GENETICS and the DNA code NOTES BACKGROUND DNA is the
... stop codon, signaling the end of the polypeptide. This polypeptide is then folding to make a protein. Some proteins are made of a single polypeptide, while others are made up of multiple polypeptides bonded together. Mutations are changes in a gene in the DNA, which may cause the protein to not form ...
... stop codon, signaling the end of the polypeptide. This polypeptide is then folding to make a protein. Some proteins are made of a single polypeptide, while others are made up of multiple polypeptides bonded together. Mutations are changes in a gene in the DNA, which may cause the protein to not form ...
The Role of Genetics in Growth Hormone Deficiency and Combined
... and extrinsic transcription factors and signalling molecules have been implicated in normal anterior pituitary development. The transcription factors include homeobox genes that encode homeodomain factors. These contain a DNA-binding region called the homeodomain which can then bind to target DNA an ...
... and extrinsic transcription factors and signalling molecules have been implicated in normal anterior pituitary development. The transcription factors include homeobox genes that encode homeodomain factors. These contain a DNA-binding region called the homeodomain which can then bind to target DNA an ...
, 479-283-0154 A plan to assess student
... K. Mutations in DNA that pass from one generation to the next occur at what seems like a fairly low frequency, for instance, copying errors during replications occur at a rate of about one error per one billion base pairs copied. However, since many organisms have more than one billion base pairs of ...
... K. Mutations in DNA that pass from one generation to the next occur at what seems like a fairly low frequency, for instance, copying errors during replications occur at a rate of about one error per one billion base pairs copied. However, since many organisms have more than one billion base pairs of ...
DNA: Sample Storage - Sacramento County District Attorney
... Amplified DNA from casework will be retained in frozen storage until the case has been technically and administratively reviewed. After the review process has been completed, the amplified DNA may be destroyed. NOTE: Exceptions to this process are when ...
... Amplified DNA from casework will be retained in frozen storage until the case has been technically and administratively reviewed. After the review process has been completed, the amplified DNA may be destroyed. NOTE: Exceptions to this process are when ...
Chap 8-11, pt 2 Mendel through Biotechnology
... Structural and numerical deviations that affect many genes at once are aberrations also called mutations. (An actual mutation is a change in the gene that results in alteration of bases within the DNA sequence) Once mutated, a gene will faithfully reproduce itself as is. Helpful or Not Helpful ...
... Structural and numerical deviations that affect many genes at once are aberrations also called mutations. (An actual mutation is a change in the gene that results in alteration of bases within the DNA sequence) Once mutated, a gene will faithfully reproduce itself as is. Helpful or Not Helpful ...
Evolution-
... Four conditions required for natural selection: 1. Variation- Individuals in a population are not _______________ to each other. 2. Inheritance- Traits are passed to _________________; traits have a genetic basis 3. Environmental population limits- Environmental ________________ ____________ prevent ...
... Four conditions required for natural selection: 1. Variation- Individuals in a population are not _______________ to each other. 2. Inheritance- Traits are passed to _________________; traits have a genetic basis 3. Environmental population limits- Environmental ________________ ____________ prevent ...
Unit 2 – Genetics Content Map
... Unit Essential Question: What makes organisms unique? GPS Standard(s): SB2. Students will analyze how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. A. Distinguish between DNA and RNA. B. Explain the role of DNA in storing and transmitting cellular information. C. Using Mendel’s laws, ex ...
... Unit Essential Question: What makes organisms unique? GPS Standard(s): SB2. Students will analyze how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. A. Distinguish between DNA and RNA. B. Explain the role of DNA in storing and transmitting cellular information. C. Using Mendel’s laws, ex ...
point mutation
... If a base was instead deleted, it would also be a type of frame-shift mutation. They both drastically change the code following the insertion or deletion. The message goes from making biological sense to being gibberish. ...
... If a base was instead deleted, it would also be a type of frame-shift mutation. They both drastically change the code following the insertion or deletion. The message goes from making biological sense to being gibberish. ...
Lecture_28.pps
... structures are currently known in model organisms • Homologs for most vertebrate “glyco” genes have been described, but in only a few cases have corresponding activities been demonstrated in vitro • In many cases, developmental biologists have stumbled into glycobiology • Reverse genetic methods (mu ...
... structures are currently known in model organisms • Homologs for most vertebrate “glyco” genes have been described, but in only a few cases have corresponding activities been demonstrated in vitro • In many cases, developmental biologists have stumbled into glycobiology • Reverse genetic methods (mu ...
Introduction - Milan Area Schools
... • In the 1990s, people who had eaten beef from cows with TSE contracted a human version of TSE. • Kuru is a TSE disease found in the Fore tribe of New Guinea before they ceased their practice of ritual cannibalism. It was transmitted via the brains of infected people. • Tikva Alper provided evidence ...
... • In the 1990s, people who had eaten beef from cows with TSE contracted a human version of TSE. • Kuru is a TSE disease found in the Fore tribe of New Guinea before they ceased their practice of ritual cannibalism. It was transmitted via the brains of infected people. • Tikva Alper provided evidence ...
Introduction - Cedar Crest College
... Prenatal genetic screening, screening of newborns, and screening of asymptomatic people whose relatives have a genetic disease are often beneficial to individuals and their offspring, although these techniques also raise ...
... Prenatal genetic screening, screening of newborns, and screening of asymptomatic people whose relatives have a genetic disease are often beneficial to individuals and their offspring, although these techniques also raise ...
I. Microbial Genetics (Chapter 7) A. Overview 1. all of the information
... a. point mutation = involves changing single base pair (affects only a single gene) b. frameshift mutations = insertion or deletion so that the natural order of message is shifted (1) loss or change in entire or large portion of chromosome (deletion or insertion) (2) could occur as a point mutation ...
