... 1A. (4 pts) True & false (circle the correct answer). T or F: All 20 amino acids contain at least one chiral center. T or F: The peptide bond is planar and usually cis. T or F: Non-polar residues are found in the core of globular proteins due to van der Waals forces. T or F: Disulfide bonds are usua ...
A1981MS54300001
... phenylpropanoid metabolism were controlled quite differently than those of later flavonoid biosynthesis.2 This was a clear demonstration that PAL controls only part of phenylpropanoid metabolism. Recent work on phenylpropanoid metabolism is reviewed by Towers and Wat.3 "Since the time of the origina ...
... phenylpropanoid metabolism were controlled quite differently than those of later flavonoid biosynthesis.2 This was a clear demonstration that PAL controls only part of phenylpropanoid metabolism. Recent work on phenylpropanoid metabolism is reviewed by Towers and Wat.3 "Since the time of the origina ...
L11 Biochem alterations postharv storage - e
... In vitro studies with casein as a substrate demonstrate that that there is sufficient plasmin in milk to cause substantial proteolysis. Does not account the presence of plasmin inhibitors. Plasmin is thermostable. Plasmin and plasminogen accompany the casein micelles on the chymosin coagulation of m ...
... In vitro studies with casein as a substrate demonstrate that that there is sufficient plasmin in milk to cause substantial proteolysis. Does not account the presence of plasmin inhibitors. Plasmin is thermostable. Plasmin and plasminogen accompany the casein micelles on the chymosin coagulation of m ...
107105_pku
... screening program for PKU. The diagnosis of her disease was made late in her first year of life when she developed convulsions. It was too late for treatment and she has never known the benefits of early diagnosis and treatment as I know them. Our picture is on this web site so that parents of newly ...
... screening program for PKU. The diagnosis of her disease was made late in her first year of life when she developed convulsions. It was too late for treatment and she has never known the benefits of early diagnosis and treatment as I know them. Our picture is on this web site so that parents of newly ...
Tertiary Structure
... • The globin fold usually consists of eight alpha helices (AH). The two helices at the end of the chain are antiparallel, forming a helix-turn-helix motif, but the remainder of the fold does not include any characterized supersecondary structures. • These helices pack against each other with larger ...
... • The globin fold usually consists of eight alpha helices (AH). The two helices at the end of the chain are antiparallel, forming a helix-turn-helix motif, but the remainder of the fold does not include any characterized supersecondary structures. • These helices pack against each other with larger ...
The Aerobic Fate of Pyruvate
... metabolism occurs. The 2 moles of NADH produced by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase are oxidized in the electron transport chain back to NAD+. The electron transport chain generates a proton gradient that drives the synthesis of 5 ATP molecules from ADP and Pi. Further more, the pyruvate for ...
... metabolism occurs. The 2 moles of NADH produced by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase are oxidized in the electron transport chain back to NAD+. The electron transport chain generates a proton gradient that drives the synthesis of 5 ATP molecules from ADP and Pi. Further more, the pyruvate for ...
General Amino Acid Metabolism
... The first step in the catabolism of most amino acids is the transfer of their α - amino group to α -ketoglutarate where the products are α - ketoacids and glutamate. This transfer of amino groups from one carbon skeleton to another is catalyzed by a family of transaminases which are also called amin ...
... The first step in the catabolism of most amino acids is the transfer of their α - amino group to α -ketoglutarate where the products are α - ketoacids and glutamate. This transfer of amino groups from one carbon skeleton to another is catalyzed by a family of transaminases which are also called amin ...
17. Amino acids are precursors of many specialized biomolecules
... 28. dTMP is synthesized by methylation of dUMP • dUTP is first formed from either dUDP (via phosphorylation) or dCTP (via deamination). • dUMP is then formed from dUTP in a reaction catalyzed by dUTPase (keeping dUTP at a low level to prevent its incorporation into DNA). • dUMP is then converted to ...
... 28. dTMP is synthesized by methylation of dUMP • dUTP is first formed from either dUDP (via phosphorylation) or dCTP (via deamination). • dUMP is then formed from dUTP in a reaction catalyzed by dUTPase (keeping dUTP at a low level to prevent its incorporation into DNA). • dUMP is then converted to ...
Participation of DDDD and KPAR
... in the LCL environment. The metagenome-derived MerA enzyme (ATII-LCL MerA) has simple and limited alterations in its primary structure relative to that of an ortholog from uncultured soil bacterium. Both enzymes are >91% identical and 67% of the substitutions in the ATII-LCL enzyme are acidic residu ...
... in the LCL environment. The metagenome-derived MerA enzyme (ATII-LCL MerA) has simple and limited alterations in its primary structure relative to that of an ortholog from uncultured soil bacterium. Both enzymes are >91% identical and 67% of the substitutions in the ATII-LCL enzyme are acidic residu ...
1 Proteins: Workshop I Amino Acids
... investigate the structure of amino acids and how they affect the structure of a protein. We will also investigate the affect of structure on the function of a protein. Why learn about proteins? Of the three classes of biomolecules - lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins – proteins have some of the mos ...
