Supplemental Table 2. Definition of nine
... Heterozygous mutations as defined in the category III. Patient may be a carrier of such highly-likely disease-causing mutations. Such mutations in heterozygous format may not be disease-causing, but may significantly increase the genetic risk for offspring if both parents carry the same mutations or ...
... Heterozygous mutations as defined in the category III. Patient may be a carrier of such highly-likely disease-causing mutations. Such mutations in heterozygous format may not be disease-causing, but may significantly increase the genetic risk for offspring if both parents carry the same mutations or ...
human genetic disorders part 2–diagnosis and treatment
... [5]. For example, citrate-stabilized blood may afford better quality of RNA and DNA than other anticoagulants would, also, EDTA is good for DNA-based assays, but it will influence Mg2+ concentration, and it may interfere for example with cytogenetic analyses [5]. Many biochemical biomarkers may be a ...
... [5]. For example, citrate-stabilized blood may afford better quality of RNA and DNA than other anticoagulants would, also, EDTA is good for DNA-based assays, but it will influence Mg2+ concentration, and it may interfere for example with cytogenetic analyses [5]. Many biochemical biomarkers may be a ...
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers
... • Demethylation at the 5’ end of the gene and the promoter region is necessary for transcription. • CpG islands surround the promoters of constitutively expressed genes where they are unmethylated. • They are also found at the promoters of some tissue-regulated genes. • There are ~29,000 CpG islands ...
... • Demethylation at the 5’ end of the gene and the promoter region is necessary for transcription. • CpG islands surround the promoters of constitutively expressed genes where they are unmethylated. • They are also found at the promoters of some tissue-regulated genes. • There are ~29,000 CpG islands ...
Notes - Haiku Learning
... complementary bases of triplet anticodon of tRNA 6. tRNA moves sequentially through the three binding sites from A, to P, to E site 7. Growing polypeptide chain exits the ribosome through a tunnel in the large subunit ...
... complementary bases of triplet anticodon of tRNA 6. tRNA moves sequentially through the three binding sites from A, to P, to E site 7. Growing polypeptide chain exits the ribosome through a tunnel in the large subunit ...
Document
... they are knocked out. The fraction of essential TFs shows an almost monotomic increase with number of active conditions. TFs active under more conditions are more likely to be essential than those that are only active under specific conditions. ...
... they are knocked out. The fraction of essential TFs shows an almost monotomic increase with number of active conditions. TFs active under more conditions are more likely to be essential than those that are only active under specific conditions. ...
385 Genetic Transformation : a Retrospective Appreciation
... regions marked ‘ A’ carry genes which determine biosynthetic steps common to both pathways, the mutation in the recipient being indicated by the cross, while the ‘ B’ region is concerned with capsular specificity. Note that in transformation, as in other forms of bacterial sexuality, the fragmentary ...
... regions marked ‘ A’ carry genes which determine biosynthetic steps common to both pathways, the mutation in the recipient being indicated by the cross, while the ‘ B’ region is concerned with capsular specificity. Note that in transformation, as in other forms of bacterial sexuality, the fragmentary ...
Leture 19, work session 12
... chromosome separates during cell division .The centromere is a structure of noncoding DNA( DNA that does not convey genetic information). When the cell divides the strands of the chromatids migrate in opposite directions (pull apart) at the centromere. In a photomicrograph, the centromere appears as ...
... chromosome separates during cell division .The centromere is a structure of noncoding DNA( DNA that does not convey genetic information). When the cell divides the strands of the chromatids migrate in opposite directions (pull apart) at the centromere. In a photomicrograph, the centromere appears as ...
Unit 05 - Delivery guide
... OCR has collaborated with current practitioners to ensure that the ideas put forward in this Delivery Guide are practical, realistic and dynamic. The Guide is structured by learning outcome so you can see how each activity helps you cover the requirements of this unit. We appreciate that practitione ...
... OCR has collaborated with current practitioners to ensure that the ideas put forward in this Delivery Guide are practical, realistic and dynamic. The Guide is structured by learning outcome so you can see how each activity helps you cover the requirements of this unit. We appreciate that practitione ...
Cell-Specific Expression of Genes of the Lipid Transfer Protein
... (Pyee and Kolattukudy 1995), and may argue for the existence of different sub-families. Similarly, three of the LTPs identified in B. napus showed very high sequence identities of 85-92% (Soufleri et al. 1996). However, when these transcripts were compared to yet another B. napus LTP the tapetum-spe ...