... a. point mutation = involves changing single base pair (affects only a single gene) b. frameshift mutations = insertion or deletion so that the natural order of message is shifted (1) loss or change in entire or large portion of chromosome (deletion or insertion) (2) could occur as a point mutation ...
Describe the central dogma of molecular biology.
... Therefore, insertions or deletions that do not involve multiples of 3 base pairs will change the reading frame of the gene, and alter all codons downstream from the mutation. These are called frameshift mutations: ...
... Therefore, insertions or deletions that do not involve multiples of 3 base pairs will change the reading frame of the gene, and alter all codons downstream from the mutation. These are called frameshift mutations: ...
3.1 Class Notes Powerpoint
... The classic example of evolutionary change in humans is the hemoglobin mutation that makes red blood cells take on a curved, sickle-like shape. With one copy, it resists malaria, but with two copies, it causes the illness of sickle-cell anemia. ...
... The classic example of evolutionary change in humans is the hemoglobin mutation that makes red blood cells take on a curved, sickle-like shape. With one copy, it resists malaria, but with two copies, it causes the illness of sickle-cell anemia. ...
There are a variety of diseases commonly ascribed to antigenic
... ischemic (embolic) stroke risk but negatively with hemorrhagic stroke. Finally, some genes play double duty, as the same genes which can cause diabetes and hypertension also increase risk of stroke. One of the most interesting points about the Hispanic-American population of diagnosed CCM patients i ...
... ischemic (embolic) stroke risk but negatively with hemorrhagic stroke. Finally, some genes play double duty, as the same genes which can cause diabetes and hypertension also increase risk of stroke. One of the most interesting points about the Hispanic-American population of diagnosed CCM patients i ...
Protein Synthesis (Transcription and Translation)
... • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. • A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. ...
... • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. • A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. ...
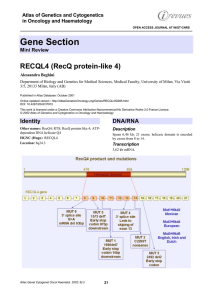
Gene Section RECQL4 (RecQ protein-like 4) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
... domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
Genetic Technology
... DNA of interest incubated with DNA polymerase, nucleotides, & ss primer DNA for synthesis DNA heated strands separate Cool primers bond DNA polymerase adds to 3’ end of each primer ...
... DNA of interest incubated with DNA polymerase, nucleotides, & ss primer DNA for synthesis DNA heated strands separate Cool primers bond DNA polymerase adds to 3’ end of each primer ...
Heredity and the Origin of Life
... • Label the next two pages “Genetic changes, what?” and date • Right page – “Genetic changes” ...
... • Label the next two pages “Genetic changes, what?” and date • Right page – “Genetic changes” ...
Sc9 - a 4.2 (teacher notes)
... What are the risks of cloning? Reproductive cloning is expensive and highly inefficient. More than 90% of cloning attempts fail to produce viable offspring. More than 100 nuclear transfer procedures could be required to produce one viable clone. In addition to low success rates, cloned animals tend ...
... What are the risks of cloning? Reproductive cloning is expensive and highly inefficient. More than 90% of cloning attempts fail to produce viable offspring. More than 100 nuclear transfer procedures could be required to produce one viable clone. In addition to low success rates, cloned animals tend ...
Section 1: Mutation and Genetic Change Preview • Bellringer • Key
... a gene rearrangement, is likely to disrupt the gene’s function in other ways. Chromosomal Mutations Gene Mutations Effects of Genetic Change Many genetic changes will cause no change in the appearance or function of organisms. The results of genetic change may be harmful, beneficial, or neutral; mos ...
... a gene rearrangement, is likely to disrupt the gene’s function in other ways. Chromosomal Mutations Gene Mutations Effects of Genetic Change Many genetic changes will cause no change in the appearance or function of organisms. The results of genetic change may be harmful, beneficial, or neutral; mos ...
7. Evolution
... 3. Describe the types of homozygous genotypes that can occur in an individual. 4. What is a heterozygous genotype? 5. What is an example of a disease caused by recessive lethal alleles? 6. Under what conditions do recessive lethal alleles cause death? 7. How can healthy heterozygous individuals carr ...
... 3. Describe the types of homozygous genotypes that can occur in an individual. 4. What is a heterozygous genotype? 5. What is an example of a disease caused by recessive lethal alleles? 6. Under what conditions do recessive lethal alleles cause death? 7. How can healthy heterozygous individuals carr ...
2006
... You decide to isolate an rII mutant using proflavin as a mutagen. Proflavin induces frameshift mutations when phage are grown in cells treated with proflavin. A). (2 points). Which E. coli strain would you use for the mutagenesis? Why? [E. coli B because rII mutants can grow in E. coli B but cannot ...
... You decide to isolate an rII mutant using proflavin as a mutagen. Proflavin induces frameshift mutations when phage are grown in cells treated with proflavin. A). (2 points). Which E. coli strain would you use for the mutagenesis? Why? [E. coli B because rII mutants can grow in E. coli B but cannot ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis
... Mutations can change the amino acids in a protein. Mutations can involve large regions of a chromosome or just a single nucleotide pair, as occurs in sickle-cell disease. ...
... Mutations can change the amino acids in a protein. Mutations can involve large regions of a chromosome or just a single nucleotide pair, as occurs in sickle-cell disease. ...
PHYSgeneticsnotes
... 1. Structural proteins are the big structural components of tissue (e.g. muscle, epithelial, etc.) 2. Enzymes are proteins that serve as catalysts, aiding chemical reactions in the body. 3. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. ...
... 1. Structural proteins are the big structural components of tissue (e.g. muscle, epithelial, etc.) 2. Enzymes are proteins that serve as catalysts, aiding chemical reactions in the body. 3. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.