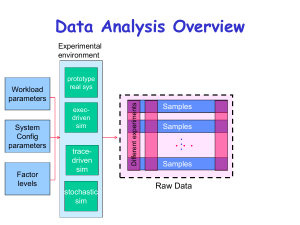
Quiz 1 2pm Class
... describe numerically the center of a distribution. The range, Interquartile Range and the standard deviation help to quantify the variability of a distribution of measures of spread. That’s all true but doesn’t answer the question. For measures of center its preferly to use the mean and the median. ...
... describe numerically the center of a distribution. The range, Interquartile Range and the standard deviation help to quantify the variability of a distribution of measures of spread. That’s all true but doesn’t answer the question. For measures of center its preferly to use the mean and the median. ...
Presentation
... approximately 2.5 people. Question: Which is the standard deviation? (a) 0.014 (b) 0.14 (c) 1.4 (d) 14.0 Response: ( c) 1.4 Hint: Ask if any students grew up in a household with number of people quite close to the mean; what is the distance of that value from the mean? Next, a student whose househol ...
... approximately 2.5 people. Question: Which is the standard deviation? (a) 0.014 (b) 0.14 (c) 1.4 (d) 14.0 Response: ( c) 1.4 Hint: Ask if any students grew up in a household with number of people quite close to the mean; what is the distance of that value from the mean? Next, a student whose househol ...
Section 1.3 Powerpoint
... Another common measure of center is the median. The median describes the midpoint of a distribution. The median, M, is the midpoint of a distribution, the number such that half the observations are smaller and the other half are larger. The median is the midpoint of a distribution, the number such t ...
... Another common measure of center is the median. The median describes the midpoint of a distribution. The median, M, is the midpoint of a distribution, the number such that half the observations are smaller and the other half are larger. The median is the midpoint of a distribution, the number such t ...
CHAPTER 3: NUMERICAL DESCRIPTIVE MEASURES
... empirical rule, while the proportion within one standard deviation of the mean for the female distribution is lower than what would be expected from the empirical rule. Therefore, these distributions may not be mound shaped. 3.22 (a) As have weekly sales for all 52 weeks in the year this is populati ...
... empirical rule, while the proportion within one standard deviation of the mean for the female distribution is lower than what would be expected from the empirical rule. Therefore, these distributions may not be mound shaped. 3.22 (a) As have weekly sales for all 52 weeks in the year this is populati ...