Structure, mechanism and function of prenyltransferases
... sequences of these enzymes show amino-acid sequence homology and two common DDxxD motifs [47], suggesting that they evolved from the same origin (Fig. 2) [48,49]. These Asp-rich motifs were recognized from the 3D structure [50] and site-directed mutagenesis studies [51–56] to be involved in substrat ...
... sequences of these enzymes show amino-acid sequence homology and two common DDxxD motifs [47], suggesting that they evolved from the same origin (Fig. 2) [48,49]. These Asp-rich motifs were recognized from the 3D structure [50] and site-directed mutagenesis studies [51–56] to be involved in substrat ...
INDUCIBLE INOS)
... a substrate of iNOS (PDB: 1NSI), and naproxen as an inhibitor to COX-2 (PDB: 3NT1) were conducted to ensure whether the method is valid. The amino acid residues that bind compounds produced by the re-docking process are then compared with amino acid residues that bind crystal molecules, with RMSD th ...
... a substrate of iNOS (PDB: 1NSI), and naproxen as an inhibitor to COX-2 (PDB: 3NT1) were conducted to ensure whether the method is valid. The amino acid residues that bind compounds produced by the re-docking process are then compared with amino acid residues that bind crystal molecules, with RMSD th ...
exam1ans_2007 - algebra
... Asp and Lys). This is largely an enthalpic (ΔH) effect. It has very little influence on stabi lizing either the folded or unfolded form of the protein, all other effects are more important. i) the hydrophobic effect ii) hydrogen bonds iii) van der Waals forces iv) Conformational entropy i) the hydro ...
... Asp and Lys). This is largely an enthalpic (ΔH) effect. It has very little influence on stabi lizing either the folded or unfolded form of the protein, all other effects are more important. i) the hydrophobic effect ii) hydrogen bonds iii) van der Waals forces iv) Conformational entropy i) the hydro ...
A novel assay method for an amino acid racemase reaction based
... The new assay method established in the present study for the measurement of the catalytic activity of ALR is based on the CD spectra of both enantiomers of Ala. The method is highly quantitative and provides visible data that reflect the exhaustive reaction of ALR. We conclude that the CD assay met ...
... The new assay method established in the present study for the measurement of the catalytic activity of ALR is based on the CD spectra of both enantiomers of Ala. The method is highly quantitative and provides visible data that reflect the exhaustive reaction of ALR. We conclude that the CD assay met ...
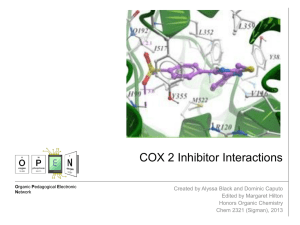
COX 2 Inhibitor Interactions - Center for Selective C–H
... Aspirin can act as a COX-2 inhibitor, yet it is not as selective as most COX-2 inhibitors. Thus, it will also react with COX-1 enzymes, causing undesired side effects. When aspirin interacts with the COX-2 active site, it permanently acetylates a residue in the active site, according to the followin ...
... Aspirin can act as a COX-2 inhibitor, yet it is not as selective as most COX-2 inhibitors. Thus, it will also react with COX-1 enzymes, causing undesired side effects. When aspirin interacts with the COX-2 active site, it permanently acetylates a residue in the active site, according to the followin ...
Allosteric pathways in imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase
... llostery is a fundamental property that allows for the regulation of function and dynamic adaptability of enzymes and proteins. Allosteric enzymes contain at least two distant binding sites, including the active site responsible for catalytic activity, which binds the substrate, and the allosteric s ...
... llostery is a fundamental property that allows for the regulation of function and dynamic adaptability of enzymes and proteins. Allosteric enzymes contain at least two distant binding sites, including the active site responsible for catalytic activity, which binds the substrate, and the allosteric s ...
Nucleotides
... • The coenzyme is covalently attached to a flexible lysine sidechain in the enzyme active site. O HN ...
... • The coenzyme is covalently attached to a flexible lysine sidechain in the enzyme active site. O HN ...
Calvin Cycle
... phosphate from the active site, and carbamate formation. Since photosynthetic light reactions produce ATP, the ATP dependence of RuBisCO activation provides a mechanism for light-dependent activation of the enzyme. The activase is a member of the AAA family of ATPases, many of which have chaperone-l ...
... phosphate from the active site, and carbamate formation. Since photosynthetic light reactions produce ATP, the ATP dependence of RuBisCO activation provides a mechanism for light-dependent activation of the enzyme. The activase is a member of the AAA family of ATPases, many of which have chaperone-l ...
04. Proteins
... Group 2. Amino acids with polar, uncharged side chains Serine, cysteine, threonine, tyrosine, asparagine, glutamine Side chains of these amino acids have heteroatom (N, O or S) with electron pair available for hydrogen bonding to water and other molecules ...
