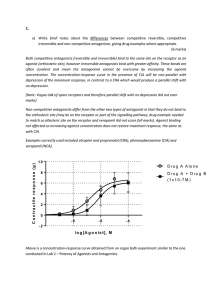
Lecture 4
... cellular response that ultimately increases drowsiness – fatigue sensor. • The caffeine molecule is structurally similar to adenosine, and is capable of binding to adenosine receptors without activating them, acting as a ...
... cellular response that ultimately increases drowsiness – fatigue sensor. • The caffeine molecule is structurally similar to adenosine, and is capable of binding to adenosine receptors without activating them, acting as a ...
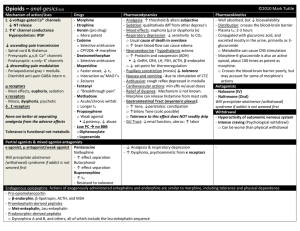
Opioids – anal-gesics (lol) ©2010 Mark Tuttle Mechanism of action
... - Sedation: qualitatively diff from other depress’s - Distribution: crosses the blood-brain barrier - Heroin (pro drug) - Mood effects: euphoria (μ) or dysphoria (κ) - Plasma t½: 2-3 hours o More potent - Respiratory depression: ↓ sensitivity to CO2 - Conjugated with glucuronic acid, and - Codeine o ...
... - Sedation: qualitatively diff from other depress’s - Distribution: crosses the blood-brain barrier - Heroin (pro drug) - Mood effects: euphoria (μ) or dysphoria (κ) - Plasma t½: 2-3 hours o More potent - Respiratory depression: ↓ sensitivity to CO2 - Conjugated with glucuronic acid, and - Codeine o ...
5HT1F- and 5HT7-Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Migraines
... order of potencies for serotonergic ligands at this new receptor: 5-HT > sumatriptan >> 5-carboxyamidotryptamine > 8hydroxy-2(di-1-propylamino)tetralin > spiperone. 5-HT produced a dose-dependent inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation (EC50 = 7.9 nM) in transfected cells. These propert ...
... order of potencies for serotonergic ligands at this new receptor: 5-HT > sumatriptan >> 5-carboxyamidotryptamine > 8hydroxy-2(di-1-propylamino)tetralin > spiperone. 5-HT produced a dose-dependent inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation (EC50 = 7.9 nM) in transfected cells. These propert ...
to file - Planet Ross 2K2
... Stimulates release of norepinephrine, dopamine and seratonin from peripheral and CNS Effects similar to norepinephrine; enters CNS; tolerance to central effects Toxicity includes hypertension, negative psychic effects, nausea and vomiting, dependence. 1. Amphetamine, methamphetamine, methylphenidate ...
... Stimulates release of norepinephrine, dopamine and seratonin from peripheral and CNS Effects similar to norepinephrine; enters CNS; tolerance to central effects Toxicity includes hypertension, negative psychic effects, nausea and vomiting, dependence. 1. Amphetamine, methamphetamine, methylphenidate ...
Histamine, Serotonin and Bradykinin
... intracellular cAMP. H3 activation in CNS leads to decreased histamine release. Overall, principal cells that store histamine (blood basophils and tissue mast cells) are involved in Type I immediate ...
... intracellular cAMP. H3 activation in CNS leads to decreased histamine release. Overall, principal cells that store histamine (blood basophils and tissue mast cells) are involved in Type I immediate ...
Pharmacology Definitions
... zipper mechanism, which results in the receptor being taken from its resting state to an activated state which consequently results in a response from the cell. If the agonist can give a maximum response it is called a full agonist, whereas a partial agonist is not able to achieve the maximum respon ...
... zipper mechanism, which results in the receptor being taken from its resting state to an activated state which consequently results in a response from the cell. If the agonist can give a maximum response it is called a full agonist, whereas a partial agonist is not able to achieve the maximum respon ...
2 receptor
... picking vegetables. His gait is unsteady and he walks with support from his colleague. JM has difficulty speaking and swallowing, his vision is blurred, and his eyes are filled with tears. His coworker notes that JM was working in a field that had been sprayed early in the morning with a material th ...
... picking vegetables. His gait is unsteady and he walks with support from his colleague. JM has difficulty speaking and swallowing, his vision is blurred, and his eyes are filled with tears. His coworker notes that JM was working in a field that had been sprayed early in the morning with a material th ...
Nicotinic agonist

A nicotinic agonist is a drug that mimics the action of acetylcholine (ACh) at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The nAChR is named for its affinity for nicotine.Examples include nicotine (by definition), acetylcholine (the endogenous agonist of nAChRs), choline, epibatidine, lobeline, varenicline and cytisine.