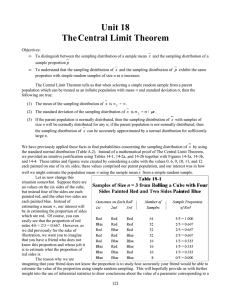
Introduction to Statistics
... of 0.04. What does this mean? It means that there is a 0.04 or 4% chance that the difference between the two means is due to chance. This is very different from the first case. In general, when scientists see that there is a p-value of less than 0.05, they accept that the differences between the two ...
... of 0.04. What does this mean? It means that there is a 0.04 or 4% chance that the difference between the two means is due to chance. This is very different from the first case. In general, when scientists see that there is a p-value of less than 0.05, they accept that the differences between the two ...
Sampling Distribution
... The article describing the poll says that it “is based on telephone interviews conducted from Sept. 13 to Sept. 18 with 1,664 adults around the United States, excluding Alaska and Hawaii…The telephone numbers were formed by random digits, thus permitting access to both listed and unlisted residentia ...
... The article describing the poll says that it “is based on telephone interviews conducted from Sept. 13 to Sept. 18 with 1,664 adults around the United States, excluding Alaska and Hawaii…The telephone numbers were formed by random digits, thus permitting access to both listed and unlisted residentia ...
CORP: Minimizing the chances of false positives
... hypothesis—we get a false positive— or we can fail to reject a false null hypothesis—we get a false negative.1 We control the chance that we get a false positive when we define the critical significance level ␣, the probability that we reject the null hypothesis given that the null hypothesis is tru ...
... hypothesis—we get a false positive— or we can fail to reject a false null hypothesis—we get a false negative.1 We control the chance that we get a false positive when we define the critical significance level ␣, the probability that we reject the null hypothesis given that the null hypothesis is tru ...