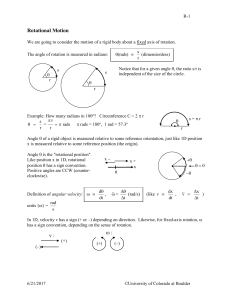
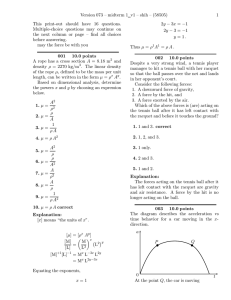
Causes of circular motion
... a rigid object is located along the line for which it will balance. As shown below, when gravity is the only force acting on a rotating object, it will rotate around its center of mass (technically that point would be the object’s center of gravity, but for this book you can treat center of mass and ...
... a rigid object is located along the line for which it will balance. As shown below, when gravity is the only force acting on a rotating object, it will rotate around its center of mass (technically that point would be the object’s center of gravity, but for this book you can treat center of mass and ...
Recitation
... (c) The original kinetic energy was converted into thermal energy by the negative work of friction. Reflect: To stop the car friction must do negative work equal in magnitude to the initial kinetic energy of the car. 7-21 You throw a 20 N rock into the air from ground level and observe that, when it ...
... (c) The original kinetic energy was converted into thermal energy by the negative work of friction. Reflect: To stop the car friction must do negative work equal in magnitude to the initial kinetic energy of the car. 7-21 You throw a 20 N rock into the air from ground level and observe that, when it ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Examples A pitcher throws a fastball with a velocity of 43.5 m/s. It is determined that during the windup and delivery the ball covers a displacement of 2.5 meters. This is from the point behind the body to the point of release. Calculate the acceleration during his throwing motion. What do I know? ...
... Examples A pitcher throws a fastball with a velocity of 43.5 m/s. It is determined that during the windup and delivery the ball covers a displacement of 2.5 meters. This is from the point behind the body to the point of release. Calculate the acceleration during his throwing motion. What do I know? ...
Asymptotic Freedom: From Paradox to Paradigm 1 A Pair of Paradoxes ∗
... contain several copies of the originals, or different particles altogether. A plethora of new particles was discovered in this way. Although these particles, generically called hadrons, are unstable, they otherwise behave in ways that broadly resemble the way protons and neutrons behave. So the char ...
... contain several copies of the originals, or different particles altogether. A plethora of new particles was discovered in this way. Although these particles, generically called hadrons, are unstable, they otherwise behave in ways that broadly resemble the way protons and neutrons behave. So the char ...
Apply
... kinetic energy of a moving object to zero, we need to apply a force. The work done by this force is negative according to work-energy theorem because W K 0 . This is also clear when we realize that the direction of this force must be opposing the velocity of the object to cause it to slow down. ...
... kinetic energy of a moving object to zero, we need to apply a force. The work done by this force is negative according to work-energy theorem because W K 0 . This is also clear when we realize that the direction of this force must be opposing the velocity of the object to cause it to slow down. ...
Lecture-11-10
... Motion about the Center of Mass The center of mass of a complex or composite object follows a trajectory as if it were a single particle - with mass equal to the complex object, and experiencing a force equal to the sum of all external forces on that complex object ...
... Motion about the Center of Mass The center of mass of a complex or composite object follows a trajectory as if it were a single particle - with mass equal to the complex object, and experiencing a force equal to the sum of all external forces on that complex object ...
Science 2nd prep 2nd term final exercise Important Laws: 1
... 8-the longest wavelength is for the ………….. color of the spectrum seven colors. 9-The German scientist …………………… proved that the energy of light waves is composed of energy quanta known as ………………………. 10-Photon energy = plank's constant × ………………………… 11-Objects can't be seen behind the ……………………. medium. ...
... 8-the longest wavelength is for the ………….. color of the spectrum seven colors. 9-The German scientist …………………… proved that the energy of light waves is composed of energy quanta known as ………………………. 10-Photon energy = plank's constant × ………………………… 11-Objects can't be seen behind the ……………………. medium. ...
How does friction, air resistance and gravity affect the motion of
... 1. More friction causes an object to move (slower/faster). Less friction causes an object to move (slower/faster) 2. Suppose you roll a ball with your hand, the ball speeds up as you push it and then keeps moving after it leaves your hand. What ends up happening to the ball’s speed if it is moving o ...
... 1. More friction causes an object to move (slower/faster). Less friction causes an object to move (slower/faster) 2. Suppose you roll a ball with your hand, the ball speeds up as you push it and then keeps moving after it leaves your hand. What ends up happening to the ball’s speed if it is moving o ...
Motion Characteristics for Circular Motion
... would cover the same linear distance in each second of time. When moving in a circle, an object traverses a distance around the perimeter of the circle. So if your car were to move in a circle with a constant speed of 5 m/s, then the car would travel 5 meters along the perimeter of the circle in eac ...
... would cover the same linear distance in each second of time. When moving in a circle, an object traverses a distance around the perimeter of the circle. So if your car were to move in a circle with a constant speed of 5 m/s, then the car would travel 5 meters along the perimeter of the circle in eac ...
Free fall
... during which of the 4 seconds does the ball’s speed increase the most? • If you drop a ball from a height of 4.9 m, it will hit the ground 1 s later. If you fire a bullet exactly horizontally from a height of 4.9 m, it will also hit the ground exactly 1 s later. Explain. • If a golf ball and a bowli ...
... during which of the 4 seconds does the ball’s speed increase the most? • If you drop a ball from a height of 4.9 m, it will hit the ground 1 s later. If you fire a bullet exactly horizontally from a height of 4.9 m, it will also hit the ground exactly 1 s later. Explain. • If a golf ball and a bowli ...
File - Ms. Quack`s Physics Page
... 25. A jet- powered car called The Spirit of America required 9600 meters to stop from its highest speed. If the car decelerated at a rate of -2.0 m/s2, what was the initial speed of the car? 26. A ball is launched straight up into the air with a velocity of 50 m/s. Assuming the acceleration due to g ...
... 25. A jet- powered car called The Spirit of America required 9600 meters to stop from its highest speed. If the car decelerated at a rate of -2.0 m/s2, what was the initial speed of the car? 26. A ball is launched straight up into the air with a velocity of 50 m/s. Assuming the acceleration due to g ...