Complex Piping Design Guide
... gathered in Step 1 can now be applied to determine which cable(s) meet or exceed the requirements. For installations in hazardous (classified) areas (see Approvals at right), the heating cable may also be required to meet a temperature classification rating, T-rating, to ensure safe operation even d ...
... gathered in Step 1 can now be applied to determine which cable(s) meet or exceed the requirements. For installations in hazardous (classified) areas (see Approvals at right), the heating cable may also be required to meet a temperature classification rating, T-rating, to ensure safe operation even d ...
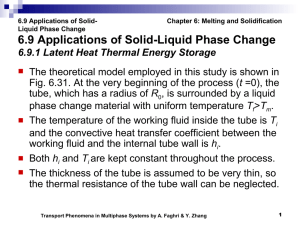
Applications of Solid-Liquid Phase Change - Thermal
... Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with wavelengths ranging from 1 cm to 1 m. The heat generation within the microwave-irradiated frozen materials results from dipole excitation and ion migration. There may also be other mechanisms of interaction between the material and the electromagnetic field ...
... Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with wavelengths ranging from 1 cm to 1 m. The heat generation within the microwave-irradiated frozen materials results from dipole excitation and ion migration. There may also be other mechanisms of interaction between the material and the electromagnetic field ...
Errors Due to Shared Leadwires in Parallel Strain Gage Circuits
... gauge selection is based on single-conductor (solid) wires, for which there is a well-defined relationship between AWG number and the conductor cross-sectional area. Since the wire is normally drawn to a specified diameter, rather than resistance, precise compensation may require measurement of the ...
... gauge selection is based on single-conductor (solid) wires, for which there is a well-defined relationship between AWG number and the conductor cross-sectional area. Since the wire is normally drawn to a specified diameter, rather than resistance, precise compensation may require measurement of the ...
PowerPoint
... The longer the conductor, the more resistance in that conductor. The smaller the cross-sectional area of a conductor, the more resistance in that conductor. ...
... The longer the conductor, the more resistance in that conductor. The smaller the cross-sectional area of a conductor, the more resistance in that conductor. ...
High Temperature Guide (Rev. E)
... changes to its semiconductor products and services per JESD46, latest issue, and to discontinue any product or service per JESD48, latest issue. Buyers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All semiconduct ...
... changes to its semiconductor products and services per JESD46, latest issue, and to discontinue any product or service per JESD48, latest issue. Buyers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All semiconduct ...
Chapter 22-23 Assignment Solutions
... 42) Compare the amount of current entering a junction in a parallel circuit with that leaving the junction. (A junction is a point where three or more conductors are joined.) (23.1) The amount of current entering a junction is equal to the amount of current leaving the junction. The is known as Kir ...
... 42) Compare the amount of current entering a junction in a parallel circuit with that leaving the junction. (A junction is a point where three or more conductors are joined.) (23.1) The amount of current entering a junction is equal to the amount of current leaving the junction. The is known as Kir ...
General-Purpose Failsafe Moulded Wirewound Resistors
... All resistor types have resistance alloy winding on a braided fibreglass substrate. Intermediate silicone coatings are used to enhance processibility and to provide protection to the resistive element. ...
... All resistor types have resistance alloy winding on a braided fibreglass substrate. Intermediate silicone coatings are used to enhance processibility and to provide protection to the resistive element. ...
Document
... The Seebeck effect causes an electrical potential when two dissimilar wires are joined and the end is heated. ...
... The Seebeck effect causes an electrical potential when two dissimilar wires are joined and the end is heated. ...
Lumped element model
The lumped element model (also called lumped parameter model, or lumped component model) simplifies the description of the behaviour of spatially distributed physical systems into a topology consisting of discrete entities that approximate the behaviour of the distributed system under certain assumptions. It is useful in electrical systems (including electronics), mechanical multibody systems, heat transfer, acoustics, etc.Mathematically speaking, the simplification reduces the state space of the system to a finite dimension, and the partial differential equations (PDEs) of the continuous (infinite-dimensional) time and space model of the physical system into ordinary differential equations (ODEs) with a finite number of parameters.