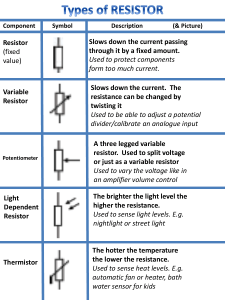
fight heat generated by semiconductors employed in electronic systems
... power transistors, CPUs and power diodes – produce a significant amount of heat and measures may be necessary to take account of this in order to prolong their working life and increase reliability. If we consider a heat producing electronic component in isolation then, its temperature will rise duri ...
... power transistors, CPUs and power diodes – produce a significant amount of heat and measures may be necessary to take account of this in order to prolong their working life and increase reliability. If we consider a heat producing electronic component in isolation then, its temperature will rise duri ...
Q 1: One gram molecule of monoatomic gas is taken at S
... Q 11: When a coil of copper is kept at a certain distance above W1 = W2 ...
... Q 11: When a coil of copper is kept at a certain distance above W1 = W2 ...
Lab_Thermometric properties
... a plastic tool handle on a cold day can be done with bare hands without too much discomfort, however a metal bar setting next to the tool handle will be quite uncomfortable. If one wishes to communicate the coldness of the objects, it is difficult to do unless the exact same situation is available t ...
... a plastic tool handle on a cold day can be done with bare hands without too much discomfort, however a metal bar setting next to the tool handle will be quite uncomfortable. If one wishes to communicate the coldness of the objects, it is difficult to do unless the exact same situation is available t ...
High Temperature Specific Components
... Leakage current in a semiconductor junction is heavily dependent on temperature. This means that isolation will be lost at high temperature in a junction isolated process while an SOI-process is still operational. Elevated temperature also accelerates ageing effects in an integrated circuit. One exa ...
... Leakage current in a semiconductor junction is heavily dependent on temperature. This means that isolation will be lost at high temperature in a junction isolated process while an SOI-process is still operational. Elevated temperature also accelerates ageing effects in an integrated circuit. One exa ...
10th Electricity – Remember these terms before solving Numerical problems
... 4. If the current I, flowing in a metallic wire and the potential difference across its terminals is V . Then potential difference, V, across the ends of a given metallic wire in an electric circuit is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, provided its temperature remains the same ...
... 4. If the current I, flowing in a metallic wire and the potential difference across its terminals is V . Then potential difference, V, across the ends of a given metallic wire in an electric circuit is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, provided its temperature remains the same ...
Techniques for Thermal Analysis of Switching Power
... the exact same temperature by driving them individually. For example, we would drive the inductor with a DC current so that in steady state we would get the same infrared temperature measurement. The dissipated power needed to warm the device up to the same level as with the complete power design ru ...
... the exact same temperature by driving them individually. For example, we would drive the inductor with a DC current so that in steady state we would get the same infrared temperature measurement. The dissipated power needed to warm the device up to the same level as with the complete power design ru ...
dms application note 8 - Murata Power Solutions
... ambient temperature, i.e., at +77°F (+25°C), the LM34’s output is 0.77Vdc while the LM35’s is 0.25Vdc. Neither device requires any external calibration or trimming circuits to provide typical accuracies of ±½°F (±¼°C) at room temperature and ±1½°F (±¾°C) over a full –50 to +300°F (–55 to +150°C) ope ...
... ambient temperature, i.e., at +77°F (+25°C), the LM34’s output is 0.77Vdc while the LM35’s is 0.25Vdc. Neither device requires any external calibration or trimming circuits to provide typical accuracies of ±½°F (±¼°C) at room temperature and ±1½°F (±¾°C) over a full –50 to +300°F (–55 to +150°C) ope ...
Lumped element model
The lumped element model (also called lumped parameter model, or lumped component model) simplifies the description of the behaviour of spatially distributed physical systems into a topology consisting of discrete entities that approximate the behaviour of the distributed system under certain assumptions. It is useful in electrical systems (including electronics), mechanical multibody systems, heat transfer, acoustics, etc.Mathematically speaking, the simplification reduces the state space of the system to a finite dimension, and the partial differential equations (PDEs) of the continuous (infinite-dimensional) time and space model of the physical system into ordinary differential equations (ODEs) with a finite number of parameters.