File
... 7. A car starts from rest and accelerates 6 m/s2 for 5 s after which it travels with a constant velocity for 9 s. The brakes are then applied so that it decelerates at 4 m/s2. Find the total distance traveled by the car. 8. An object starts from rest and accelerates 4 m/s2. a) How far will it travel ...
... 7. A car starts from rest and accelerates 6 m/s2 for 5 s after which it travels with a constant velocity for 9 s. The brakes are then applied so that it decelerates at 4 m/s2. Find the total distance traveled by the car. 8. An object starts from rest and accelerates 4 m/s2. a) How far will it travel ...
Concept Summary
... o Acceleration changes the velocity (in magnitude, direction, or both). o Acceleration can speed you up or slow you down (often called deceleration). o Constant velocity means the acceleration is zero and visa versa. o Average acceleration = change in velocity/elapsed time vector quantity = magnit ...
... o Acceleration changes the velocity (in magnitude, direction, or both). o Acceleration can speed you up or slow you down (often called deceleration). o Constant velocity means the acceleration is zero and visa versa. o Average acceleration = change in velocity/elapsed time vector quantity = magnit ...
Document
... during which of the 4 seconds does the ball’s speed increase the most? • If you drop a ball from a height of 4.9 m, it will hit the ground 1 s later. If you fire a bullet exactly horizontally from a height of 4.9 m, it will also hit the ground exactly 1 s later. Explain. • If a golf ball and a bowli ...
... during which of the 4 seconds does the ball’s speed increase the most? • If you drop a ball from a height of 4.9 m, it will hit the ground 1 s later. If you fire a bullet exactly horizontally from a height of 4.9 m, it will also hit the ground exactly 1 s later. Explain. • If a golf ball and a bowli ...
RevfinQans
... 2. You know the acceleration of a particle at all times. What do you know about the direction of the velocity of the particle? Green: You know nothing about the direction of the velocity. Yellow: You know that the direction of the velocity is either parallel to or anti-parallel to the direction of t ...
... 2. You know the acceleration of a particle at all times. What do you know about the direction of the velocity of the particle? Green: You know nothing about the direction of the velocity. Yellow: You know that the direction of the velocity is either parallel to or anti-parallel to the direction of t ...
Unit 1 Problem Set
... Earth? Repeat for Jupiter, where g is 2.64 times that on Earth. Find the mass of the bag of sugar in kilograms at each of the three locations. 2. A freight train has a mass of 1.5 x 107 kg. If the locomotive can exert a constant pull of 7.5 x 105 N, how long does it take to increase the speed of the ...
... Earth? Repeat for Jupiter, where g is 2.64 times that on Earth. Find the mass of the bag of sugar in kilograms at each of the three locations. 2. A freight train has a mass of 1.5 x 107 kg. If the locomotive can exert a constant pull of 7.5 x 105 N, how long does it take to increase the speed of the ...
Simulation Tools for Passive Waveguides
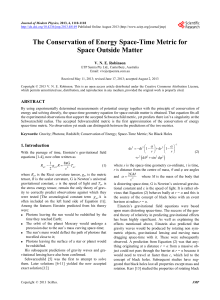
... the transformations of special relativity as well as the quantum field theory of electrodynamics ...
... the transformations of special relativity as well as the quantum field theory of electrodynamics ...
Chapter 7 Motion
... • An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
... • An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
Circular Motion Review
... a horizontal circle at a constant speed of 10. meters per second. If the magnitude of the force applied to the string by the student's hand is increased, the magnitude of the acceleration of the ball in its circular path will A. decrease B. increase C. remain the same ...
... a horizontal circle at a constant speed of 10. meters per second. If the magnitude of the force applied to the string by the student's hand is increased, the magnitude of the acceleration of the ball in its circular path will A. decrease B. increase C. remain the same ...
Laws of Motion
... Newton placed the first law of motion to establish frames of reference for which the other laws are applicable. The first law of motion postulates the existence of at least one frame of reference called a Newtonian or inertial reference frame, relative to which the motion of a particle not subject t ...
... Newton placed the first law of motion to establish frames of reference for which the other laws are applicable. The first law of motion postulates the existence of at least one frame of reference called a Newtonian or inertial reference frame, relative to which the motion of a particle not subject t ...