Baltica upside down: A new plate tectonic model for Rodinia and the
... These events continued into the late Vendian–Early Cambrian collision of microcontinents, including the ca. 580–550 Ma Timanian obduction of the Timan and Pechora blocks onto Baltica (Gee et al., 2000; Roberts, 2001), the 630–573 Ma metamorphism and deformation related to the Baikalian obduction of ...
... These events continued into the late Vendian–Early Cambrian collision of microcontinents, including the ca. 580–550 Ma Timanian obduction of the Timan and Pechora blocks onto Baltica (Gee et al., 2000; Roberts, 2001), the 630–573 Ma metamorphism and deformation related to the Baikalian obduction of ...
Evolution of the Paleo-Asian Ocean (Altai−Sayan Region, Central
... diaphthorites after eclogites of the Chagan−Uzun massif are 473±13 and 487±22 Ma (Buslov and Watanabe, 1996), i.e., Ordovician (Table 1). This suggests the final stage of exhumation of eclogite with deformation and retrograde metamorphism. Uplift ages of granite−gneiss rocks which are located to the ...
... diaphthorites after eclogites of the Chagan−Uzun massif are 473±13 and 487±22 Ma (Buslov and Watanabe, 1996), i.e., Ordovician (Table 1). This suggests the final stage of exhumation of eclogite with deformation and retrograde metamorphism. Uplift ages of granite−gneiss rocks which are located to the ...
Late Proterozoic – Paleozoic Tectonostratigraphic Development and
... and quartz or arkosic sandstones. Recently, the sediments of the earliest Cambrian, most likely Platysolenites antiquissimus Zone, have been detetected in a borehole SE of Brno in SE part of the Brunovistulian Terrane (Vavrdová et al. 2002). The sediments of Holmia Zone show also a wider distributio ...
... and quartz or arkosic sandstones. Recently, the sediments of the earliest Cambrian, most likely Platysolenites antiquissimus Zone, have been detetected in a borehole SE of Brno in SE part of the Brunovistulian Terrane (Vavrdová et al. 2002). The sediments of Holmia Zone show also a wider distributio ...
as a PDF - University of Innsbruck
... documented by the green-gray shales of the Middle Bischofalm Shale Formation. A return to the deeper water graptolitic sequence is seen in the late Pridoli to Lochkov. The evidence from the Silurian indicates faunal affinities, e.g. conodonts, trilobites, brachiopods, molluscs, chitinozoa and archit ...
... documented by the green-gray shales of the Middle Bischofalm Shale Formation. A return to the deeper water graptolitic sequence is seen in the late Pridoli to Lochkov. The evidence from the Silurian indicates faunal affinities, e.g. conodonts, trilobites, brachiopods, molluscs, chitinozoa and archit ...
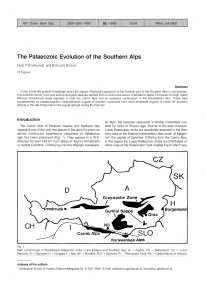
The Palaeozoic of the Southern Alps
... persculptus (H. P. SCHÖNLAUB 1996). If so it may have lasted during the early and middle Hirnantian Stage for not more than 0.5 to 1 million years. It resulted in channeling, erosion and local non-deposition. In fact, the succeeding basal Silurian strata generally disconformably rest upon the late O ...
... persculptus (H. P. SCHÖNLAUB 1996). If so it may have lasted during the early and middle Hirnantian Stage for not more than 0.5 to 1 million years. It resulted in channeling, erosion and local non-deposition. In fact, the succeeding basal Silurian strata generally disconformably rest upon the late O ...
Introduction to the Silurian
... The aim of stratigraphy is to study rock successions preserved from the past and to bring them to life as sequences of events through geological time. By correlating events such as sea-level changes, climatic variations and crustal deformation against the standard geological timescale, stratigraphic ...
... The aim of stratigraphy is to study rock successions preserved from the past and to bring them to life as sequences of events through geological time. By correlating events such as sea-level changes, climatic variations and crustal deformation against the standard geological timescale, stratigraphic ...
