed needed for an object to soar off into space and not return 2GME v esc RE For the earth, vesc is about 11.2 km/s Note, v is independent of the mass of the object ...
... The escape speed is the speed needed for an object to soar off into space and not return 2GME v esc RE For the earth, vesc is about 11.2 km/s Note, v is independent of the mass of the object ...
Physics 107 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #7
... 16 A 55-kg swimmer is standing on a stationary 210-kg floating raft. The swimmer then runs off the raft horizontally with a velocity of +4.6 m/s relative to the shore. Find the recoil velocity that the raft would have if there were no friction and resistance due to the water. *19 To view an interact ...
... 16 A 55-kg swimmer is standing on a stationary 210-kg floating raft. The swimmer then runs off the raft horizontally with a velocity of +4.6 m/s relative to the shore. Find the recoil velocity that the raft would have if there were no friction and resistance due to the water. *19 To view an interact ...
Document
... – A coord system fixed on the Earth is accelerating (Earth’s rotation + orbital motion) & is thus non-inertial! – For many problems, this is not important. For some, we cannot ignore it! ...
... – A coord system fixed on the Earth is accelerating (Earth’s rotation + orbital motion) & is thus non-inertial! – For many problems, this is not important. For some, we cannot ignore it! ...
Days 11-12 (Work/Energy Review)
... 17. A 6 kg block moving to the right at 10 m/s collides head on with a 4 kg block moving to the left at 8 m/s. After they hit, the 4 kg block is moving to the right at 10 m/s. Determine the final velocity of the 6 kg block after the collision (using the conservation of momentum). 18. Was the collisi ...
... 17. A 6 kg block moving to the right at 10 m/s collides head on with a 4 kg block moving to the left at 8 m/s. After they hit, the 4 kg block is moving to the right at 10 m/s. Determine the final velocity of the 6 kg block after the collision (using the conservation of momentum). 18. Was the collisi ...
Tutorial 8 Angular Momentum and Planar Kinematics
... forces are neglected, what velocity will it attain? The booster has two stages whose total mass is 9000 kg. Eighty percent of the mass of each stage is fuel, and the exhaust velocity of each stage is 1200 m/s. When the fuel of stage 1 is expended, it is discarded and the motor of stage 2 is ignited. ...
... forces are neglected, what velocity will it attain? The booster has two stages whose total mass is 9000 kg. Eighty percent of the mass of each stage is fuel, and the exhaust velocity of each stage is 1200 m/s. When the fuel of stage 1 is expended, it is discarded and the motor of stage 2 is ignited. ...
AP Physics 1- Circular Motion and Rotation Practice Problems FACT
... Q4. An object of mass 5 kg moves at a constant speed of 6 m/s in a circular path of radius 2 m. Find the object’s acceleration and the net force responsible for the motion. Q5. A 10.0 kg mass is attached to a string that has a breaking strength of 200N. If the mass is whirled in a horizontal circle ...
... Q4. An object of mass 5 kg moves at a constant speed of 6 m/s in a circular path of radius 2 m. Find the object’s acceleration and the net force responsible for the motion. Q5. A 10.0 kg mass is attached to a string that has a breaking strength of 200N. If the mass is whirled in a horizontal circle ...
ACTIVITY: Objective 1: Identifying Common Simple and Compound
... refer to this outward force as ___________________________ force. Centrifugal means __________________________________ or away from the center. When the string breaks, the whirling can moves in a __________________, tangent to—NOT _____________________ from the center of—its circular path. The pictu ...
... refer to this outward force as ___________________________ force. Centrifugal means __________________________________ or away from the center. When the string breaks, the whirling can moves in a __________________, tangent to—NOT _____________________ from the center of—its circular path. The pictu ...
We can then look at a particular
... Gravity is constantly pulling downward. If you throw a ball up, it will be decelerated by gravity. As the ball moves upward, gravity will cause its speed to decrease by 9.8m/s each second. If an object is moving downward, it will be accelerated by gravity. Its speed, v, will increase by 9.8 m/s eac ...
... Gravity is constantly pulling downward. If you throw a ball up, it will be decelerated by gravity. As the ball moves upward, gravity will cause its speed to decrease by 9.8m/s each second. If an object is moving downward, it will be accelerated by gravity. Its speed, v, will increase by 9.8 m/s eac ...
lecture23
... speed is v2. What is the angular speed ω of the stick after the collision? External forces: weight of the stick and force on the stick by the pivoting axle produce no torque. Weight of the bullet is negligible. ...
... speed is v2. What is the angular speed ω of the stick after the collision? External forces: weight of the stick and force on the stick by the pivoting axle produce no torque. Weight of the bullet is negligible. ...