Separate-and-Conquer Rule Learning
... rules starts with a rule whose body is always true. As long as its still covers negative examples the current rule is specialized by adding conditions to its body. Possible conditions are tests on the presence of certain values of various attributes. In order to move towards the goal of finding a ru ...
... rules starts with a rule whose body is always true. As long as its still covers negative examples the current rule is specialized by adding conditions to its body. Possible conditions are tests on the presence of certain values of various attributes. In order to move towards the goal of finding a ru ...
Philosophical Aspects in Pattern Recognition Research
... (e.g., biology and physics) and, even more profoundly, to the philosophical investigation. Hence, it is not surprising that many constitutive documents as well as psychological considerations or biological concepts, includes also many philosophical assertions ([66, 114] spring to mind). The same Dar ...
... (e.g., biology and physics) and, even more profoundly, to the philosophical investigation. Hence, it is not surprising that many constitutive documents as well as psychological considerations or biological concepts, includes also many philosophical assertions ([66, 114] spring to mind). The same Dar ...
Document
... Our Working Definition of AI Artificial intelligence is the study of how to make computers do things that people are better at or would be better at if: • they could extend what they do to a World Wide Web-sized amount of data, and • not make mistakes. ...
... Our Working Definition of AI Artificial intelligence is the study of how to make computers do things that people are better at or would be better at if: • they could extend what they do to a World Wide Web-sized amount of data, and • not make mistakes. ...
Deep Learning for Artificial General Intelligence
... The presentation is organized with a view towards the integration of additional abilities into deep learning architectures, including: planning; reasoning and logic; data efficient learning and one-shot learning; program induction; additional learning algorithms other than backpropagation; more soph ...
... The presentation is organized with a view towards the integration of additional abilities into deep learning architectures, including: planning; reasoning and logic; data efficient learning and one-shot learning; program induction; additional learning algorithms other than backpropagation; more soph ...
Cognitive Science: An Introduction to the Study of Mind
... special. The major ideas that motivate each perspective and the problems each attempts to solve are laid out. Following this, we present factual background information that we believe is important and describe the approach’s methodology. The bulk of each chapter is devoted to detailing the specific ...
... special. The major ideas that motivate each perspective and the problems each attempts to solve are laid out. Following this, we present factual background information that we believe is important and describe the approach’s methodology. The bulk of each chapter is devoted to detailing the specific ...
Artificial Intelligence – Agents and Environments
... AI programming languages and NetLogo Several programming languages have been proposed over the years as being well suited to building computer systems for Artificial Intelligence. Historically, the most notable AI programming languages have been Lisp and Prolog. Lisp (and related dialects such as Co ...
... AI programming languages and NetLogo Several programming languages have been proposed over the years as being well suited to building computer systems for Artificial Intelligence. Historically, the most notable AI programming languages have been Lisp and Prolog. Lisp (and related dialects such as Co ...
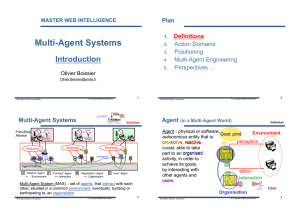
Multi-Agent Systems Introduction
... social, social able to take part to an organised activity, in order to achieve its goals, by interacting with action other agents and Interaction users users. ...
... social, social able to take part to an organised activity, in order to achieve its goals, by interacting with action other agents and Interaction users users. ...
On the Implementation of MIPS
... very common in single state exploration to avoid duplicates in the search. Usually, the memory structure is realized as a hash table which in this context is referred to by the term transposition table. For symbolic search this technique is called forward set simplification. Let reached be the BDD r ...
... very common in single state exploration to avoid duplicates in the search. Usually, the memory structure is realized as a hash table which in this context is referred to by the term transposition table. For symbolic search this technique is called forward set simplification. Let reached be the BDD r ...
integrating ai techniques in sdlc: requirements phase perspective
... AI(E3):Keyword Mapping: Many system development failures occur because the stakeholders cannot describe their requirements correctly, or developers and domain experts neglect “observable” words that contribute basically to system requirements. These challenges can be avoided by mapping each keyword ...
... AI(E3):Keyword Mapping: Many system development failures occur because the stakeholders cannot describe their requirements correctly, or developers and domain experts neglect “observable” words that contribute basically to system requirements. These challenges can be avoided by mapping each keyword ...
Hardness-Aware Restart Policies
... Gomes et al. [7] demonstrated the effectiveness of randomized restarts on a variety of problems in scheduling, theorem-proving, and planning. In this approach, randomness is added to the branching heuristic of a systematic search algorithm; if the search algorithm does not find a solution within a g ...
... Gomes et al. [7] demonstrated the effectiveness of randomized restarts on a variety of problems in scheduling, theorem-proving, and planning. In this approach, randomness is added to the branching heuristic of a systematic search algorithm; if the search algorithm does not find a solution within a g ...
Supervised and unsupervised learning.
... Petr Pošík Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Dept. of Cybernetics This lecture is based on the book Ten Lectures on Statistical and Structural Pattern Recognition ...
