Section 21.1 - CPO Science
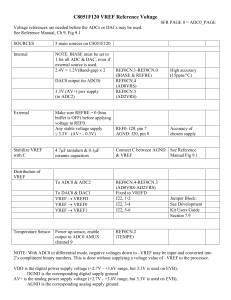
... Rearrange Ohm’s law to solve for voltage Use current to find each voltage drop V=IxR V1 = (3 A) x (1 Ω) = 3 volts V2 = (3 A) x (2 Ω) = 6 volts (3 + 6 ) = 9 V ...
... Rearrange Ohm’s law to solve for voltage Use current to find each voltage drop V=IxR V1 = (3 A) x (1 Ω) = 3 volts V2 = (3 A) x (2 Ω) = 6 volts (3 + 6 ) = 9 V ...
Simple Electrical Circuits
... If the circuit components are connected end to end to form a single loop the circuit is known as a series circuit. In any series circuit the same current passes through all the components Remember that current is the movement of electrons through a circuit. So like several hoses connected together i ...
... If the circuit components are connected end to end to form a single loop the circuit is known as a series circuit. In any series circuit the same current passes through all the components Remember that current is the movement of electrons through a circuit. So like several hoses connected together i ...
ATP-Y/Analog Input to Pulse (Relay)
... Be sure to follow all local electrical codes. Refer to wiring diagram for connection information. Make all connections with the power off. 1.) The secondary supply voltage to the interface should be between 22 and 28 volts AC or DC and isolated from earth ground, chassis ground, and neutral leg of t ...
... Be sure to follow all local electrical codes. Refer to wiring diagram for connection information. Make all connections with the power off. 1.) The secondary supply voltage to the interface should be between 22 and 28 volts AC or DC and isolated from earth ground, chassis ground, and neutral leg of t ...
SUBARTICLE 620-2.1 is deleted and the following substituted: 620
... 620-3.2 Minimum Grounding Resistance: Obtain a resistance to ground of 5 ohms or less for the following elements. Install multiple ground rod assemblies totaling a maximum length of up to 80 feet, as required to achieve minimum grounding resistance. 1. Power service for traffic control devices 2. Si ...
... 620-3.2 Minimum Grounding Resistance: Obtain a resistance to ground of 5 ohms or less for the following elements. Install multiple ground rod assemblies totaling a maximum length of up to 80 feet, as required to achieve minimum grounding resistance. 1. Power service for traffic control devices 2. Si ...
Physics 536 - Assignment #6 - Due March 19
... in which J1 is to be modelled using .MODEL ANOTHERJFET NJF(VTO=-4V IS=1NA BETA=0.00125 CGS=2P CGD=2P) which has IDSS ≈ 20 mA and VP = −4 V. The voltage source, Vin (t) has a peak-to-peak amplitude of 10 mV and a frequency of 10 kHz, modelled using VIN 5 0 DC 0 SIN(0 0.01V 10KHZ) and where R1 = 10 kΩ ...
... in which J1 is to be modelled using .MODEL ANOTHERJFET NJF(VTO=-4V IS=1NA BETA=0.00125 CGS=2P CGD=2P) which has IDSS ≈ 20 mA and VP = −4 V. The voltage source, Vin (t) has a peak-to-peak amplitude of 10 mV and a frequency of 10 kHz, modelled using VIN 5 0 DC 0 SIN(0 0.01V 10KHZ) and where R1 = 10 kΩ ...
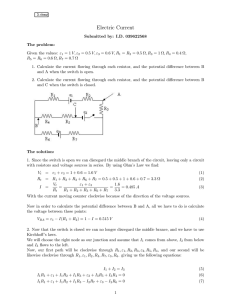
Electric Current
... With the current moving counter clockwise because of the direction of the voltage sources. Now in order to calculate the potential difference between B and A, all we have to do is calculate the voltage between these points: VBA = ε1 − I(R1 + R2 ) = 1 − I = 0.515 V ...
... With the current moving counter clockwise because of the direction of the voltage sources. Now in order to calculate the potential difference between B and A, all we have to do is calculate the voltage between these points: VBA = ε1 − I(R1 + R2 ) = 1 − I = 0.515 V ...
a AN-534 APPLICATION NOTE
... signal and allows a host application (master) to get two or more digital updates per second from a field device. As the digital FSK signal is phase continuous, there is no interference with the 4 mA–20 mA signal. Two different frequencies, 1200 Hz and 2200 Hz respectively, are used to represent bina ...
... signal and allows a host application (master) to get two or more digital updates per second from a field device. As the digital FSK signal is phase continuous, there is no interference with the 4 mA–20 mA signal. Two different frequencies, 1200 Hz and 2200 Hz respectively, are used to represent bina ...
Common Impedance Coupling
... Most effective from dc to 20 kHz, should not be used above 100kHz. Benefits: control of the return current, simplicity. Drawbacks: common-mode impedance (series), number of ground conductors (parallel) ...
... Most effective from dc to 20 kHz, should not be used above 100kHz. Benefits: control of the return current, simplicity. Drawbacks: common-mode impedance (series), number of ground conductors (parallel) ...
Univox DLS 50 - Gordon Morris Ltd Hearing Specailists
... 0.25kg (0.4kg including power supply) 202050 (no power supply) Technical data may vary due to different power supplies Variable attack/release times holding peak and average level constant Use the 13A microphone. It can be attached on your TV’s speaker grid ...
... 0.25kg (0.4kg including power supply) 202050 (no power supply) Technical data may vary due to different power supplies Variable attack/release times holding peak and average level constant Use the 13A microphone. It can be attached on your TV’s speaker grid ...