Book Review Lost History - Journal of the Islamic Medical
... in a halt to the rapid expansion of the Muslim empire and set it free to turn its energy to invention and creation. The manner in which Charles Martel’s army defeated the better-equipped and larger army led by `Abd al-Raḥmān al-Ghāfiqī makes interesting reading with many relevant lessons for all of ...
... in a halt to the rapid expansion of the Muslim empire and set it free to turn its energy to invention and creation. The manner in which Charles Martel’s army defeated the better-equipped and larger army led by `Abd al-Raḥmān al-Ghāfiqī makes interesting reading with many relevant lessons for all of ...
Islam and Al-Andalus
... The Medina (city): It was the central part of the city, surrounded by walls. Inside the medina were the main mosque and the madrasa (Muslim college). Near the main mosque there are souks (a type of open market) with workshops (talleres), shops (tiendas) and storehouses (almacenes) for merchandise (m ...
... The Medina (city): It was the central part of the city, surrounded by walls. Inside the medina were the main mosque and the madrasa (Muslim college). Near the main mosque there are souks (a type of open market) with workshops (talleres), shops (tiendas) and storehouses (almacenes) for merchandise (m ...
As Word (text only) - Discover Islamic Art
... The Sassanian (Persian) army conquers Palestine during a campaign of occupation of Great Syria and Egypt. The conquest is very destructive, tens of churches are destroyed, and monasteries are sacked and ...
... The Sassanian (Persian) army conquers Palestine during a campaign of occupation of Great Syria and Egypt. The conquest is very destructive, tens of churches are destroyed, and monasteries are sacked and ...
Two Accounts of the Battle of Pointers, 732: Chronicle of the Franks
... Two Accounts of the Muslim Conquest of Spain, 711: The Chronicle of 754 The anonymous Latin Chronicle of 754 was written by a Christian living in al-Andalus during the second generation after the conquest of 711. It was designed as an installment in the ongoing “universal chronicle” begun in the fo ...
... Two Accounts of the Muslim Conquest of Spain, 711: The Chronicle of 754 The anonymous Latin Chronicle of 754 was written by a Christian living in al-Andalus during the second generation after the conquest of 711. It was designed as an installment in the ongoing “universal chronicle” begun in the fo ...
7.21 Islam 570–1100
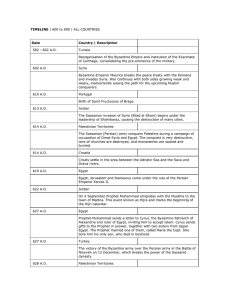
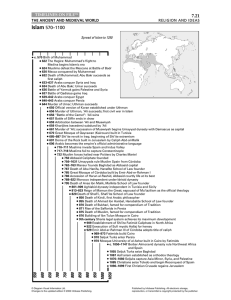
... ● 685–687 Shi’ite revolt in Iraq; beginning of Shi’ite extremism ● 691 Dome of the Rock built in Jerusalem by Caliph Abd-al-Malik ● 696 Arabic becomes the empire’s official administrative language ● 710–711 Muslims invade Spain and Indus Valley ● 717–718 Muslims fail to capture Constantinople ● 732 ...
... ● 685–687 Shi’ite revolt in Iraq; beginning of Shi’ite extremism ● 691 Dome of the Rock built in Jerusalem by Caliph Abd-al-Malik ● 696 Arabic becomes the empire’s official administrative language ● 710–711 Muslims invade Spain and Indus Valley ● 717–718 Muslims fail to capture Constantinople ● 732 ...
8.8 The Umayyad Dynasty
... people of the empire. In addition, Arabs took over as top officials. People bought goods with new Arab coins. While it was not policy to force conversion to Islam, some non-Muslims began to embrace the new faith for a variety of reasons. These included personal belief in the message of Islam and soc ...
... people of the empire. In addition, Arabs took over as top officials. People bought goods with new Arab coins. While it was not policy to force conversion to Islam, some non-Muslims began to embrace the new faith for a variety of reasons. These included personal belief in the message of Islam and soc ...
Warm Up Activity #4 - South Pointe Middle
... invasion of the Iberian Peninsula and conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom. Battle of Guadalete: Umayyad Moors' victory over the Visigothic army. Visigothic king Roderic (Rodrigo in Spanish and Portuguese) dies in the battle. After pirates plunder an Arab ship near the mouth of the Indus River, Arab ...
... invasion of the Iberian Peninsula and conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom. Battle of Guadalete: Umayyad Moors' victory over the Visigothic army. Visigothic king Roderic (Rodrigo in Spanish and Portuguese) dies in the battle. After pirates plunder an Arab ship near the mouth of the Indus River, Arab ...
Umayyad conquest of Hispania

The Umayyad conquest of Hispania was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania, largely extending from 711 to 788. The conquest resulted in the destruction of the Visigothic Kingdom and the establishment of the independent Emirate of Cordova under Abd ar-Rahman I, who completed the unification of Muslim-ruled Iberia, or al-Andalus (756–788). The conquest marks the westernmost expansion of both the Umayyad Caliphate and Muslim rule into Europe.Forces commanded by Tariq ibn Ziyad disembarked in early 711 at Gibraltar at the head of an army consisting of Berber Northwest Africans and Arabs. He campaigned his way northward after the decisive Battle of Guadalete against the usurper Roderic. By 717, the Berber-Arabs had crossed the Pyrenees onto Septimania and Provence (734).