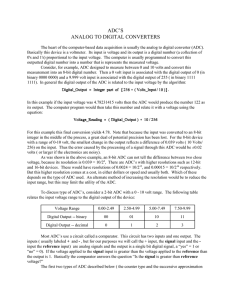
ADC`S ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS
... with a range of 0-10 volt, the smallest change in the output reflects a difference of 0.039 volts ( 10 Volts/ 256) on the input. Thus the error caused by the processing of a signal through this ADC would be ±0.02 volts ( or larger if the electronics are noisy). As was shown in the above example, an ...
... with a range of 0-10 volt, the smallest change in the output reflects a difference of 0.039 volts ( 10 Volts/ 256) on the input. Thus the error caused by the processing of a signal through this ADC would be ±0.02 volts ( or larger if the electronics are noisy). As was shown in the above example, an ...
Design of High-Speed Multi Bit Logic Decoder for Current Mode
... seventy mos transistors with single resistor or sixty seven mos transistors with four resistors. It has five level of quantization with 3-bit outputs that can be extended as per requirement. Encoding module has been added in the design with suitable decoder to generate the logic on the basis of curr ...
... seventy mos transistors with single resistor or sixty seven mos transistors with four resistors. It has five level of quantization with 3-bit outputs that can be extended as per requirement. Encoding module has been added in the design with suitable decoder to generate the logic on the basis of curr ...
Synchronous Motors
... any load condition can be calculated. Hence regulation of the alternator at any load condition and load power factor can be determined. • Limitation: This method gives large values of synchronous reactance. This leads to high values of % regulation than the actual. Hence this method is called Pessim ...
... any load condition can be calculated. Hence regulation of the alternator at any load condition and load power factor can be determined. • Limitation: This method gives large values of synchronous reactance. This leads to high values of % regulation than the actual. Hence this method is called Pessim ...
LOC05b Resistors in Series and Parallel
... parallel across a power supply as shown in Figure 4, the potential difference across each resistor is equal to that supplied by the power supply. What about the current? A current I flows out of the power supply. Let I 1 be the current flowing through R1 and let I 2 be the current flowing through R2 ...
... parallel across a power supply as shown in Figure 4, the potential difference across each resistor is equal to that supplied by the power supply. What about the current? A current I flows out of the power supply. Let I 1 be the current flowing through R1 and let I 2 be the current flowing through R2 ...
LOC12a Resistors in Series and Parallel
... parallel across a power supply as shown in Figure 4, the potential difference across each resistor is equal to that supplied by the power supply. What about the current? A current I flows out of the power supply. Let I 1 be the current flowing through R1 and let I 2 be the current flowing through R2 ...
... parallel across a power supply as shown in Figure 4, the potential difference across each resistor is equal to that supplied by the power supply. What about the current? A current I flows out of the power supply. Let I 1 be the current flowing through R1 and let I 2 be the current flowing through R2 ...
LM2681 Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter
... High capacitance, low ESR capacitors can reduce both the output reslistance and the voltage ripple. The Schottky diode D1 is only needed for start-up. The internal oscillator circuit uses the OUT pin and the GND pin. Voltage across OUT and GND must be larger than 1.8V to insure the operation of the ...
... High capacitance, low ESR capacitors can reduce both the output reslistance and the voltage ripple. The Schottky diode D1 is only needed for start-up. The internal oscillator circuit uses the OUT pin and the GND pin. Voltage across OUT and GND must be larger than 1.8V to insure the operation of the ...
LF155/LF156/LF256/LF257/LF355/LF356/LF357 JFET Input Operational Amplifiers General Description
... Note 4: The Temperature Coefficient of the adjusted input offset voltage changes only a small amount (0.5µV/˚C typically) for each mV of adjustment from its original unadjusted value. Common-mode rejection and open loop voltage gain are also unaffected by offset adjustment. Note 5: The input bias cu ...
... Note 4: The Temperature Coefficient of the adjusted input offset voltage changes only a small amount (0.5µV/˚C typically) for each mV of adjustment from its original unadjusted value. Common-mode rejection and open loop voltage gain are also unaffected by offset adjustment. Note 5: The input bias cu ...
Fundamentals of Electricity - Franklin County Amateur Radio Club
... Very Large and Very Small Numeric Values: Units • resistor values may be ohms (Ω), kilo ohms (kΩ) or mega ohms (MΩ) • capacitor values typically are microfarads (μf) or pico farads (pf) • inductance values are typically milli henrys (mh) or micro henrys (μh) • frequencies are typically kilo hertz (k ...
... Very Large and Very Small Numeric Values: Units • resistor values may be ohms (Ω), kilo ohms (kΩ) or mega ohms (MΩ) • capacitor values typically are microfarads (μf) or pico farads (pf) • inductance values are typically milli henrys (mh) or micro henrys (μh) • frequencies are typically kilo hertz (k ...
Chapter 6: Transistors and Gain
... C. The Emitter-Follower Amplifier The most important circuit in this chapter is the emitter follower (see figure 6.4 below). This is a very easy circuit to design, and its normal operating conditions do not depend on . An input voltage on the base produces a base current and an amplified collector ...
... C. The Emitter-Follower Amplifier The most important circuit in this chapter is the emitter follower (see figure 6.4 below). This is a very easy circuit to design, and its normal operating conditions do not depend on . An input voltage on the base produces a base current and an amplified collector ...
ECE1250F14_Lab4_ThevEquiv
... voltage. Verify that the measured and predicted values are consistent. The circuit model of a Thevenin equivalent is shown in Fig. 2. Since the Thevenin equivalent voltage of your circuit is the same as the voltage you have just measured at the output, you now know the value of the voltage source, v ...
... voltage. Verify that the measured and predicted values are consistent. The circuit model of a Thevenin equivalent is shown in Fig. 2. Since the Thevenin equivalent voltage of your circuit is the same as the voltage you have just measured at the output, you now know the value of the voltage source, v ...
BP-1 Pressure Monitor - World Precision Instruments
... measurements the ADJ amplification position on the Gain selector switch rather than the other gain positions. With no external pressure applied, the AVERAGE should be carefully zeroed using the Position knob. Tighten the concentric collar of this knob to lock the zero setting. Apply a known constant ...
... measurements the ADJ amplification position on the Gain selector switch rather than the other gain positions. With no external pressure applied, the AVERAGE should be carefully zeroed using the Position knob. Tighten the concentric collar of this knob to lock the zero setting. Apply a known constant ...
Multimeter
A multimeter or a multitester, also known as a VOM (Volt-Ohm meter or Volt-Ohm-milliammeter ), is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter would include basic features such as the ability to measure voltage, current, and resistance. Analog multimeters use a microammeter whose pointer moves over a scale calibrated for all the different measurements that can be made. Digital multimeters (DMM, DVOM) display the measured value in numerals, and may also display a bar of a length proportional to the quantity being measured. Digital multimeters are now far more common but analog multimeters are still preferable in some cases, for example when monitoring a rapidly varying value. A multimeter can be a hand-held device useful for basic fault finding and field service work, or a bench instrument which can measure to a very high degree of accuracy. They can be used to troubleshoot electrical problems in a wide array of industrial and household devices such as electronic equipment, motor controls, domestic appliances, power supplies, and wiring systems.Multimeters are available in a wide range of features and prices. Cheap multimeters can cost less than US$10, while laboratory-grade models with certified calibration can cost more than US$5,000.