PDF - SystemsX.ch
... Deplancke’s colleague at EPFL, Johan Auwerx, works with 60 inbred mouse strains. Each mouse from any one of these strains can be traced back to one female and one male mouse, which also came from inbred strains. Normal mice possess two sets of genes, one from the mother and one from the father. This ...
... Deplancke’s colleague at EPFL, Johan Auwerx, works with 60 inbred mouse strains. Each mouse from any one of these strains can be traced back to one female and one male mouse, which also came from inbred strains. Normal mice possess two sets of genes, one from the mother and one from the father. This ...
The Source of Heredity “Chapter 21”
... Paired chromosomes segregate during meiosis. Each sex cell or gamete has half the number of chromosomes found in a somate cell. Chromosomes assort independently during meiosis. This means that each gamete receives one of the pairs and that one chromosome has no influence on the movement of a member ...
... Paired chromosomes segregate during meiosis. Each sex cell or gamete has half the number of chromosomes found in a somate cell. Chromosomes assort independently during meiosis. This means that each gamete receives one of the pairs and that one chromosome has no influence on the movement of a member ...
An introduction to genetics and molecular biology
... Then the 3’ UTR is found after the last exon. Over 90% of human genes undergo alternative splicing: there are multiple mRNA molecules that can be made from the gene. This is possible because the gene can use just some of the exons, or use different 5’ and 3’ UTRs, and some genes even have multiple s ...
... Then the 3’ UTR is found after the last exon. Over 90% of human genes undergo alternative splicing: there are multiple mRNA molecules that can be made from the gene. This is possible because the gene can use just some of the exons, or use different 5’ and 3’ UTRs, and some genes even have multiple s ...
Biotechnology - BHSBiology-Cox
... – Ecologists to determine parentage of endangered species for breeding purposes – Wildlife biologists/customs agents to identify illegally poached or transported animals (bear gall ...
... – Ecologists to determine parentage of endangered species for breeding purposes – Wildlife biologists/customs agents to identify illegally poached or transported animals (bear gall ...
Pan-genomics: Unmasking the gene diversity hidden in the bacteria
... in bacteria differences in genome size correlates directly with coding sequences, the larger of your bacterial genome, the more functions you can potentially perform with the genes coded in your genome. S. agalactiae’s variation in conservancy of genes are huge, when comparing different eukaryote sp ...
... in bacteria differences in genome size correlates directly with coding sequences, the larger of your bacterial genome, the more functions you can potentially perform with the genes coded in your genome. S. agalactiae’s variation in conservancy of genes are huge, when comparing different eukaryote sp ...
Supplementary Information
... The crtP and crtQ genes were newly acquired in cyanobacteria and subsequently maintained in photosynthetic eukaryotes, and phylogenetic analysis showed that these proteins may have evolved originally from bacterial desaturases involved in the formation of aromatic end groups [1]. Both the P. tricorn ...
... The crtP and crtQ genes were newly acquired in cyanobacteria and subsequently maintained in photosynthetic eukaryotes, and phylogenetic analysis showed that these proteins may have evolved originally from bacterial desaturases involved in the formation of aromatic end groups [1]. Both the P. tricorn ...
At the Forefront in PGD
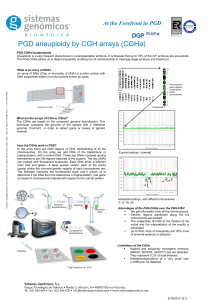
... chromosomal PGD is based on CGH arrays technology. It allows to identify the altered embryos (unbalanced) in relation to the translocation/inversion and it also allows us to study aneuploidy for 24 chromosomes, simultaniously and in the same cell. The information of the non involved chromosomes in t ...
... chromosomal PGD is based on CGH arrays technology. It allows to identify the altered embryos (unbalanced) in relation to the translocation/inversion and it also allows us to study aneuploidy for 24 chromosomes, simultaniously and in the same cell. The information of the non involved chromosomes in t ...
