Pharm 3010 - Fall 2016 - Assignment 3 Solutions out of 30 points 1
... toxemia. It has the smallest absolute value of the T statistic. It’s also OK to calculate p-values, and report that toxemia has the largest p-value, but that’s not necessary. ...
... toxemia. It has the smallest absolute value of the T statistic. It’s also OK to calculate p-values, and report that toxemia has the largest p-value, but that’s not necessary. ...
Statistics Chapter 1
... group, the group that does not receive any special treatment is called the CONTROL group. If the groups are not chosen randomly, the study is quasi-experimental. If the subjects know they are participating in a study, it may have an effect on the dependent variable. This is known as the HAWTHORNE EF ...
... group, the group that does not receive any special treatment is called the CONTROL group. If the groups are not chosen randomly, the study is quasi-experimental. If the subjects know they are participating in a study, it may have an effect on the dependent variable. This is known as the HAWTHORNE EF ...
Limitation of ridge regression
... The expected sum of the squared errors in the least squares standardized regression coefficient is nearly 460 times as large as it would be if the x variables were uncorrelated . Multicollinearity problem ? ...
... The expected sum of the squared errors in the least squares standardized regression coefficient is nearly 460 times as large as it would be if the x variables were uncorrelated . Multicollinearity problem ? ...
The Quadratic Regression Model
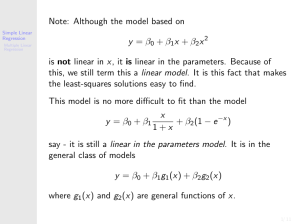
... • Even though the quadratic model employs the squared term x2 and, as a result, assumes a curved relationship between the mean value of y and x, this model is a linear regression model • This is because b0 + b1x + b2x2 expresses the mean value y as a linear function of the parameters b0, b1, and b2 ...
... • Even though the quadratic model employs the squared term x2 and, as a result, assumes a curved relationship between the mean value of y and x, this model is a linear regression model • This is because b0 + b1x + b2x2 expresses the mean value y as a linear function of the parameters b0, b1, and b2 ...
Statistics 2014, Fall 2001
... Sometimes we have several predictors, and one or more of them is only weakly related to the response variable. After including some of the stronger predictors in the model, we want to know whether it would make sense to include any of the weaker predictors as well. Anytime we include another predict ...
... Sometimes we have several predictors, and one or more of them is only weakly related to the response variable. After including some of the stronger predictors in the model, we want to know whether it would make sense to include any of the weaker predictors as well. Anytime we include another predict ...