The Tien Shan Early Paleozoic tectonics and geodynamics
... latter contain Vendian microfossils and Early Cambrian accritarches. [15] These deposits seem to have accumulated in a basin of rift origin. They are overlain with a stratigraphic unconformity by the rocks containing Early Cambrian fossils. ...
... latter contain Vendian microfossils and Early Cambrian accritarches. [15] These deposits seem to have accumulated in a basin of rift origin. They are overlain with a stratigraphic unconformity by the rocks containing Early Cambrian fossils. ...
Click here to view pdf version
... objective was to provide more complete documentaAlthough biogeographic, magnetostratigraphic, and tion of the early Paleozoic history of southern Monchemostratigraphic data have not been collected sys- golia. Our three main goals were to: (1) develop tematically in the terrane, many important lithol ...
... objective was to provide more complete documentaAlthough biogeographic, magnetostratigraphic, and tion of the early Paleozoic history of southern Monchemostratigraphic data have not been collected sys- golia. Our three main goals were to: (1) develop tematically in the terrane, many important lithol ...
Paleozoic large igneous provinces of Northern Eurasia: Correlation
... African and Pacific plumes observed today. Superplumes could gradually move with their coupled supercontinents toward equatorial locations through true polar wander events, eventually leading to the breakup of the supercontinents. This would indicate that some of the antipodal plumes occurred in the ...
... African and Pacific plumes observed today. Superplumes could gradually move with their coupled supercontinents toward equatorial locations through true polar wander events, eventually leading to the breakup of the supercontinents. This would indicate that some of the antipodal plumes occurred in the ...
The Paleozoic Era - AC Reynolds High
... Cambrian was a side-by-side, or lateral, sequence from shallow to deeper water. Why, then, are the layers of sandstone, shale, and limestone stacked one on top of the other in the Grand Canyon? The sediments themselves reflect the energy of the water and often, the water depth. Thus, any changes in ...
... Cambrian was a side-by-side, or lateral, sequence from shallow to deeper water. Why, then, are the layers of sandstone, shale, and limestone stacked one on top of the other in the Grand Canyon? The sediments themselves reflect the energy of the water and often, the water depth. Thus, any changes in ...
Chapter 23: The Paleozoic Era
... Cambrian was a side-by-side, or lateral, sequence from shallow to deeper water. Why, then, are the layers of sandstone, shale, and limestone stacked one on top of the other in the Grand Canyon? The sediments themselves reflect the energy of the water and often, the water depth. Thus, any changes in ...
... Cambrian was a side-by-side, or lateral, sequence from shallow to deeper water. Why, then, are the layers of sandstone, shale, and limestone stacked one on top of the other in the Grand Canyon? The sediments themselves reflect the energy of the water and often, the water depth. Thus, any changes in ...
lecture notes
... and Appalachian. Figure 10.1 Major Cratonic Structures and Mobile Belts 2. Six major continents and numerous microcontinents and island arcs existed at the beginning of the Paleozoic Era. During the Early Paleozoic (Ordovician-Silurian), Gondwana moved to a southward, as indicated by tillite deposit ...
... and Appalachian. Figure 10.1 Major Cratonic Structures and Mobile Belts 2. Six major continents and numerous microcontinents and island arcs existed at the beginning of the Paleozoic Era. During the Early Paleozoic (Ordovician-Silurian), Gondwana moved to a southward, as indicated by tillite deposit ...
The Geology of Kentucky
... low coastal plains, land plants & animals thrived. So their fossils are present. Since this area was a shallow sea we can also find amphibians. These were nonexistent in the state until one was found in western Kentucky. ...
... low coastal plains, land plants & animals thrived. So their fossils are present. Since this area was a shallow sea we can also find amphibians. These were nonexistent in the state until one was found in western Kentucky. ...
No Slide Title
... Early Paleozoic Evolution of North America • The geologic history of the North American craton may be divided into two parts – the first dealing with the relatively stable continental interior over which epeiric seas transgressed and regressed, – and the other dealing with the mobile belts where mo ...
