L00D MGS8110 Statist.. - Georgia State University
... consistent. The 5% values calculated as Mean – 2(Sigma) was 5’-5” where as the 1% value calculated as a Percentile was 5’-6”. Answer – These types of inconsistencies (i.e., errors) will occur with small samples. The procedure used by the PERCENTILE function is based on an interpolated calculation wi ...
... consistent. The 5% values calculated as Mean – 2(Sigma) was 5’-5” where as the 1% value calculated as a Percentile was 5’-6”. Answer – These types of inconsistencies (i.e., errors) will occur with small samples. The procedure used by the PERCENTILE function is based on an interpolated calculation wi ...
Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals for Two Populations
... First, I observe that the sample sizes both exceed 30. This is important. If the sample sizes equal or exceed 30, the central theorem may be assumed, which in turn assures the distributions are normally distributed. Both sample sizes must be equal to or exceed 30 for me to apply the large size sampl ...
... First, I observe that the sample sizes both exceed 30. This is important. If the sample sizes equal or exceed 30, the central theorem may be assumed, which in turn assures the distributions are normally distributed. Both sample sizes must be equal to or exceed 30 for me to apply the large size sampl ...
Article (Author postprint)
... After much exertion and care to run an experiment in social science, the analysis of data should not be ruined by an improper analysis. Often, classical methods, like the mean, the usual simple and multiple linear regressions, and the ANOVA require normality and absence of outliers, which rarely occ ...
... After much exertion and care to run an experiment in social science, the analysis of data should not be ruined by an improper analysis. Often, classical methods, like the mean, the usual simple and multiple linear regressions, and the ANOVA require normality and absence of outliers, which rarely occ ...
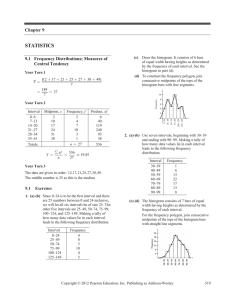
Descriptive Statistics Frequency Distributions and Their Graphs
... drawn through the middle of a graph of the distribution and the resulting halves are approximately the mirror images. A frequency distribution is uniform (or rectangular) when all entries, or classes, in the distribution have equal frequencies. A uniform distribution is also symmetric. A frequency d ...
... drawn through the middle of a graph of the distribution and the resulting halves are approximately the mirror images. A frequency distribution is uniform (or rectangular) when all entries, or classes, in the distribution have equal frequencies. A uniform distribution is also symmetric. A frequency d ...
Chapter 2: Descriptive Statistics
... can be drawn through the middle of a graph of the distribution and the resulting halves are approximately the mirror images. A frequency distribution is uniform (or rectangular) when all entries, or classes, in the distribution have equal frequencies. A uniform distribution is also symmetric. A freq ...
... can be drawn through the middle of a graph of the distribution and the resulting halves are approximately the mirror images. A frequency distribution is uniform (or rectangular) when all entries, or classes, in the distribution have equal frequencies. A uniform distribution is also symmetric. A freq ...
statistics - Anvari.Net
... are 25 numbers between 0 and 24 inclusive, we will let all six intervals be of size 25. The other five intervals are 25–49, 50–74, 75–99, 100–124, and 125–149. Making a tally of how many data values lie in each interval leads to the following frequency distribution. ...
... are 25 numbers between 0 and 24 inclusive, we will let all six intervals be of size 25. The other five intervals are 25–49, 50–74, 75–99, 100–124, and 125–149. Making a tally of how many data values lie in each interval leads to the following frequency distribution. ...
Bootstrapping (statistics)

In statistics, bootstrapping can refer to any test or metric that relies on random sampling with replacement. Bootstrapping allows assigning measures of accuracy (defined in terms of bias, variance, confidence intervals, prediction error or some other such measure) to sample estimates. This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods. Generally, it falls in the broader class of resampling methods.Bootstrapping is the practice of estimating properties of an estimator (such as its variance) by measuring those properties when sampling from an approximating distribution. One standard choice for an approximating distribution is the empirical distribution function of the observed data. In the case where a set of observations can be assumed to be from an independent and identically distributed population, this can be implemented by constructing a number of resamples with replacement, of the observed dataset (and of equal size to the observed dataset).It may also be used for constructing hypothesis tests. It is often used as an alternative to statistical inference based on the assumption of a parametric model when that assumption is in doubt, or where parametric inference is impossible or requires complicated formulas for the calculation of standard errors.