Optical Comms 2004 (Summer)
... Loss mechanisms in a Silica Optical Fibre Intrinsic absorption loss: Intrinsic absorption is caused by the interaction of the light with one or more of the components of the glass itself. For silica glass there is a low loss window between 800 and 1600 nm where intrinsic absorption is negligible, by ...
... Loss mechanisms in a Silica Optical Fibre Intrinsic absorption loss: Intrinsic absorption is caused by the interaction of the light with one or more of the components of the glass itself. For silica glass there is a low loss window between 800 and 1600 nm where intrinsic absorption is negligible, by ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... (Electronics and Telecommunication, Babasaheb Gawde Institute of Technology/MSBTE, India) (Electronics and Telecommunication, Babasaheb Gawde Institute of Technology/MSBTE, India) ...
... (Electronics and Telecommunication, Babasaheb Gawde Institute of Technology/MSBTE, India) (Electronics and Telecommunication, Babasaheb Gawde Institute of Technology/MSBTE, India) ...
Template BR_Rec_2002.dot
... Visible and non-visible radiation from laser diodes and LEDs used in optical fibre communications systems is considered to be a safe application of laser technology. Light output is entirely confined to the core of the interconnected fibre, and does not leak through the cladding or outer sheath. If ...
... Visible and non-visible radiation from laser diodes and LEDs used in optical fibre communications systems is considered to be a safe application of laser technology. Light output is entirely confined to the core of the interconnected fibre, and does not leak through the cladding or outer sheath. If ...
Lab 14 - FIber Optics Principles and Position Sensor
... Starting from zero displacement, why does the detected light intensity first INCREASE from zero (region 1) in above figure and then decrease (region 2)? Is there any displacement region where this displacement sensor is linear? What the range of detection (not necessarily when the sensor is line ...
... Starting from zero displacement, why does the detected light intensity first INCREASE from zero (region 1) in above figure and then decrease (region 2)? Is there any displacement region where this displacement sensor is linear? What the range of detection (not necessarily when the sensor is line ...
Fiber Optic Cable Beam Delivery Systems
... Lee Laser uses only the highest quality, low-loss optical transmission fibers. The single-fiber cable features a high-purity silica glass core available in diameters from 200 m to 1000 m. Core size is determined by the desired laser beam power throughput, with the largest size used to handle the mul ...
... Lee Laser uses only the highest quality, low-loss optical transmission fibers. The single-fiber cable features a high-purity silica glass core available in diameters from 200 m to 1000 m. Core size is determined by the desired laser beam power throughput, with the largest size used to handle the mul ...
IJFTR 12(2) 100-102
... There are some limitations encountered in the back-scattering technique in the case of polymeric fibres. These are: (1) The complete back-scattered fringe pattern is localized in the range = ± 20°C. (2) Some discrepancies may arise owing to the incomplete circularity of some fibres and to the dra ...
... There are some limitations encountered in the back-scattering technique in the case of polymeric fibres. These are: (1) The complete back-scattered fringe pattern is localized in the range = ± 20°C. (2) Some discrepancies may arise owing to the incomplete circularity of some fibres and to the dra ...
optical fibre communication
... communication fibres. This means collecting light from one source and transferring that light to the optical fibre. This demands COUPLING light from core to the fibre, in a efficient way. Larger light sources are generally easy to align with fibres, but their lower intensity generally delivers less ...
... communication fibres. This means collecting light from one source and transferring that light to the optical fibre. This demands COUPLING light from core to the fibre, in a efficient way. Larger light sources are generally easy to align with fibres, but their lower intensity generally delivers less ...
Fiber Optic Sensors and Their Applications
... interferometric sensors. Due to the small core size (~4 μm) alignment becomes a critical factor. The SM fibre mentioned above is not truly single mode in that two modes with degenerate polarization states can propagate in the fibre. This can lead to signal interference and noise in the measurement. ...
... interferometric sensors. Due to the small core size (~4 μm) alignment becomes a critical factor. The SM fibre mentioned above is not truly single mode in that two modes with degenerate polarization states can propagate in the fibre. This can lead to signal interference and noise in the measurement. ...
