The experience of Banamex: French bankers and banking models in
... which focuses on Mexico, the latter are placed at center stage through a brief case study of the largest bank in the country -Banco Nacional de México -during the period 1882 to 1910. It should be noted, however, that this was not the first bank established in Mexico. Another paper in this same sess ...
... which focuses on Mexico, the latter are placed at center stage through a brief case study of the largest bank in the country -Banco Nacional de México -during the period 1882 to 1910. It should be noted, however, that this was not the first bank established in Mexico. Another paper in this same sess ...
(2) Trade Policy and Investment Framework
... Mexico has 12 preferential agreements with 44 countries; the agreements with Japan and Uruguay were signed during the period under review. Preferential agreements have led to the substantial liberalization of Mexico's trade regime. Nevertheless, their large number has altered economic incentives and ...
... Mexico has 12 preferential agreements with 44 countries; the agreements with Japan and Uruguay were signed during the period under review. Preferential agreements have led to the substantial liberalization of Mexico's trade regime. Nevertheless, their large number has altered economic incentives and ...
Project Name - World bank documents
... [ ] A [ ] B [X] C [ ] FI [ ] TBD [ ] S1 [ ] S2 [X] S3 [ ] SF [ ] TBD March 2, 2005 February 18, 2005 May 19, 2005 ...
... [ ] A [ ] B [X] C [ ] FI [ ] TBD [ ] S1 [ ] S2 [X] S3 [ ] SF [ ] TBD March 2, 2005 February 18, 2005 May 19, 2005 ...
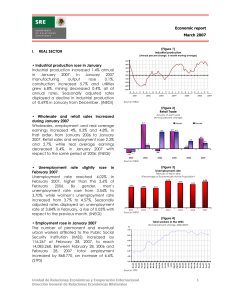
Quarterly report
... The ratio of private-sector bank lending to GDP is a mere 56% (source: Bank for International Settlements, 2016), and lending is showing healthy, sustainable growth. Moreover, private-sector banks have high profit margins. On the other hand, because the country’s public-sector banks lack the capital ...
... The ratio of private-sector bank lending to GDP is a mere 56% (source: Bank for International Settlements, 2016), and lending is showing healthy, sustainable growth. Moreover, private-sector banks have high profit margins. On the other hand, because the country’s public-sector banks lack the capital ...
Pugel Chapter 19 Problems What Determines Exchange Rates ?
... a. Since there is no interest differential between US and Japanese bonds, there should be no difference between the current spot rate and the expected forward rate. b. Expected dollar appreciation (it will cost less to buy one yen -- not one cent but 0.95 cents) is more considerable than the fourth ...
... a. Since there is no interest differential between US and Japanese bonds, there should be no difference between the current spot rate and the expected forward rate. b. Expected dollar appreciation (it will cost less to buy one yen -- not one cent but 0.95 cents) is more considerable than the fourth ...
Corporate Presentation
... • Founded in 1967, with leading position in high value-added dairy: flavored milk and yogurt • 50/50 Joint Venture with TCCC • Consolidating AC as one of the most important consumer companies in Ecuador ...
... • Founded in 1967, with leading position in high value-added dairy: flavored milk and yogurt • 50/50 Joint Venture with TCCC • Consolidating AC as one of the most important consumer companies in Ecuador ...
MEXICO`S MARKET REFORMS: PROGRESS AND CHALLENGES
... Q: What was the politics of reform in Mexico? Often it is an economic crisis that pushes politicians into initiating reform, was that the case in Mexico? And how did the President push the reforms through in the face of opposition parties? There was no economic crisis in the usual sense that provide ...
... Q: What was the politics of reform in Mexico? Often it is an economic crisis that pushes politicians into initiating reform, was that the case in Mexico? And how did the President push the reforms through in the face of opposition parties? There was no economic crisis in the usual sense that provide ...
Mexico`s new challenges under shifts on the US politics and policy
... The immediate effects of Trump’s policy proposals would be for Mexican exports to decline, a reduction of FDI, and potentially a weakening in remittances sent back to Mexico. The precise magnitude of these changes is difficult to forecast until more concrete proposals are put forward by the Trump ad ...
