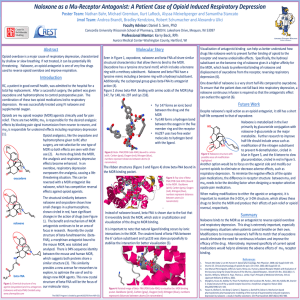
2-GENERAL PRINCIPLES FINAL
... requirement for this interaction. Drug targets include receptors for endogenous substances (neurotransmitters, hormones, etc.), enzymes, transport proteins, ion channels, etc. Some pharmacologists prefer the term "drug targets," and reserve the term "receptor" to describe the macromolecules that ser ...
... requirement for this interaction. Drug targets include receptors for endogenous substances (neurotransmitters, hormones, etc.), enzymes, transport proteins, ion channels, etc. Some pharmacologists prefer the term "drug targets," and reserve the term "receptor" to describe the macromolecules that ser ...
Pharmacodynamics – How Drugs Work
... are generally produced by concentrations of the ligand that are well below those that would bind to all the receptors necessary to produce a complete response, this means that above a certain level of binding, a partial agonist may bind to receptors without producing any further increase in effect. ...
... are generally produced by concentrations of the ligand that are well below those that would bind to all the receptors necessary to produce a complete response, this means that above a certain level of binding, a partial agonist may bind to receptors without producing any further increase in effect. ...
Antihypertensives:
... Duration of actions: The half-lives of the BDZs are very important clinically, because the duration of action may determine the therapeutic usefulness. The BDZs can be roughly divided into short-, intermediate-, and long-acting groups . The longer-acting agents form active metabolites with long half ...
... Duration of actions: The half-lives of the BDZs are very important clinically, because the duration of action may determine the therapeutic usefulness. The BDZs can be roughly divided into short-, intermediate-, and long-acting groups . The longer-acting agents form active metabolites with long half ...