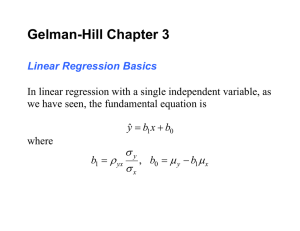
Document
... show the relationship between two variables
Correlation analysis is used to measure
strength of the association (linear
relationship) between two variables
◦ Only concerned with strength of the
...
IBM SPSS Regression 24
... categorical; if categorical, they should be dummy or indicator coded (there is an option in the procedure
to recode categorical variables automatically).
Assumptions. Logistic regression does not rely on distributional assumptions in the same sense that
discriminant analysis does. However, your solu ...
Regression toward the mean
In statistics, regression toward (or to) the mean is the phenomenon that if a variable is extreme on its first measurement, it will tend to be closer to the average on its second measurement—and if it is extreme on its second measurement, it will tend to have been closer to the average on its first. To avoid making incorrect inferences, regression toward the mean must be considered when designing scientific experiments and interpreting data.The conditions under which regression toward the mean occurs depend on the way the term is mathematically defined. Sir Francis Galton first observed the phenomenon in the context of simple linear regression of data points. Galton developed the following model: pellets fall through a quincunx forming a normal distribution centered directly under their entrance point. These pellets could then be released down into a second gallery (corresponding to a second measurement occasion. Galton then asked the reverse question ""from where did these pellets come?"" ""The answer was not 'on average directly above'. Rather it was 'on average, more towards the middle', for the simple reason that there were more pellets above it towards the middle that could wander left than there were in the left extreme that could wander to the right, inwards"" (p 477) A less restrictive approach is possible. Regression towards the mean can be defined for any bivariate distribution with identical marginal distributions. Two such definitions exist. One definition accords closely with the common usage of the term “regression towards the mean”. Not all such bivariate distributions show regression towards the mean under this definition. However, all such bivariate distributions show regression towards the mean under the other definition.Historically, what is now called regression toward the mean has also been called reversion to the mean and reversion to mediocrity.In finance, the term mean reversion has a different meaning. Jeremy Siegel uses it to describe a financial time series in which ""returns can be very unstable in the short run but very stable in the long run."" More quantitatively, it is one in which the standard deviation of average annual returns declines faster than the inverse of the holding period, implying that the process is not a random walk, but that periods of lower returns are systematically followed by compensating periods of higher returns, in seasonal businesses for example.