Reference fibres and artefacts
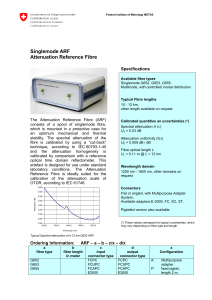
... The Attenuation Reference Fibre (ARF) consists of a spool of singlemode fibre, which is mounted in a protective case for an optimum mechanical and thermal stability. The spectral attenuation of the fibre is calibrated by using a “cut-back” technique, according to IEC 60793-1-40 and the attenuation h ...
... The Attenuation Reference Fibre (ARF) consists of a spool of singlemode fibre, which is mounted in a protective case for an optimum mechanical and thermal stability. The spectral attenuation of the fibre is calibrated by using a “cut-back” technique, according to IEC 60793-1-40 and the attenuation h ...
An optical fibre based evanescent wave sensor to
... by the granular nature of films, but it may still be used for relative measurement of the average film thickness. The photometric method uses the oscillatory nature of the interference effect of a reflected or transmitted beam from the film–substrate combination during deposition. This method is mai ...
... by the granular nature of films, but it may still be used for relative measurement of the average film thickness. The photometric method uses the oscillatory nature of the interference effect of a reflected or transmitted beam from the film–substrate combination during deposition. This method is mai ...
Optical Cable and Accessory for TV Camera
... cables have been developed. These high-reliability optical cables for information transmission with excellent flexibility are based on our expertise in TV camera cables. ...
... cables have been developed. These high-reliability optical cables for information transmission with excellent flexibility are based on our expertise in TV camera cables. ...
The Physics of the Optical Fibre
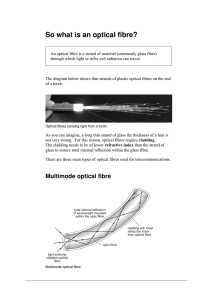
... Optical fibres offer huge communication capacity. A single fibre can carry the conversations of every man, woman and child on the face of this planet, at the same time, twice over. The latest generations of optical transmission systems are beginning to exploit a significant part of this huge capacit ...
... Optical fibres offer huge communication capacity. A single fibre can carry the conversations of every man, woman and child on the face of this planet, at the same time, twice over. The latest generations of optical transmission systems are beginning to exploit a significant part of this huge capacit ...
Optical Fibre Communications
... • The waveguide structure: — "Theoretical and experimental studies indicate that a fibre of glassy material ... cladded structure with a core ....and an overall diameter of about 100 l represents a practical waveguide with important potential as a new form of communication medium.” • The Loss: — "Th ...
... • The waveguide structure: — "Theoretical and experimental studies indicate that a fibre of glassy material ... cladded structure with a core ....and an overall diameter of about 100 l represents a practical waveguide with important potential as a new form of communication medium.” • The Loss: — "Th ...
OFC - GEOCITIES.ws
... has higher dispersion, i.e. less efficient transmission. Easy to manufacture and less costly. Graded Index (GRIN) Fibre: Multimode fibre with a core consisting of concentric layers of different refractive indices. It has higher value at the centre and falls of with increasing radial distance from th ...
... has higher dispersion, i.e. less efficient transmission. Easy to manufacture and less costly. Graded Index (GRIN) Fibre: Multimode fibre with a core consisting of concentric layers of different refractive indices. It has higher value at the centre and falls of with increasing radial distance from th ...
Transmission Media
... Optical Fiber works in three different types of modes (or we can say that we have 3 types of communication using Optical fiber). Optical fibers are available in two varieties; Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF) and Single-Mode Fiber (SMF). For multi-mode fiber the core and cladding diameter lies in the range 50 ...
... Optical Fiber works in three different types of modes (or we can say that we have 3 types of communication using Optical fiber). Optical fibers are available in two varieties; Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF) and Single-Mode Fiber (SMF). For multi-mode fiber the core and cladding diameter lies in the range 50 ...
Long-distance vision
... amplification techniques. The larger effective area of this fibre delivers around 1.5dB OSNR advantage compared with an ultra-low-loss fibre whose effective area is constrained by the G.652 standard. Compression and the bends In determining which larger effective area fibres are suitable for operati ...
... amplification techniques. The larger effective area of this fibre delivers around 1.5dB OSNR advantage compared with an ultra-low-loss fibre whose effective area is constrained by the G.652 standard. Compression and the bends In determining which larger effective area fibres are suitable for operati ...
