Enzymes: Introduction notes
... See also Berg et al., Table 8.2 (for reference, not for memorization) ...
... See also Berg et al., Table 8.2 (for reference, not for memorization) ...
CHANNELING OF SUBSTRATES AND INTERMEDIATES IN
... β-subunit inserts directly into the channel (35). Strikingly, exchange of potassium or cesium ions for sodium ions results in a movement of this Phe-280 side chain out of the tunnel, which suggests that this residue may indeed play a role as a molecular gate (35). The second site of close interactio ...
... β-subunit inserts directly into the channel (35). Strikingly, exchange of potassium or cesium ions for sodium ions results in a movement of this Phe-280 side chain out of the tunnel, which suggests that this residue may indeed play a role as a molecular gate (35). The second site of close interactio ...
103 Lecture Ch20a
... • Through resonance, the lone pair electrons on nitrogen and the pi electrons of the carbonyl are delocalized - this gives some double bond character to the C-N bond, preventing free rotation around that bond - this also makes the nitrogen less basic, since the lone pair is not very available for bo ...
... • Through resonance, the lone pair electrons on nitrogen and the pi electrons of the carbonyl are delocalized - this gives some double bond character to the C-N bond, preventing free rotation around that bond - this also makes the nitrogen less basic, since the lone pair is not very available for bo ...
Proteins in the Diet - Nutrition and Food Technology-just
... • Our genes code for proteins. • Proteins are polymers of amino acids. • Ribosome (Synthesis of Proteins). ...
... • Our genes code for proteins. • Proteins are polymers of amino acids. • Ribosome (Synthesis of Proteins). ...
ASPARTIC ACID, ASPARAGINE, GLUTAMIC ACID, AND
... any disulphide bonds present (Hirs 1956). This is particularly important for proteins with a high cystine content. For example, Hill and Schmidt (1962) found it necessary to oxidize the disulphide bonds of ribonuclease in order to achieve complete proteolysis. We have found in the case of wool that ...
... any disulphide bonds present (Hirs 1956). This is particularly important for proteins with a high cystine content. For example, Hill and Schmidt (1962) found it necessary to oxidize the disulphide bonds of ribonuclease in order to achieve complete proteolysis. We have found in the case of wool that ...
The Specificity of Enzymes Adding Amino Acids in the
... nucleotide dipeptide, UDP-MurNAc-Gly-Glu, or the most common nucleotide dipeptide, UDP-MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu. Table I shows that both UDP-Mur-NAc-Gly and UDPMurNAc-L-Ala are good substrates for the D-glutamic acid-adding enzyme. The glutamic acid occurring as amino acid residue 2 of the muramyl pentape ...
... nucleotide dipeptide, UDP-MurNAc-Gly-Glu, or the most common nucleotide dipeptide, UDP-MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu. Table I shows that both UDP-Mur-NAc-Gly and UDPMurNAc-L-Ala are good substrates for the D-glutamic acid-adding enzyme. The glutamic acid occurring as amino acid residue 2 of the muramyl pentape ...
Pipecleaner Proteins Lab
... 5. Be sure to have a cut up straw in between each amino acid so that you know where one ends and the next begins! You may need multiple pipe cleaners to fit all of your amino acids! 6. You will begin by creating the mRNA strand of a gene (transcription). Remember that for every… a. G in DNA you woul ...
... 5. Be sure to have a cut up straw in between each amino acid so that you know where one ends and the next begins! You may need multiple pipe cleaners to fit all of your amino acids! 6. You will begin by creating the mRNA strand of a gene (transcription). Remember that for every… a. G in DNA you woul ...
Pipecleaner Proteins Lab
... 5. Be sure to have a cut up straw in between each amino acid so that you know where one ends and the next begins! You may need multiple pipe cleaners to fit all of your amino acids! 6. You will begin by creating the mRNA strand of a gene (transcription). Remember that for every… a. G in DNA you woul ...
... 5. Be sure to have a cut up straw in between each amino acid so that you know where one ends and the next begins! You may need multiple pipe cleaners to fit all of your amino acids! 6. You will begin by creating the mRNA strand of a gene (transcription). Remember that for every… a. G in DNA you woul ...
