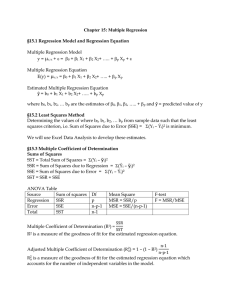
Power 10
... Procedure for Regression Diagnostics • Develop a model that has a theoretical basis. • Gather data for the two variables in the model. • Draw the scatter diagram to determine whether a linear model appears to be appropriate. • Determine the regression equation. • Check the required conditions for t ...
... Procedure for Regression Diagnostics • Develop a model that has a theoretical basis. • Gather data for the two variables in the model. • Draw the scatter diagram to determine whether a linear model appears to be appropriate. • Determine the regression equation. • Check the required conditions for t ...
Stat 2501 - Ohio Northern University
... Point estimation, confidence intervals, and hypotheses tests: for a single mean for the difference between two means (independent and paired samples) for the ratio of two variances (optional) for a single proportion and the difference of two proportions (both optional) Study design Experimental vs. ...
... Point estimation, confidence intervals, and hypotheses tests: for a single mean for the difference between two means (independent and paired samples) for the ratio of two variances (optional) for a single proportion and the difference of two proportions (both optional) Study design Experimental vs. ...
Two-Sample Inference Procedures
... Two competing headache remedies claim to give fastacting relief. An experiment was performed to compare the mean lengths of time required for bodily absorption of brand A and brand B. Assume the absorption time is normally distributed. Twelve people were randomly selected and given an oral dosage o ...
... Two competing headache remedies claim to give fastacting relief. An experiment was performed to compare the mean lengths of time required for bodily absorption of brand A and brand B. Assume the absorption time is normally distributed. Twelve people were randomly selected and given an oral dosage o ...