... investigate the structure of amino acids and how they affect the structure of a protein. We will also investigate the affect of structure on the function of a protein. Why learn about proteins? Of the three classes of biomolecules - lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins – proteins have some of the mos ...
The following equations and constants may be useful:
... a 10 µM solution of this protein at λ=280 nm, assuming a path length of 1 cm. The extinction coefficients (molar absorption coefficients) can be found on the face page. ...
... a 10 µM solution of this protein at λ=280 nm, assuming a path length of 1 cm. The extinction coefficients (molar absorption coefficients) can be found on the face page. ...
7.6 Hydrolysis of Amides
... and most of the penicillin drugs currently used (penicillin V and amoxicillin) survive exposure in the hydrochloric acid in the stomach. (Admittedly, since they all still have the strained 4-membered amide ring, it isn’t obvious why that should be the case.) ...
... and most of the penicillin drugs currently used (penicillin V and amoxicillin) survive exposure in the hydrochloric acid in the stomach. (Admittedly, since they all still have the strained 4-membered amide ring, it isn’t obvious why that should be the case.) ...
revised
... Using the TMHMM program, a total of 21473 TMs for the mesophilic set of proteins and 13340 for the thermophilic organims were predicted. The average length of the predicted TMs was 22 for both sets of proteins (thermophilic and mesophilic), which is in good agreement with the average length of TMs p ...
... Using the TMHMM program, a total of 21473 TMs for the mesophilic set of proteins and 13340 for the thermophilic organims were predicted. The average length of the predicted TMs was 22 for both sets of proteins (thermophilic and mesophilic), which is in good agreement with the average length of TMs p ...
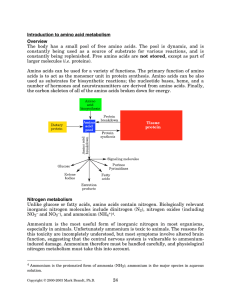
Introduction to amino acid metabolism Overview - Rose
... to a-ketoglutarate, glutamate, and glycine. All other amino acids receive their nitrogen by transfer of organic nitrogen from one amino acid to another. In amino acid metabolism, the most common nitrogen donor is glutamate, and the most common acceptor is a-ketoglutarate. This is logical, since glut ...
... to a-ketoglutarate, glutamate, and glycine. All other amino acids receive their nitrogen by transfer of organic nitrogen from one amino acid to another. In amino acid metabolism, the most common nitrogen donor is glutamate, and the most common acceptor is a-ketoglutarate. This is logical, since glut ...
The following equations and constants may be useful:
... a 10 M solution of this protein at =280 nm, assuming a path length of 1 cm. The extinction coefficients (molar absorption coefficients) can be found on the face page. ...
... a 10 M solution of this protein at =280 nm, assuming a path length of 1 cm. The extinction coefficients (molar absorption coefficients) can be found on the face page. ...
PLP-dependent Enzymes: a Powerful Tool for - Beilstein
... and evolutionary pressure may have worked to shape enzymes’ active sites so as to confer narrower substrate and reaction specificity. Catalytic promiscuity offers very important biotechnological opportunities. Many enzymes may be used as such for the enzymatic synthesis of unnatural compounds. Alter ...
... and evolutionary pressure may have worked to shape enzymes’ active sites so as to confer narrower substrate and reaction specificity. Catalytic promiscuity offers very important biotechnological opportunities. Many enzymes may be used as such for the enzymatic synthesis of unnatural compounds. Alter ...
Enzymes - Clayton State University
... • All catalysts share three basic properties – They increase reaction rates by lowering the EA required – They form transient, reversible complexes with substrate molecules – They change the rate at which equilibrium is achieved, not the position of the equilibrium ...
... • All catalysts share three basic properties – They increase reaction rates by lowering the EA required – They form transient, reversible complexes with substrate molecules – They change the rate at which equilibrium is achieved, not the position of the equilibrium ...
biochemistry-n-6-protein-metabolism
... 3- When amino acids are degraded, the nitrogen is converted to urea, and the carbon skeletons are classified as either glucogenic (a precursor of glucose) or ketogenic (a precursor of ketone bodies). • Amino acid catabolism Amino acid catabolism occurs in two main stages. • First stage is the remov ...
... 3- When amino acids are degraded, the nitrogen is converted to urea, and the carbon skeletons are classified as either glucogenic (a precursor of glucose) or ketogenic (a precursor of ketone bodies). • Amino acid catabolism Amino acid catabolism occurs in two main stages. • First stage is the remov ...
The Citric acid cycle (2)
... • It also has a central role in gluconeogenesis, lipogenesis, and interconversion of amino acids. – So, components of the cycle have a direct or indirect controlling effects in key enzymes of other pathways. ...
... • It also has a central role in gluconeogenesis, lipogenesis, and interconversion of amino acids. – So, components of the cycle have a direct or indirect controlling effects in key enzymes of other pathways. ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.