PXR (N-16): sc-9690
... interacting with specific intracellular receptors to regulate gene expression. This superfamily of receptors includes both steroid and nonsteroid receptors. Like many nonsteroid hormone receptors, PXR (Pregnane X Receptor) binds as a heterodimer with RXR to a DNA sequence typical of a nonsteroid hor ...
... interacting with specific intracellular receptors to regulate gene expression. This superfamily of receptors includes both steroid and nonsteroid receptors. Like many nonsteroid hormone receptors, PXR (Pregnane X Receptor) binds as a heterodimer with RXR to a DNA sequence typical of a nonsteroid hor ...
Neuraxial Opioid-Induced Pruritus: A Review
... antagonist strychnine in cats produces similar itch & scratch behavior as large doses of intrathecal morphine. ...
... antagonist strychnine in cats produces similar itch & scratch behavior as large doses of intrathecal morphine. ...
Antipsychotics
... • Recommended use: Clozapine 12.5 mg orally, twice daily initially, increasing as tolerated and according to patient response. Usual effective daily dose is 200 to 600 mg. The maximum dose is 900 mg daily, but this is not usually required ...
... • Recommended use: Clozapine 12.5 mg orally, twice daily initially, increasing as tolerated and according to patient response. Usual effective daily dose is 200 to 600 mg. The maximum dose is 900 mg daily, but this is not usually required ...
Glucocorticoids
... CORTISOL [hydrocortisone] • Synthetized from 17-OH-pregnenolone • 95% is bound in the plasma by corticosteroid-binding globulin • As a drug: • Short action • Good oral availability • Cleared by the liver • Poor transdermal availability, but absorbed across inflamed skin • Salt retention activity = h ...
... CORTISOL [hydrocortisone] • Synthetized from 17-OH-pregnenolone • 95% is bound in the plasma by corticosteroid-binding globulin • As a drug: • Short action • Good oral availability • Cleared by the liver • Poor transdermal availability, but absorbed across inflamed skin • Salt retention activity = h ...
MIGRAINE
... to increase their absorption. No withdrawal symptoms on sudden withdrawal. Main adverse effects Gastric Upset. ...
... to increase their absorption. No withdrawal symptoms on sudden withdrawal. Main adverse effects Gastric Upset. ...
ADRENERGIC SYSTEM - LEC.2 2008
... according to mechanism of action : They can be classified according to the way that can act through it to three types : 1- direct – acting adrenoceptor agonists: This group of drugs act directly on alpha or beta receptors producing effects similar to those that occur following stimulation of sympath ...
... according to mechanism of action : They can be classified according to the way that can act through it to three types : 1- direct – acting adrenoceptor agonists: This group of drugs act directly on alpha or beta receptors producing effects similar to those that occur following stimulation of sympath ...
PDF - SAS Publishers
... (△9- THC) were developed which include HU-210, JWH-018, JWH-073, JWH-398, JWH-250CP47, 497 and others. SC’s are structurally unrelated to △9- THC and are mostly marketed through head shops and internet. Inter-brand and intrabrand variations in SC content are well documented. SC’s are blended with pl ...
... (△9- THC) were developed which include HU-210, JWH-018, JWH-073, JWH-398, JWH-250CP47, 497 and others. SC’s are structurally unrelated to △9- THC and are mostly marketed through head shops and internet. Inter-brand and intrabrand variations in SC content are well documented. SC’s are blended with pl ...
Name ______________________________ CH 204, Fall 2014 Assignment 8 – Opioids
... resulting in drug accumulation. Which of the following analgesics is metabolized primarily through glucuronidation, versus CYP-oxidation, allowing more predictable pharmacokinetics in its use ...
... resulting in drug accumulation. Which of the following analgesics is metabolized primarily through glucuronidation, versus CYP-oxidation, allowing more predictable pharmacokinetics in its use ...
Mechanism of Drug Action and Drug Targets Receptors
... In this lecture, the diversity of receptors for and responses to a single kind of neurotransmitter is illustrated by acetylcholine. Synapses in which acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter are termed cholinergic synapses. Acetylcholine receptors that cause excitatory responses lasting only milliseco ...
... In this lecture, the diversity of receptors for and responses to a single kind of neurotransmitter is illustrated by acetylcholine. Synapses in which acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter are termed cholinergic synapses. Acetylcholine receptors that cause excitatory responses lasting only milliseco ...
The use of cannabinoids in animals and therapeutic implications for
... are present in the resin of the herb. It has been found that these plants contain over 100 phytocannabinoids (Hill et al. 2012). The most studied cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa include e.g. delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol, tetrahydrocannabivarin, tetrahydrocannabiorcol, cannabichr ...
... are present in the resin of the herb. It has been found that these plants contain over 100 phytocannabinoids (Hill et al. 2012). The most studied cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa include e.g. delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol, tetrahydrocannabivarin, tetrahydrocannabiorcol, cannabichr ...
GRADED DOSE RESPONSE CURVE An all-or-non
... Agonist and Antagonist compete ( only one is bound) ...