Molecular modeling of HIV-1 reverse
... G190E mutation impairs protein folding of the recombinant enzyme, as indicated by a reduction in solubility. In our hands, however, a recombinant HIV-1 RT containing the G190E mutation was readily soluble. The V106 and Y188 mutations, shown in blue, retain at least 75% of the original activity upon ...
... G190E mutation impairs protein folding of the recombinant enzyme, as indicated by a reduction in solubility. In our hands, however, a recombinant HIV-1 RT containing the G190E mutation was readily soluble. The V106 and Y188 mutations, shown in blue, retain at least 75% of the original activity upon ...
Enzymes
... Some enzymes require coenzymes • Some enzymes require a coenzyme (another compound) to be bound to them before they can catalyze reactions. • Coenzymes are non-protein organic compounds. • Eg. of coenzymes: Vitamin B complex ...
... Some enzymes require coenzymes • Some enzymes require a coenzyme (another compound) to be bound to them before they can catalyze reactions. • Coenzymes are non-protein organic compounds. • Eg. of coenzymes: Vitamin B complex ...
Pipe Cleaner Protein Modeling C. Kohn, Waterford WI Name: Hour
... 5. Be sure to have a cut up straw in between each amino acid so that you know where one ends and the next begins! You may need multiple pipe cleaners to fit all of your amino acids! 6. You will begin by creating the mRNA strand of a gene (transcription). Remember that for every… a. G in DNA you woul ...
... 5. Be sure to have a cut up straw in between each amino acid so that you know where one ends and the next begins! You may need multiple pipe cleaners to fit all of your amino acids! 6. You will begin by creating the mRNA strand of a gene (transcription). Remember that for every… a. G in DNA you woul ...
Pipe Cleaner Protein Modeling C. Kohn, Waterford WI Name: Hour
... won’t bother with neutral amino acids). Red and blue beads near each other should for a bond (if they can); similarly colored blues or reds should be as far apart as possible. 3. Cysteine bonds – we’ll use green to represent the amino acids cysteine; green beads should form pairs whenever they can. ...
... won’t bother with neutral amino acids). Red and blue beads near each other should for a bond (if they can); similarly colored blues or reds should be as far apart as possible. 3. Cysteine bonds – we’ll use green to represent the amino acids cysteine; green beads should form pairs whenever they can. ...
L14_Adv06PDHwebCT
... Excellent animation of PDH reactions if you can access it: (not examinable, but might help understanding!) ...
... Excellent animation of PDH reactions if you can access it: (not examinable, but might help understanding!) ...
Title Effect of Glutamine Analogs on Glutaminase Formation in
... medium or an amino acid free medium were supplemented with L-asparagine (24). Only among species of Pseudomonashas there been evidence of a marked inducible formation of asparaginase by asparagine or aspartic acid (25). Glutaminase of Acinetobacterglutaminasfcans was reported to be induced by L-glut ...
... medium or an amino acid free medium were supplemented with L-asparagine (24). Only among species of Pseudomonashas there been evidence of a marked inducible formation of asparaginase by asparagine or aspartic acid (25). Glutaminase of Acinetobacterglutaminasfcans was reported to be induced by L-glut ...
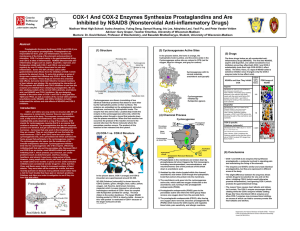
COX-1 And COX-2 Enzymes Synthesize Prostaglandins and Are
... COX-1 and COX-2 are very similar in structure (60- 65% of the sequence is conserved), however they are expressed in different parts of the body. The enzymes convert arachidonic acid, a fatty acid in cell membranes, into prostaglandins, modified fatty acids attached to a ring of five carbons. COX sta ...
... COX-1 and COX-2 are very similar in structure (60- 65% of the sequence is conserved), however they are expressed in different parts of the body. The enzymes convert arachidonic acid, a fatty acid in cell membranes, into prostaglandins, modified fatty acids attached to a ring of five carbons. COX sta ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.