... (Pyee and Kolattukudy 1995), and may argue for the existence of different sub-families. Similarly, three of the LTPs identified in B. napus showed very high sequence identities of 85-92% (Soufleri et al. 1996). However, when these transcripts were compared to yet another B. napus LTP the tapetum-spe ...
Crossing-Over Introduction
... due to a process our chromosomes undergo, known as genetic recombination. Genetic recombination happens during meiosis. Inside the cells that produce sperm and eggs, homologous chromosomes become paired. Homologous chromosomes contain all same genes, but may have different versions of these genes ca ...
... due to a process our chromosomes undergo, known as genetic recombination. Genetic recombination happens during meiosis. Inside the cells that produce sperm and eggs, homologous chromosomes become paired. Homologous chromosomes contain all same genes, but may have different versions of these genes ca ...
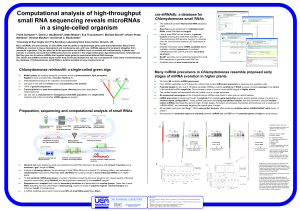
View Poster - Technology Networks
... To find potential miRNA-precursors, a number of windows containing the locus sequence and varying lengths of flanking sequence were folded using RNAfold1 and the significance assessed by the randfold2 program. Sequences were mapped back onto the secondary structures and assembled into overlap groups ...
... To find potential miRNA-precursors, a number of windows containing the locus sequence and varying lengths of flanking sequence were folded using RNAfold1 and the significance assessed by the randfold2 program. Sequences were mapped back onto the secondary structures and assembled into overlap groups ...
Student Materials - Scope, Sequence, and Coordination
... for only the left side (side one) of the DNA. Determine what DNA code you will be using. As messenger RNA nucleotides move into the nucleus, the DNA unzips. The complementary mRNA bases pair with the DNA bases. Glue a phosphoric acid at one end of the dark purple strips and then a base strip that is ...
... for only the left side (side one) of the DNA. Determine what DNA code you will be using. As messenger RNA nucleotides move into the nucleus, the DNA unzips. The complementary mRNA bases pair with the DNA bases. Glue a phosphoric acid at one end of the dark purple strips and then a base strip that is ...
Identification and Characterization of a Novel Human Testis
... substrate gene that maps to chromosome 19q13.3. Screening of expressed sequence tags and reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction of total RNA from human tissues allowed us to establish the expression of the gene and delineate its genomic organization (GenBank Accession No. AF200923). This ge ...
... substrate gene that maps to chromosome 19q13.3. Screening of expressed sequence tags and reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction of total RNA from human tissues allowed us to establish the expression of the gene and delineate its genomic organization (GenBank Accession No. AF200923). This ge ...
Stature in adolescent twins - UCSD Genetics Training Program
... In population genetics, linkage disequilibrium is the non-random association of alleles at two or more loci. Linkage disequilibrium describes a situation in which some combinations of alleles or genetic markers occur more or less frequently in a population than would be expected from a random format ...
... In population genetics, linkage disequilibrium is the non-random association of alleles at two or more loci. Linkage disequilibrium describes a situation in which some combinations of alleles or genetic markers occur more or less frequently in a population than would be expected from a random format ...
Identifying Chromosomal Abnormalities Using Infinium
... ►Jackson EM, Sievert AJ, Gai X, Hakonarson H, Judkins AR, et al. (2009) Genomic analysis using high-density single nucleotide polymorphism-based oligonucleotide arrays and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification provides a comprehensive analysis of INI1/SMARCB1 in malignant rhabdoid tumors. ...
... ►Jackson EM, Sievert AJ, Gai X, Hakonarson H, Judkins AR, et al. (2009) Genomic analysis using high-density single nucleotide polymorphism-based oligonucleotide arrays and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification provides a comprehensive analysis of INI1/SMARCB1 in malignant rhabdoid tumors. ...
Causes and consequences of nuclear gene positioning
... While candidate approaches are powerful in elucidating a specific positioning mechanism, they are unable to identify unanticipated pathways and it is often difficult to establish the global relevance of factors identified using these approaches. A powerful alternative approach to discover and charac ...
... While candidate approaches are powerful in elucidating a specific positioning mechanism, they are unable to identify unanticipated pathways and it is often difficult to establish the global relevance of factors identified using these approaches. A powerful alternative approach to discover and charac ...
Lab 9: Web Applications for Gene Family Evolution
... link. This links to the Sanger Trust Institute database on protein families. This page is specifically for this domain. So, it's the transporter part of the protein and it is also involved in ATP-hydrolysis. Click on the “Domain Organization” tab over on the left. This shows a list of all the other ...