... Early Paleozoic Evolution of North America • The geologic history of the North American craton may be divided into two parts – the first dealing with the relatively stable continental interior over which epeiric seas transgressed and regressed, – and the other dealing with the mobile belts where mo ...
- Heritage Manitoba
... In North America and Europe, the Ordovician was a time of shallow continental seas rich in aquatic life. In the Early Ordovician, trilobites (extinct marine anthropods) were joined by many new types of organisms, including tabulate corals, strophomenid, rhynchonellid, and many new orthid brachiop ...
... In North America and Europe, the Ordovician was a time of shallow continental seas rich in aquatic life. In the Early Ordovician, trilobites (extinct marine anthropods) were joined by many new types of organisms, including tabulate corals, strophomenid, rhynchonellid, and many new orthid brachiop ...
sequences
... – during the Late Proterozoic and Early Cambrian – was limited to the passive shelf areas of the – Appalachian and Cordilleran borders of the craton ...
... – during the Late Proterozoic and Early Cambrian – was limited to the passive shelf areas of the – Appalachian and Cordilleran borders of the craton ...
Fethard
... Discharge in this groundwater body is to the surface water bodies and also to the sea. Discharge is not expected to be large as much of the area is considered to be a poor aquifer. There are three main surface water discharge locations, to the southwest at Waterford Harbour, South at Bannow Bay and ...
... Discharge in this groundwater body is to the surface water bodies and also to the sea. Discharge is not expected to be large as much of the area is considered to be a poor aquifer. There are three main surface water discharge locations, to the southwest at Waterford Harbour, South at Bannow Bay and ...
No Slide Title
... – during the Late Proterozoic and Early Cambrian – was limited to the passive shelf areas of the – Appalachian and Cordilleran borders of the craton ...
... – during the Late Proterozoic and Early Cambrian – was limited to the passive shelf areas of the – Appalachian and Cordilleran borders of the craton ...
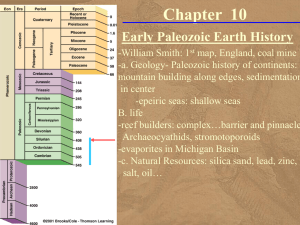
Chapter 10—Early Paleozoic Events
... life”), Mesozoic (“middle life”), and Cenozoic (“recent life”). This chapter looks specifically at Early Paleozoic and specifically the oldest three geologic periods: Cambrian, Ordovician, and Silurian. These three periods together lasted about 126 million years. The geologic history of the Paleozoi ...
... life”), Mesozoic (“middle life”), and Cenozoic (“recent life”). This chapter looks specifically at Early Paleozoic and specifically the oldest three geologic periods: Cambrian, Ordovician, and Silurian. These three periods together lasted about 126 million years. The geologic history of the Paleozoi ...
GEOLOGY AND ECONOMIC MINERALS the plains including those
... of the world. Present and potential production of potash in southern Saskatchewan represents a major source in terms of world supply. These Middle Devonian evaporites are estimated to contain more than 100,000,000,000 tons of potash. Coal is being or has been produced from many places in the Great P ...
... of the world. Present and potential production of potash in southern Saskatchewan represents a major source in terms of world supply. These Middle Devonian evaporites are estimated to contain more than 100,000,000,000 tons of potash. Coal is being or has been produced from many places in the Great P ...
Science Affiliates Workshop NY Geology Powerpoint
... Geologic Time Scale for the first 3.8 Billion Years of Earth's Existence ...
... Geologic Time Scale for the first 3.8 Billion Years of Earth's Existence ...
Syseca normal blank template - Manchester Geological Association
... The Cambrian to Tremadocian succession is marked by subsidence in a number of discrete basins and formation of a Tremadoc arc (<489 to >478 Ma) illustrating attenuation of the Gondwanan margin in response to both the onset of Iapetan subduction and opening of the Rheic ocean. Palaeogeographic affini ...
... The Cambrian to Tremadocian succession is marked by subsidence in a number of discrete basins and formation of a Tremadoc arc (<489 to >478 Ma) illustrating attenuation of the Gondwanan margin in response to both the onset of Iapetan subduction and opening of the Rheic ocean. Palaeogeographic affini ...