... Agonist and Antagonist compete ( only one is bound) ...
Opioid Pharmacology
... • Agonists produce a maximum biologic effect • Antagonists have no intrinsic activity and prevent the access of agonists to the receptors • Partial agonists have a submaximal response ...
... • Agonists produce a maximum biologic effect • Antagonists have no intrinsic activity and prevent the access of agonists to the receptors • Partial agonists have a submaximal response ...
H. Sodium Channel Blockers
... 1. Drug distributed to site of action 2. Protein binding 3. Blood brain barrier C. Metabolism 1. Liver 2. Hepatic First Pass Effect 3. Infants and Elderly have a decreased ability to metabolize drugs D. Excretion 1. Drugs eliminated from body primarily by kidneys but also intestines, lungs, and mamm ...
... 1. Drug distributed to site of action 2. Protein binding 3. Blood brain barrier C. Metabolism 1. Liver 2. Hepatic First Pass Effect 3. Infants and Elderly have a decreased ability to metabolize drugs D. Excretion 1. Drugs eliminated from body primarily by kidneys but also intestines, lungs, and mamm ...
lec.11-426
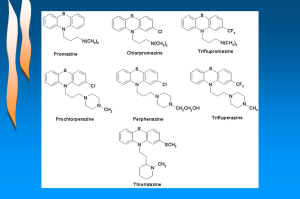
... Considerable variation is possible in the tertiary amino group with retention of neuroleptic activity. The basic nitrogen could be a part of a six membered ring, (piperidine, 1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridyl, or piperazinyl). Replacement of the sixmembered basic heterocycle by larger or smaller or uncycliz ...
... Considerable variation is possible in the tertiary amino group with retention of neuroleptic activity. The basic nitrogen could be a part of a six membered ring, (piperidine, 1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridyl, or piperazinyl). Replacement of the sixmembered basic heterocycle by larger or smaller or uncycliz ...
Page Selective D3 receptor antagonist The dopamine D3
... although no effect was observed on reducing alcohol consumption in rats (data on file). GSK598809 dose dependently reduced the expression of nicotine-induced CPP in rats, with an effect proportional to the exposure and occupancy of brain D3Rs at every time point, and 100% effect at occupancy of brai ...
... although no effect was observed on reducing alcohol consumption in rats (data on file). GSK598809 dose dependently reduced the expression of nicotine-induced CPP in rats, with an effect proportional to the exposure and occupancy of brain D3Rs at every time point, and 100% effect at occupancy of brai ...
PSYC550 Psychopharmacology
... • THC (marijuana) interacts with cannabinoid (CB) receptors in brain to produce analgesia and sedation • There are two endogenous ligands for the CB receptors, each is derived from lipid precursors – Anandamide – 2-arachidonyl glycerol (2-AG) ...
... • THC (marijuana) interacts with cannabinoid (CB) receptors in brain to produce analgesia and sedation • There are two endogenous ligands for the CB receptors, each is derived from lipid precursors – Anandamide – 2-arachidonyl glycerol (2-AG) ...
Analgesics Power Point - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... prevention, arthritis, *? prevention of Alzheimer’s Dementia ...
... prevention, arthritis, *? prevention of Alzheimer’s Dementia ...
Pharmacology Ch 9 110-126 Cholinergic Pharmacology
... -antiport channel is a target of vesamicol, acts to cause deficit of ACh storage and release -cholinergic vesicles also contain ATP and heparan sulfate proteoglycans which serve as counter ions to neutralize the positive charge of ACh and disperse electrostatic forces that prevent dense packing of A ...
... -antiport channel is a target of vesamicol, acts to cause deficit of ACh storage and release -cholinergic vesicles also contain ATP and heparan sulfate proteoglycans which serve as counter ions to neutralize the positive charge of ACh and disperse electrostatic forces that prevent dense packing of A ...
NV and antidiarrheal drugs
... vomiting caused by uremia, radiation, viral gastroenteritis; severe morning sickness of pregnancy. These drugs are only used in special cases due to their side effects profile. 2) Metoclopramide (PlasilR): It is a prokinetic agent and commonly used for vomiting caused by uremia, radiation, gastroint ...
... vomiting caused by uremia, radiation, viral gastroenteritis; severe morning sickness of pregnancy. These drugs are only used in special cases due to their side effects profile. 2) Metoclopramide (PlasilR): It is a prokinetic agent and commonly used for vomiting caused by uremia, radiation, gastroint ...
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist

The discovery of the endogenous cannabinoid system led to the development of CB1 receptor antagonists. The first cannabinoid receptor antagonist, rimonabant, was described in 1994. Rimonabant blocks the CB1 receptor selectively and it has been shown to decrease food intake and regulate body-weight gain. The prevalence of obesity worldwide is increasing dramatically and has a great impact on public health. The lack of efficient and well-tolerated drugs to cure obesity has led to an increased interest in research and development of cannabinoid antagonists. Cannabidiol, a naturally occurring cannabinoid, is a non-competitive CB1/2 antagonist.