Total Internal Reflection and Critical Angle File
... Optical fibres are replacing electrical cables for the transmission of information. ...
... Optical fibres are replacing electrical cables for the transmission of information. ...
Communication Cables
... The connectors of these coaxial cables are either of a bayonet style coupling for ease of assembly or a screw-type coupling for better protection from moisture. The BNC connector, a bayonet style is used extensively with test equipment when the cables need to be removed and reattached numerous numbe ...
... The connectors of these coaxial cables are either of a bayonet style coupling for ease of assembly or a screw-type coupling for better protection from moisture. The BNC connector, a bayonet style is used extensively with test equipment when the cables need to be removed and reattached numerous numbe ...
Optical Fibre
... The speed of a light signal in an optical fibre is slower than the speed of an electrical signal in a metal wire. ...
... The speed of a light signal in an optical fibre is slower than the speed of an electrical signal in a metal wire. ...
optical fibres
... travel much further than light that barely touched the edges. This causes impulses to arrive at their destination at slightly different times. Graded optical fibres have a higher refractive index material towards the centre of the fibre. The refractive index gradually decreases towards the outer edg ...
... travel much further than light that barely touched the edges. This causes impulses to arrive at their destination at slightly different times. Graded optical fibres have a higher refractive index material towards the centre of the fibre. The refractive index gradually decreases towards the outer edg ...
Chapter 4
... The significant problem is that signal echoes caused by the reflections from the impedance discontinuities will strike the ...
... The significant problem is that signal echoes caused by the reflections from the impedance discontinuities will strike the ...
Lecture 13-15
... Transmission media Open wire Twisted pair Coaxial cable Optical fiber Air ...
... Transmission media Open wire Twisted pair Coaxial cable Optical fiber Air ...
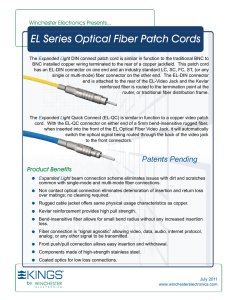
EL Series Optical Fiber Patch Cords
... The Expanded Light Quick Connect (EL-QC) is similar in function to a copper video patch cord. With the EL-QC connector on either end of a 5mm bend-insensitive rugged fiber, when inserted into the front of the EL Optical Fiber Video Jack, it will automatically switch the optical signal being routed t ...
... The Expanded Light Quick Connect (EL-QC) is similar in function to a copper video patch cord. With the EL-QC connector on either end of a 5mm bend-insensitive rugged fiber, when inserted into the front of the EL Optical Fiber Video Jack, it will automatically switch the optical signal being routed t ...
Optical attached cable

Optical attached cable (OPAC) is a type of fibre optic cable that is installed by being attached to a host conductor along overhead power lines. The attachment system varies and can include wrapping, lashing or clipping the fibre optic cable to the host. Installation is typically performed using a specialised piece of equipment that travels along the host conductor from pole to pole or tower to tower, wrapping, clipping or lashing the fibre optic cable in place. Different manufacturers have different systems and the installation equipment, cable designs and hardware are not interchangeable.Although lashed cable systems and clipped cable systems have been investigated as a means of attaching optical fibre cables to overhead power lines, wrapped cables were the first type to be developed and are the only type in common use today.Wrapped cable systems were developed independently in the UK (SkyWrap) and Japan (GWWOP) during the 1980s and have been widely used, with installations in every continent except Antarctica. Through licensing and through independent development, wrapped cable systems have also been supplied by French, Italian, German and Russian companies.The installation process for wrapped cables involves passing a drum of cable around and around the host conductor as the carrying device moves across the span. For installation on hosts within 10m of the ground (medium or low voltage overhead lines), it is possible to pull the wrapping machine by hand from the ground below the line. However, a radio controlled power unit using batteries or a petrol engine is normally required when the host conductor is on a high voltage transmission line. Wrapped cables can be applied to earth wires (ground wires, shield wires) on power transmission lines and to phase conductors on transmission, sub-transmission or distribution lines.SkyWrap is the most successful example of OPAC (optical attached cable) and is used together with more familiar optical fibre cables such as OPGW and ADSS to build communications networks for power utilities