... link. This links to the Sanger Trust Institute database on protein families. This page is specifically for this domain. So, it's the transporter part of the protein and it is also involved in ATP-hydrolysis. Click on the “Domain Organization” tab over on the left. This shows a list of all the other ...
Ch 15b
... From the results, Morgan reasoned that body color and wing size are usually inherited together in specific combinations (parental phenotypes) because the genes are on the same chromosome ...
... From the results, Morgan reasoned that body color and wing size are usually inherited together in specific combinations (parental phenotypes) because the genes are on the same chromosome ...
High-throughput reverse genetics: RNAi screens in
... fungal, invertebrate and plant worlds. Many of these organisms may be sequenced over the next few years. Even for those that arent, RNAi can be scaled up to ask genome-wide questions. For example, a recent paper [12] describes RNAi on a set of C. elegans cDNAs expressed in ovaries, leading to the i ...
... fungal, invertebrate and plant worlds. Many of these organisms may be sequenced over the next few years. Even for those that arent, RNAi can be scaled up to ask genome-wide questions. For example, a recent paper [12] describes RNAi on a set of C. elegans cDNAs expressed in ovaries, leading to the i ...
The end of the male gene pool?
... The researchers studied the genes on the human Y chromosome and compared them with those on the Y chromosomes of chimpanzees and rhesus macaques. The latter split from the human lineage 25m years ago. Hughes found that only one gene had been lost from the human Y chromosome since then. The rapid dec ...
... The researchers studied the genes on the human Y chromosome and compared them with those on the Y chromosomes of chimpanzees and rhesus macaques. The latter split from the human lineage 25m years ago. Hughes found that only one gene had been lost from the human Y chromosome since then. The rapid dec ...
Recombinant DNA Technology and Molecular Cloning
... • To facilitate the study of a genes: – Clone the gene by inserting it into another DNA molecule that serves as a vehicle or vector that can be replicated in living cells. ...
... • To facilitate the study of a genes: – Clone the gene by inserting it into another DNA molecule that serves as a vehicle or vector that can be replicated in living cells. ...
A protein-based phylogenetic tree for Gram
... terial groups that diverged at almost the same time; amino acid sequence homologies, for other proteins that are not so highly conserved, and gene-fusion events may be more appropriate methods (Ahmad & Jensen, 1989; Jensen & Ahmad, 1990). Furthermore, a study based on a very small number of genes co ...
... terial groups that diverged at almost the same time; amino acid sequence homologies, for other proteins that are not so highly conserved, and gene-fusion events may be more appropriate methods (Ahmad & Jensen, 1989; Jensen & Ahmad, 1990). Furthermore, a study based on a very small number of genes co ...
Human genome

The human genome is the complete set of nucleic acid sequence for humans (Homo sapiens), encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Haploid human genomes, which are contained in germ cells (the egg and sperm gamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNA base pairs, while diploid genomes (found in somatic cells) have twice the DNA content. While there are significant differences among the genomes of human individuals (on the order of 0.1%), these are considerably smaller than the differences between humans and their closest living relatives, the chimpanzees (approximately 4%) and bonobos. Humans share 50% of their DNA with bananas.The Human Genome Project produced the first complete sequences of individual human genomes, with the first draft sequence and initial analysis being published on February 12, 2001. The human genome was the first of all vertebrates to be completely sequenced. As of 2012, thousands of human genomes have been completely sequenced, and many more have been mapped at lower levels of resolution. The resulting data are used worldwide in biomedical science, anthropology, forensics and other branches of science. There is a widely held expectation that genomic studies will lead to advances in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, and to new insights in many fields of biology, including human evolution.Although the sequence of the human genome has been (almost) completely determined by DNA sequencing, it is not yet fully understood. Most (though probably not all) genes have been identified by a combination of high throughput experimental and bioinformatics approaches, yet much work still needs to be done to further elucidate the biological functions of their protein and RNA products. Recent results suggest that most of the vast quantities of noncoding DNA within the genome have associated biochemical activities, including regulation of gene expression, organization of chromosome architecture, and signals controlling epigenetic inheritance.There are an estimated 20,000-25,000 human protein-coding genes. The estimate of the number of human genes has been repeatedly revised down from initial predictions of 100,000 or more as genome sequence quality and gene finding methods have improved, and could continue to drop further. Protein-coding sequences account for only a very small fraction of the genome (approximately 1.5%), and the rest is associated with non-coding RNA molecules, regulatory DNA sequences, LINEs, SINEs, introns, and sequences for which as yet no function has been elucidated.