Unit 5 Review
... _______ Daughter strands are formed using complementary base pairing. _______ DNA unwinds. _______ The DNA of the daughter strands winds with together with its parent strand. 14. Show the complimentary base pairing that would occur in the replication of this short DNA molecule. Use a colored pencil ...
... _______ Daughter strands are formed using complementary base pairing. _______ DNA unwinds. _______ The DNA of the daughter strands winds with together with its parent strand. 14. Show the complimentary base pairing that would occur in the replication of this short DNA molecule. Use a colored pencil ...
The Mitochondria as a Minimal Chassis:
... whole synthetic organisms. • Microbial engineering: A minimalistic cell could be more prone to accept new metabolic pathways than a more complex organism. ...
... whole synthetic organisms. • Microbial engineering: A minimalistic cell could be more prone to accept new metabolic pathways than a more complex organism. ...
12 BOC314 Practical 1
... Biological data and DNA sequence data in particular, are accumulating at a phenomenal rate. The DNA sequence of the complete human genome has been determined. Although this achievement seems like an end in itself, in reality it is only the beginning. In order to exploit the wealth of DNA sequence an ...
... Biological data and DNA sequence data in particular, are accumulating at a phenomenal rate. The DNA sequence of the complete human genome has been determined. Although this achievement seems like an end in itself, in reality it is only the beginning. In order to exploit the wealth of DNA sequence an ...
Biotechnology and the Human Genome
... • A. shorter longer • B. shorter longer (see next slide for answer) ...
... • A. shorter longer • B. shorter longer (see next slide for answer) ...
Ch. 15 Chromosomal Inheritance
... *Alleles of genes on nonhomologous assort independently during meiosis ...
... *Alleles of genes on nonhomologous assort independently during meiosis ...
Document
... resistance (R) gene sequences of wild potato, tomato and pepper genomes (the SOLAR database) ...
... resistance (R) gene sequences of wild potato, tomato and pepper genomes (the SOLAR database) ...
Livenv_genetics - OurTeachersPage.com
... • Each polypeptide consists of a combination of any or all of the 20 different amino acids. • The properties of these proteins are determined by the order in which the amino acids are joined to form the polypeptides. ...
... • Each polypeptide consists of a combination of any or all of the 20 different amino acids. • The properties of these proteins are determined by the order in which the amino acids are joined to form the polypeptides. ...
Chapter 5_DNA for website
... translation and the full length protein is not translated. 2. A substitution can result in one incorrect amino acid being present in the protein which can affect the shape of the protein and therefore its function. 3. An insertion or deletion can occur early in the gene and result in an incorrect tr ...
... translation and the full length protein is not translated. 2. A substitution can result in one incorrect amino acid being present in the protein which can affect the shape of the protein and therefore its function. 3. An insertion or deletion can occur early in the gene and result in an incorrect tr ...
Seisenberger
... -Bisulfite Sequencing (BS seq)Protection treatment: methylated cytosine do not get converted to uracil ...
... -Bisulfite Sequencing (BS seq)Protection treatment: methylated cytosine do not get converted to uracil ...
Document
... Twenty-two of these pairs are autosomes. Autosomes are chromosomes that contain genes for the same traits. The twenty-third pair of chromosomes are sex chromosomes. Females inherit two X chromosomes and males one X and one Y as their pair of sex chromosomes. Sometimes individuals inherit an abnormal ...
... Twenty-two of these pairs are autosomes. Autosomes are chromosomes that contain genes for the same traits. The twenty-third pair of chromosomes are sex chromosomes. Females inherit two X chromosomes and males one X and one Y as their pair of sex chromosomes. Sometimes individuals inherit an abnormal ...
PAG2006workshop
... (If some website features don’t work correctly, try using a different browser) ...
... (If some website features don’t work correctly, try using a different browser) ...
Workshop practical
... Run the example API script to check everything is installed correctly: perl biomart-web/scripts/new_0_5_exampleSimple.pl ...
... Run the example API script to check everything is installed correctly: perl biomart-web/scripts/new_0_5_exampleSimple.pl ...