... Group 2. Amino acids with polar, uncharged side chains Serine, cysteine, threonine, tyrosine, asparagine, glutamine Side chains of these amino acids have heteroatom (N, O or S) with electron pair available for hydrogen bonding to water and other molecules ...
Inhibition by D-Glutamate of Growth and Glutamate
... (the last by filtration) and added aseptically to the sterile medium. Strains. Most of the work was done with strain no. I from the collection of the Bacteriology Department which was sensitive to D-gh. Some experiments were done with the wild-type strain no. 262 (STA-4)obtained from Dr B. D. Sanwal ...
... (the last by filtration) and added aseptically to the sterile medium. Strains. Most of the work was done with strain no. I from the collection of the Bacteriology Department which was sensitive to D-gh. Some experiments were done with the wild-type strain no. 262 (STA-4)obtained from Dr B. D. Sanwal ...
Inhibition by D-Glutamate of Growth and Glutamate
... (the last by filtration) and added aseptically to the sterile medium. Strains. Most of the work was done with strain no. I from the collection of the Bacteriology Department which was sensitive to D-gh. Some experiments were done with the wild-type strain no. 262 (STA-4)obtained from Dr B. D. Sanwal ...
... (the last by filtration) and added aseptically to the sterile medium. Strains. Most of the work was done with strain no. I from the collection of the Bacteriology Department which was sensitive to D-gh. Some experiments were done with the wild-type strain no. 262 (STA-4)obtained from Dr B. D. Sanwal ...
Uric acid estimation in plasma
... monosodium urate needle-like crystals on the joint linings and in soft tissues around it (especialy those of the big toe) skin, kidney and other tissues. ...
... monosodium urate needle-like crystals on the joint linings and in soft tissues around it (especialy those of the big toe) skin, kidney and other tissues. ...
Peptide Design Strategy
... Human T-cell Leukemia Virus 1 Protease (HTLV PR), a 126 amino acid sequence having complex ...
... Human T-cell Leukemia Virus 1 Protease (HTLV PR), a 126 amino acid sequence having complex ...
The Synthesis and Degradation of Nucleotides
... synthesized in adequate and balanced amounts. This enzyme contains an Activity Site, a Specificity Site, and the catalytic site. The Activity Site turns the enzyme “ON” or “OFF”; the Specificity Site controls which nucleotide will be reduced; and the catalytic site performs the reduction. When the A ...
... synthesized in adequate and balanced amounts. This enzyme contains an Activity Site, a Specificity Site, and the catalytic site. The Activity Site turns the enzyme “ON” or “OFF”; the Specificity Site controls which nucleotide will be reduced; and the catalytic site performs the reduction. When the A ...
Estimation of the dietary essential amino acid requirements
... Gurure et al., 2007), because there is high correlation between the content of dietary amino acids required determined using dose-response experiments and that of amino acids in the whole body tissue (Wilson & Poe, ...
... Gurure et al., 2007), because there is high correlation between the content of dietary amino acids required determined using dose-response experiments and that of amino acids in the whole body tissue (Wilson & Poe, ...
Crude protein and amino acids content in some common
... that Oreochromis sp. can be used as a feed for juvenile grouper (Epinephelus coioides (Hamilton, 1822)). In addition, Sugama et al (2008) reported that shrimp (Mesopodytes sp.) can be consumed effectively by the grouper juvenile. However, further studies are needed to evaluate the role of these diet ...
... that Oreochromis sp. can be used as a feed for juvenile grouper (Epinephelus coioides (Hamilton, 1822)). In addition, Sugama et al (2008) reported that shrimp (Mesopodytes sp.) can be consumed effectively by the grouper juvenile. However, further studies are needed to evaluate the role of these diet ...
Essentials of Glycobiology Lecture 42 June 9, 1998 Jeff Esko
... ManNH2-Man-GlcN-PI is a poor substrate for the a2mannosyltransferase Trypanosomes selectively take up and exchange fatty acid analogs (10-(propoxy)decanoic acid) for acyl chains on glycosylphosphatidylinositol O O HO ...
... ManNH2-Man-GlcN-PI is a poor substrate for the a2mannosyltransferase Trypanosomes selectively take up and exchange fatty acid analogs (10-(propoxy)decanoic acid) for acyl chains on glycosylphosphatidylinositol O O HO ...
Lesson 8. Enzymes
... Enzymes are protein catalyst produced by a cell and responsible ‘for the high rate’ and specificity of one or more intracellular or extracellular biochemical reactions. Enzymes are biological catalysts responsible for supporting almost all of the chemical reactions that maintain animal homeostasis. ...
... Enzymes are protein catalyst produced by a cell and responsible ‘for the high rate’ and specificity of one or more intracellular or extracellular biochemical reactions. Enzymes are biological catalysts responsible for supporting almost all of the chemical reactions that maintain animal homeostasis. ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.