... The immediate effects of Trump’s policy proposals would be for Mexican exports to decline, a reduction of FDI, and potentially a weakening in remittances sent back to Mexico. The precise magnitude of these changes is difficult to forecast until more concrete proposals are put forward by the Trump ad ...
Mexico`s new challenges under shifts on the US
... The immediate effects of Trump’s policy proposals would be for Mexican exports to decline, a reduction of FDI, and potentially a weakening in remittances sent back to Mexico. The precise magnitude of these changes is difficult to forecast until more concrete proposals are put forward by the Trump ad ...
... The immediate effects of Trump’s policy proposals would be for Mexican exports to decline, a reduction of FDI, and potentially a weakening in remittances sent back to Mexico. The precise magnitude of these changes is difficult to forecast until more concrete proposals are put forward by the Trump ad ...
The Mexican Economic Crisis: Alternative Views
... How are overvaluation, trade deficits, and economic crises related? According to conventional macroeconomic theory, an overvalued currency produces current account deficits by making a country’s exports more expensive and its imports cheaper and also by artificially increasing the real value (at int ...
... How are overvaluation, trade deficits, and economic crises related? According to conventional macroeconomic theory, an overvalued currency produces current account deficits by making a country’s exports more expensive and its imports cheaper and also by artificially increasing the real value (at int ...
Assignment 3
... rate (peso/$) turns out to be lower than the exchange rate that would be obtained had the exchange rate been allowed to float freely. What implications does this have for the Mexican money supply and the Mexican central bank’s holdings of foreign reserves (dollar assets)? Answer: The only way to kee ...
... rate (peso/$) turns out to be lower than the exchange rate that would be obtained had the exchange rate been allowed to float freely. What implications does this have for the Mexican money supply and the Mexican central bank’s holdings of foreign reserves (dollar assets)? Answer: The only way to kee ...
Manuel Sánchez: Mexico`s economic modernization and outlook
... Elements that may support these forecasts include better expected economic prospects for the United States and the reactivation of government investment.5 However, there are downward risks to this scenario, including a further decline in consumer confidence; the time needed to restructure the housin ...
... Elements that may support these forecasts include better expected economic prospects for the United States and the reactivation of government investment.5 However, there are downward risks to this scenario, including a further decline in consumer confidence; the time needed to restructure the housin ...
“Doing Business in Mexico:
... • In January 1994, Mexico joined Canada and the United States in the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which will phase out all tariffs over a 15-year period. • The highest starting tariff was 20% and it is being reduced each year in accordance with the NAFTA program. Since its implementa ...
... • In January 1994, Mexico joined Canada and the United States in the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which will phase out all tariffs over a 15-year period. • The highest starting tariff was 20% and it is being reduced each year in accordance with the NAFTA program. Since its implementa ...
Document
... international reserves have raised 1,650 md. (Banxico) • Mexico’s stock market displays a growing path Mexico’s Stock Market Index (IPyC) rose 1.68% in February 23, reaching 28,747.69 points. The IPyC showed a cumulative profit of 8.69% in Mexican pesos and 6.52% in US dollars with respect to the en ...
... international reserves have raised 1,650 md. (Banxico) • Mexico’s stock market displays a growing path Mexico’s Stock Market Index (IPyC) rose 1.68% in February 23, reaching 28,747.69 points. The IPyC showed a cumulative profit of 8.69% in Mexican pesos and 6.52% in US dollars with respect to the en ...
* Director del equipo de Planeación y Evaluación de la Rectoría
... Economics define international competitiveness as a nation’s ability to offer supplies that will maintain or increase their share in the external trade market. There are several economic, social, and political-administrative factors that influence this dynamic capacity. Monetary policy, for example, ...
... Economics define international competitiveness as a nation’s ability to offer supplies that will maintain or increase their share in the external trade market. There are several economic, social, and political-administrative factors that influence this dynamic capacity. Monetary policy, for example, ...