... Petr Pošík Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Dept. of Cybernetics This lecture is based on the book Ten Lectures on Statistical and Structural Pattern Recognition ...
Unifying Instance-Based and Rule
... algorithms are prone to be cumbersome, and often achieve accuracies that lie between those of their parents, instead of matching the highest. Here a theoretical question arises. It is well known that no induction algorithm can be the best in all possible domains; each algorithm contains an explicit ...
... algorithms are prone to be cumbersome, and often achieve accuracies that lie between those of their parents, instead of matching the highest. Here a theoretical question arises. It is well known that no induction algorithm can be the best in all possible domains; each algorithm contains an explicit ...
AGAINST NARROW OPTIMIZATION AND SHORT HORIZONS: AN
... [Boehm-Hansen00], and even the mean-maximization subject to variance-limit portfolio methods [Lintner65]. Hundreds of articles appear in on project management with similar sensibilities. This paper is sympathetic to the motivations of these approaches, though not necessarily to the logic or mathemat ...
... [Boehm-Hansen00], and even the mean-maximization subject to variance-limit portfolio methods [Lintner65]. Hundreds of articles appear in on project management with similar sensibilities. This paper is sympathetic to the motivations of these approaches, though not necessarily to the logic or mathemat ...
Knowledge-based Manufacturing Enterprise and Enterprise Knowledge Management
... Knowledge management technology(KMT) is computer-based information technology that can help people produce, store, process and transfer knowledge, which is built on data management and information management technology. KMT makes knowledge management personnel and knowledge workers produce, share, a ...
... Knowledge management technology(KMT) is computer-based information technology that can help people produce, store, process and transfer knowledge, which is built on data management and information management technology. KMT makes knowledge management personnel and knowledge workers produce, share, a ...
Pattern-Database Heuristics for Partially Observable
... Eff is a finite set of partial states eff , the nondeterministic outcomes of a. The application of a nondeterministic outcome eff to a state s is the state app(eff , s) that results from updating s with eff . The application of an effect Eff to s is the set of states app(Eff , s) = {app(eff , s) | e ...
... Eff is a finite set of partial states eff , the nondeterministic outcomes of a. The application of a nondeterministic outcome eff to a state s is the state app(eff , s) that results from updating s with eff . The application of an effect Eff to s is the set of states app(Eff , s) = {app(eff , s) | e ...
LNCS 3258 - Full Dynamic Substitutability by SAT Encoding
... flipping all its occurrences in the problem. These transformations do not affect the solvability or intrinsic hardness of a problem, and can be used to find average behaviour of deterministic solvers. They are also used in solver competitions; for details on them see [10]. We applied them and took m ...
... flipping all its occurrences in the problem. These transformations do not affect the solvability or intrinsic hardness of a problem, and can be used to find average behaviour of deterministic solvers. They are also used in solver competitions; for details on them see [10]. We applied them and took m ...
A comprehensive survey of multi
... in a variety of domains, including robotics, distributed control, telecommunications, and economics. The complexity of many tasks arising in these domains makes them difficult to solve with preprogrammed agent behaviors. The agents must instead discover a solution on their own, using learning. A sig ...
... in a variety of domains, including robotics, distributed control, telecommunications, and economics. The complexity of many tasks arising in these domains makes them difficult to solve with preprogrammed agent behaviors. The agents must instead discover a solution on their own, using learning. A sig ...
A Low-Cost Approximate Minimal Hitting Set Algorithm
... cost/completeness trade-off. To the best of knowledge this heuristic approach has not been presented before and has proven to have a significant effect on MBD complexity in practice (Abreu, Zoeteweij, and Van Gemund 2009). The reminder of this paper is organized as follows. We start by introducing t ...
... cost/completeness trade-off. To the best of knowledge this heuristic approach has not been presented before and has proven to have a significant effect on MBD complexity in practice (Abreu, Zoeteweij, and Van Gemund 2009). The reminder of this paper is organized as follows. We start by introducing t ...
Narrative Intelligence - Carnegie Mellon School of Computer Science
... Intentional State Entailment: When people are acting in a narrative, the important part is not what the people do, but how they think and feel about what they do. Hermeneutic Composability: Just as a narrative comes to life from the actions of which it is composed, those actions are understood w ...
... Intentional State Entailment: When people are acting in a narrative, the important part is not what the people do, but how they think and feel about what they do. Hermeneutic Composability: Just as a narrative comes to life from the actions of which it is composed, those actions are understood w ...
The Intelligent Conversational Humanoid Robot
... “Can machines think?” This is the question asked by Alan Turing which has since spawned numerous, passionate debates on the subject of artificial intelligence [1]. It has also spawned the famous Turing Test, a test which determines if a particular machine (or algorithm) can pass as a human. Since it ...
... “Can machines think?” This is the question asked by Alan Turing which has since spawned numerous, passionate debates on the subject of artificial intelligence [1]. It has also spawned the famous Turing Test, a test which determines if a particular machine (or algorithm) can pass as a human. Since it ...