Protein Synthesis
... 3. What is the purpose of transcription? How does it differ from DNA replication? The purpose of transcription is to re-write a portion of DNA, a gene, Transcription constructs an mRNA molecule through complimentary base pairing a portion of DNA. DNA replication makes an exact copy of the entire DNA ...
... 3. What is the purpose of transcription? How does it differ from DNA replication? The purpose of transcription is to re-write a portion of DNA, a gene, Transcription constructs an mRNA molecule through complimentary base pairing a portion of DNA. DNA replication makes an exact copy of the entire DNA ...
Generuj PDF - Centralne Laboratorium Kryminalistyczne Policji
... The most difficult task faced by experts and requiring advanced expertise, proficiency and experience is the analysis of evidential material. The majority of biological traces on examination items is invisible to unaided eye. Laborious work of experts to detect biological stains is supported by opti ...
... The most difficult task faced by experts and requiring advanced expertise, proficiency and experience is the analysis of evidential material. The majority of biological traces on examination items is invisible to unaided eye. Laborious work of experts to detect biological stains is supported by opti ...
Regulating Evolution - Nicolas Gompel`s lab
... pose: animals as different as a mouse and an elephant are shaped by a common set of very similar, functionally indistinguishable body-building proteins. The same applies to humans and our closest living relatives— most of our proteins differ from those of the chimpanzee by only one or two of the sev ...
... pose: animals as different as a mouse and an elephant are shaped by a common set of very similar, functionally indistinguishable body-building proteins. The same applies to humans and our closest living relatives— most of our proteins differ from those of the chimpanzee by only one or two of the sev ...
Question How does DNA control a cell?By controlling Protein
... between the new AA and the polypeptide chain in the P-site. ...
... between the new AA and the polypeptide chain in the P-site. ...
C17.2 PPT - Destiny High School
... from parents to their children. All the characteristics you have, such as your eye color, the amount of curl in your hair, and your height, are determined by your genetic ...
... from parents to their children. All the characteristics you have, such as your eye color, the amount of curl in your hair, and your height, are determined by your genetic ...
Document
... d. Copies of DNA molecules are made. d. codon on the mRNA and the anticodon on the tRNA to which the amino acid is attached. ...
... d. Copies of DNA molecules are made. d. codon on the mRNA and the anticodon on the tRNA to which the amino acid is attached. ...
Human genome

The human genome is the complete set of nucleic acid sequence for humans (Homo sapiens), encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Haploid human genomes, which are contained in germ cells (the egg and sperm gamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNA base pairs, while diploid genomes (found in somatic cells) have twice the DNA content. While there are significant differences among the genomes of human individuals (on the order of 0.1%), these are considerably smaller than the differences between humans and their closest living relatives, the chimpanzees (approximately 4%) and bonobos. Humans share 50% of their DNA with bananas.The Human Genome Project produced the first complete sequences of individual human genomes, with the first draft sequence and initial analysis being published on February 12, 2001. The human genome was the first of all vertebrates to be completely sequenced. As of 2012, thousands of human genomes have been completely sequenced, and many more have been mapped at lower levels of resolution. The resulting data are used worldwide in biomedical science, anthropology, forensics and other branches of science. There is a widely held expectation that genomic studies will lead to advances in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, and to new insights in many fields of biology, including human evolution.Although the sequence of the human genome has been (almost) completely determined by DNA sequencing, it is not yet fully understood. Most (though probably not all) genes have been identified by a combination of high throughput experimental and bioinformatics approaches, yet much work still needs to be done to further elucidate the biological functions of their protein and RNA products. Recent results suggest that most of the vast quantities of noncoding DNA within the genome have associated biochemical activities, including regulation of gene expression, organization of chromosome architecture, and signals controlling epigenetic inheritance.There are an estimated 20,000-25,000 human protein-coding genes. The estimate of the number of human genes has been repeatedly revised down from initial predictions of 100,000 or more as genome sequence quality and gene finding methods have improved, and could continue to drop further. Protein-coding sequences account for only a very small fraction of the genome (approximately 1.5%), and the rest is associated with non-coding RNA molecules, regulatory DNA sequences, LINEs, SINEs, introns, and sequences for which as yet no function has been elucidated.