Economics 3403 - University of Colorado Boulder
... would also step in to cover creditor losses in the event of default. Most economists trace this confidence to the US-IMF response to the Mexican peso crisis of 1994-95. The Mexican government ran a very expansionary policy in 1994 to ensure re-election of the ruling party (the PRI). But they also re ...
... would also step in to cover creditor losses in the event of default. Most economists trace this confidence to the US-IMF response to the Mexican peso crisis of 1994-95. The Mexican government ran a very expansionary policy in 1994 to ensure re-election of the ruling party (the PRI). But they also re ...
Mexico
... • By 1995, past due amount on bank loans had risen to 18% of the loans. • At year end of 1995, overdue loans had also risen to account for 1/3 of total bank loans. • Problems within the banking system were compounded by the instability of the financial market. • The Mexican Crisis was further upset ...
... • By 1995, past due amount on bank loans had risen to 18% of the loans. • At year end of 1995, overdue loans had also risen to account for 1/3 of total bank loans. • Problems within the banking system were compounded by the instability of the financial market. • The Mexican Crisis was further upset ...
Mexico`s currency depreciation vs. Latin America
... negative impact on the economy will last some years. The household debt problem in the US has not been solved and its impact will affect the economy in the years to come. ...
... negative impact on the economy will last some years. The household debt problem in the US has not been solved and its impact will affect the economy in the years to come. ...
Chapter 38 Key Question Solutions
... payments into balance-no need for intervention (the current account deficit is counterbalanced by the capital account). If this country wishes to reduce its current account deficit it must make its currency ‘cheaper’ on the market. That is, it must intervene in a way that causes its currency to depr ...
... payments into balance-no need for intervention (the current account deficit is counterbalanced by the capital account). If this country wishes to reduce its current account deficit it must make its currency ‘cheaper’ on the market. That is, it must intervene in a way that causes its currency to depr ...
Monthly Report on Banking and Financial System
... term deposits may be associated with an increase in household savings, both on account of expectations of negative shocks to their income in view of the reduced dynamism of economic activity and as a result of higher interest rates which make savings in term instruments more attractive. At the end o ...
... term deposits may be associated with an increase in household savings, both on account of expectations of negative shocks to their income in view of the reduced dynamism of economic activity and as a result of higher interest rates which make savings in term instruments more attractive. At the end o ...
The International Monetary and Financial Policies of the Clinton
... Moreover, since expectations of higher import prices were a factor to which the Federal Reserve looked when forecasting inflation, a falling dollar fanned fears among financial-market participants of rising Federal Reserve discount rates. For these and other reasons, the belief that the Administrati ...
... Moreover, since expectations of higher import prices were a factor to which the Federal Reserve looked when forecasting inflation, a falling dollar fanned fears among financial-market participants of rising Federal Reserve discount rates. For these and other reasons, the belief that the Administrati ...
ECON403 sample questions for chapters 17 and 19
... 12. Everything else held constant, increased demand for a countryʹs ________ causes its currency to appreciate in the long run, while increased demand for ________ causes its currency to depreciate. A) imports; imports B) imports; exports C) exports; imports D) exports; exports ...
... 12. Everything else held constant, increased demand for a countryʹs ________ causes its currency to appreciate in the long run, while increased demand for ________ causes its currency to depreciate. A) imports; imports B) imports; exports C) exports; imports D) exports; exports ...
A Pre-NAFTA Assessment
... • The changing structure, composition and composition of production in Mexico • Uneven regional economic impact – Northern border versus other areas • A challenge to Mexico’s historic nationalism • Compromises future policy options in terms of the external debt situation ...
... • The changing structure, composition and composition of production in Mexico • Uneven regional economic impact – Northern border versus other areas • A challenge to Mexico’s historic nationalism • Compromises future policy options in terms of the external debt situation ...
Lustigre - University of Maryland Department of Economics
... middle income groups seemed to fare worse during the crisis, even worse than the poor in terms of the drop in the percentage of income to the lowest 40% relative to the next 50 % in the income distribution (p. 92). ...
... middle income groups seemed to fare worse during the crisis, even worse than the poor in terms of the drop in the percentage of income to the lowest 40% relative to the next 50 % in the income distribution (p. 92). ...